2022FY0001538716FALSEP3Y0.0625http://oportun.com/20221231#OperatingLeaseLiabilityNethttp://oportun.com/20221231#OperatingLeaseLiabilityNet00015387162022-01-012022-12-3100015387162022-06-30iso4217:USD00015387162023-03-08xbrli:shares00015387162022-12-3100015387162021-12-31iso4217:USDxbrli:shares00015387162021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:APICCommonStockMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:APICCommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:APICCommonStockMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310001538716oprt:APICCommonStockMember2020-12-310001538716us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-12-310001538716us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2020-12-3100015387162020-12-310001538716us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:APICCommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:CA2022-01-012022-12-31xbrli:pure0001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:TX2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:FL2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:IL2022-01-012022-12-310001538716stpr:NJus-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberoprt:AllOtherStatesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:CA2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:TX2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:FL2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:IL2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberoprt:AllOtherStatesMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:OfficeEquipmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:OtherCapitalizedPropertyPlantAndEquipmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:OtherCapitalizedPropertyPlantAndEquipmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:AcquiredSoftwareMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansReceivableMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:StockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:StockOptionMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesSecuritizedLoansAndReceivablesMember2022-03-312022-03-310001538716oprt:DelinquentLoanSaleMember2022-01-012022-12-3100015387162014-11-300001538716oprt:WholeLoanSaleProgramMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:WholeLoanSaleProgramMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716oprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-220001538716oprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:HelloDigitIncMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:HelloDigitIncMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:HelloDigitIncMemberus-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMember2021-12-220001538716oprt:HelloDigitIncMemberus-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716us-gaap:TradeNamesMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716oprt:AcquiredSoftwareMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-220001538716oprt:AcquiredSoftwareMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716us-gaap:SoftwareDevelopmentMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:SoftwareDevelopmentMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:AcquiredSoftwareMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AcquiredSoftwareMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:SoftwareDevelopmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:SoftwareDevelopmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:AcquiredSoftwareMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:TrademarksMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:TrademarksMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:OtherIntangibleAssetsMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:OtherIntangibleAssetsMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityCCWMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityCCWMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberoprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberoprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberoprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityCCWMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberoprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityCCWMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:CreditCardWarehouseFacilityMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberoprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityCCWMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberoprt:SecuredWarehouseFacilityCCWMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries20223Memberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries20223Memberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries20223Memberoprt:CurrentCollateralMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries20222Memberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries20222Memberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberoprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries20222Memberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2022AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2022AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2022AMemberoprt:CurrentCollateralMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2022AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021CMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021CMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberoprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021CMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021CMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021BMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021BMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberoprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021BMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021BMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021AMemberoprt:CurrentCollateralMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:AssetbackedNotesSeries2019AMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMemberoprt:AssetbackedNotesSeries2019AMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:AssetbackedNotesSeries2019AMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:AssetbackedNotesSeries2019AMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021CMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021CMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberoprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021CMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021CMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021BMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021BMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberoprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021BMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021BMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021AMemberoprt:CurrentCollateralMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2021AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:AssetbackedNotesSeries2019AMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMemberoprt:AssetbackedNotesSeries2019AMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:AssetbackedNotesSeries2019AMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:AssetbackedNotesSeries2019AMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberoprt:InitialCollateralMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:CurrentCollateralMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberoprt:OportunFinancialCorporationMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSofrOvernightIndexSwapRateMembersrt:MinimumMemberoprt:OportunFinancialCorporationMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSofrOvernightIndexSwapRateMemberoprt:OportunFinancialCorporationMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberoprt:OportunFinancialCorporationMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:OportunRFLLCMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:OportunRFLLCMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSofrOvernightIndexSwapRateMembersrt:MinimumMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:OportunRFLLCMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSofrOvernightIndexSwapRateMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:OportunRFLLCMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:OportunRFLLCMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-05-240001538716oprt:OportunRFLLCMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-07-280001538716us-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberoprt:OportunRFLLCMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersrt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberoprt:OportunRFLLCMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2022AMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-05-240001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesSeries2022AMember2022-05-242022-05-240001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-05-240001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-07-280001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesMemberus-gaap:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSofrOvernightIndexSwapRateMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesMemberus-gaap:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSofrOvernightIndexSwapRateMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2023-02-102023-02-100001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotesMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2023-02-102023-02-100001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotes20222SecuritizationMember2022-07-220001538716oprt:SeniorSecuredTermLoansMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2022-09-140001538716oprt:SeniorSecuredTermLoansMemberus-gaap:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSofrOvernightIndexSwapRateMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2022-09-142022-09-140001538716oprt:SeniorSecuredTermLoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2023-03-100001538716us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberoprt:IncrementalTrancheA1LoansMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2023-03-102023-03-100001538716srt:ScenarioForecastMemberoprt:IncrementalTrancheA2LoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2023-03-272023-03-270001538716oprt:UncommittedBorrowingsMembersrt:ScenarioForecastMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2023-03-100001538716oprt:UncommittedBorrowingsMembersrt:ScenarioForecastMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2023-04-210001538716oprt:UncommittedBorrowingsMembersrt:ScenarioForecastMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2023-06-230001538716oprt:SeniorSecuredTermLoansMemberus-gaap:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSofrOvernightIndexSwapRateMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2023-03-102023-03-100001538716oprt:SeniorSecuredTermLoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:MediumTermNotesMember2023-03-102023-03-100001538716oprt:AssetBackedNotes20223SecuritizationMemberus-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-11-030001538716us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-080001538716oprt:A2019PlanMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:A2019PlanMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:A2019PlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716srt:MinimumMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:A2021InducementPlanMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheOneMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheOneMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheThreeMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheTwoMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberoprt:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementTrancheFourMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheOneMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheTwoMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheThreeMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMemberoprt:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementTrancheFourMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716oprt:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementTrancheFiveMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberoprt:HelloDigitIncMember2021-12-222021-12-220001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:TechnologyandFacilitiesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:TechnologyandFacilitiesMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:SalesandMarketingMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:SalesandMarketingMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonnelMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonnelMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:ExpiresIn2034Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:CarryForwardIndefinitelyMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:ExpiresIn2031Member2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:ResearchMemberus-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:ResearchMemberus-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMember2021-12-310001538716oprt:UnsecuredPersonalLoansReceivableMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:SecuredPersonalLoansReceivableMember2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMembersrt:WeightedAverageMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMembersrt:WeightedAverageMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputPrepaymentRateMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputPrepaymentRateMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputPrepaymentRateMembersrt:WeightedAverageMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputPrepaymentRateMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputPrepaymentRateMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputPrepaymentRateMembersrt:WeightedAverageMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMembersrt:WeightedAverageMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMembersrt:WeightedAverageMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMembersrt:WeightedAverageMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716oprt:PersonalLoansMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMembersrt:WeightedAverageMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMemberoprt:MeasurementInputPrincipalPaymentRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMemberoprt:MeasurementInputPrincipalPaymentRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CreditCardMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2020-12-310001538716us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716us-gaap:LoansReceivableMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001538716us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310001538716us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001538716srt:MaximumMember2022-12-3100015387162022-04-012022-04-30oprt:retailLocation0001538716us-gaap:FacilityClosingMember2022-01-012022-12-310001538716us-gaap:FacilityClosingMember2021-01-012021-12-310001538716oprt:BankPartnershipProgramAndServicingAgreementLoansMember2022-01-012022-12-3100015387162022-03-040001538716oprt:RedressToEligibleCustomersMembersrt:MinimumMember2022-07-012022-09-300001538716oprt:CivilPenaltyToCFPBMember2022-07-012022-09-300001538716us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-02-092023-02-09oprt:employee0001538716srt:MinimumMembersrt:ScenarioForecastMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-310001538716srt:MaximumMembersrt:ScenarioForecastMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-310001538716oprt:IncrementalTrancheA1LoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-102023-03-100001538716oprt:IncrementalTrancheA1LoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-100001538716oprt:IncrementalTrancheA2LoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-102023-03-100001538716oprt:IncrementalTrancheBLoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-102023-03-100001538716oprt:IncrementalTrancheCLoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-102023-03-100001538716oprt:IncrementalTrancheCLoansMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2023-03-10
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
☒ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022
or
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from ___________ to ___________
Commission File Number 001-39050
OPORTUN FINANCIAL CORPORATION
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Delaware | | 45-3361983 |
State or Other Jurisdiction of
Incorporation or Organization | | I.R.S. Employer Identification No. |
| | | |
| 2 Circle Star Way | | |
| San Carlos, | CA | | 94070 |
| Address of Principal Executive Offices | | Zip Code |
(650) 810-8823
Registrant’s Telephone Number, Including Area Code
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share | OPRT | Nasdaq Global Select Market |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | ☒ |
Accelerated filer | ☒ | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant, based on the closing price of a share of common stock on June 30, 2022 as reported by the Nasdaq Global Select Market on such date was approximately $103.8 million. Shares of the registrant’s common stock held by each executive officer, director and holder of 5% or more of the outstanding common stock have been excluded in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates. This calculation does not reflect a determination that certain persons are affiliates of the registrant for any other purpose.
The number of shares of registrant’s common stock outstanding as of March 8, 2023 was 33,419,851.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant's proxy statement for the 2023 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed subsequently are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE OF CONTENTS |
| |
| | |
| PART I |
| Business | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| PART II |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| PART III |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
|
| PART IV |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| |
Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the documents referenced herein, contains forward-looking statements, within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, concerning our business, operations and financial performance and condition, as well as our plans, objectives and expectations for our business operations and financial performance and condition. Any statements contained herein that are not statements of historical facts are forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “aim,” “anticipate,” “assume,” “believe,” “contemplate,” “continue,” “could,” “due,” “estimate,” “expect,” “goal,” “intend,” “may,” “objective,” “plan,” “predict,” “potential,” “positioned,” “seek,” “should,” “target,” “will,” “would,” and other similar expressions that are predictions of or indicate future events and future trends, or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology, although not all forward-looking statements contain these words. These forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements about:
•our ability to increase the volume of loans we make;
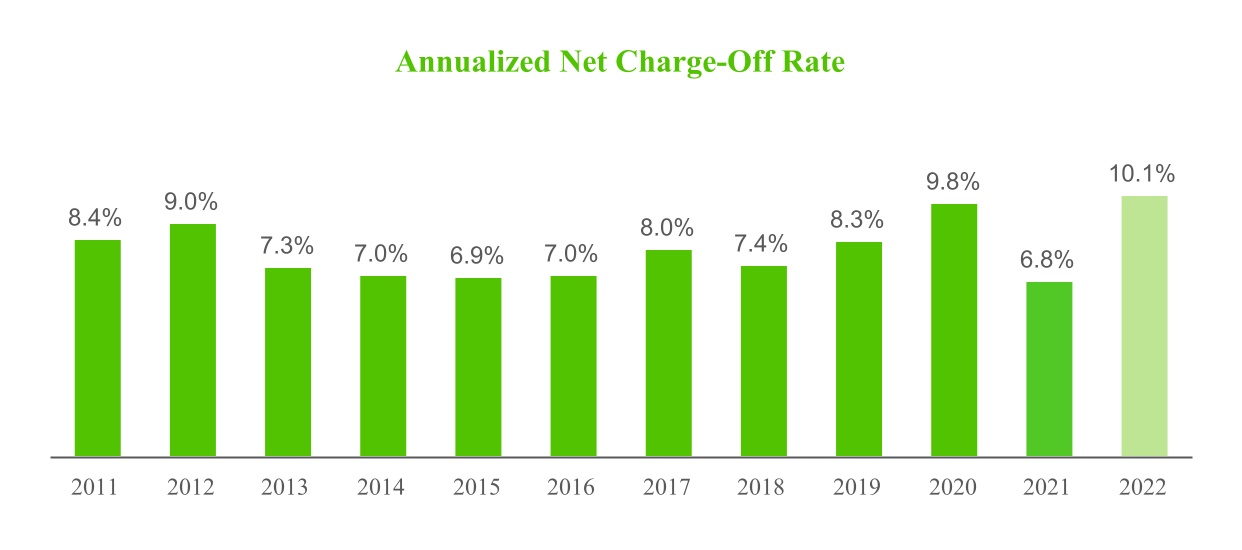
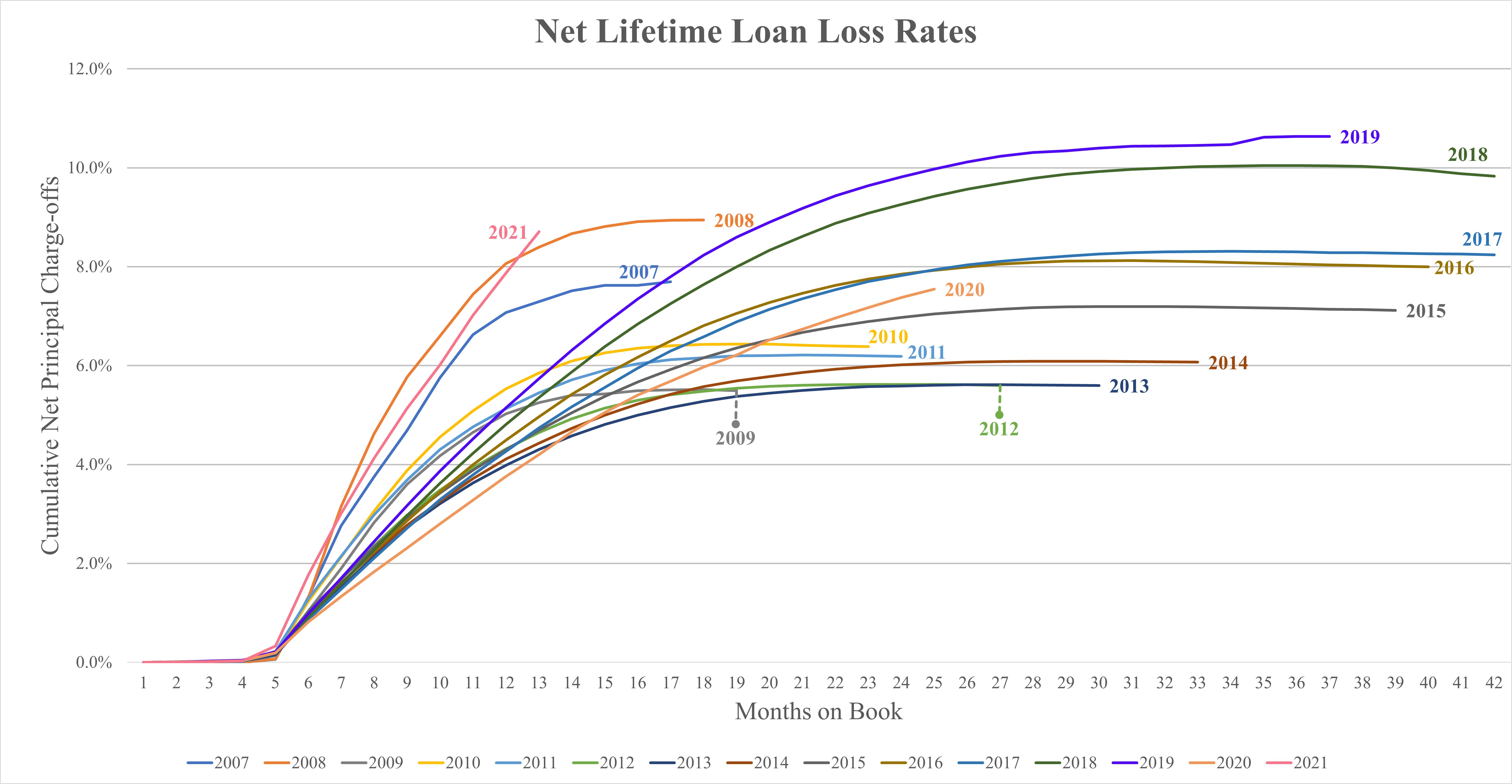
•our ability to manage loan non-performance, delinquencies and charge-off rates;
•our ability to effectively estimate the fair value of our loans receivable held for investment and our asset-backed notes;
•our expectations and management of future growth, including expanding our markets served, member base and product and service offerings, including our digital banking services;
•the successful integration of Hello Digit, Inc. ("Digit") with our business;
•our ability to successfully adjust our proprietary credit risk models and products in response to changing macroeconomic conditions and fluctuations in the credit market;
•our ability to obtain any additional financing or any refinancing of our debt;
•our ability to successfully manage our interest rate spread against our cost of capital;
•our expectations regarding the sufficiency of our cash to meet our operating and cash expenditures;
•our plans for and our ability to successfully maintain our diversified funding strategy, including warehouse facilities, loan sales and securitization transactions;
•our ability to realize the expected benefits from the reduction in workforce and other streamlining measures announced in February 2023;
•our expectations regarding our costs and seasonality;
•our ability to successfully build our brand and protect our reputation from negative publicity;
•our ability to expand our digital capabilities for origination and increase the volume of loans originated through our digital channels;
•our ability to increase the effectiveness of our marketing efforts;
•our ability to grow market share in existing markets or any new markets we may enter;
•our ability to continue to expand our demographic focus;
•our ability to maintain or expand our relationships with our current partners, including bank partners, and additional partners using our Lending as a Service model;
•our ability to provide an attractive and comprehensive user experience through our recently launched mobile application, the Oportun Mobile App, and further our position as a leading fintech;
•our ability to maintain the terms on which we lend to our borrowers;
•our ability to manage fraud risk;
•our ability to effectively secure and maintain the confidentiality of the information provided and utilized across our systems;
•our ability to successfully compete with companies that are currently in, or may in the future enter, the markets in which we operate;
•our ability to attract, integrate and retain qualified employees;
•the effect of macroeconomic conditions on our business, including the impact of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, rising interest rates and recession or slowing growth;
•our ability to effectively manage and expand the capabilities of our contact centers, outsourcing relationships and other business operations abroad; and
•our ability to successfully adapt to complex and evolving regulatory environments, including managing potential exposure in connection with new and pending investigations, proceedings and other contingencies.
Forward-looking statements are based on our management’s current expectations, estimates, forecasts, and projections about our business and the industry in which we operate and on our management’s beliefs and assumptions. In addition, statements that “we believe” and similar statements reflect our beliefs and opinions on the relevant subject. These statements are based upon information available to us as of the date of this Annual
Report on Form 10-K, and while we believe such information forms a reasonable basis for such statements, such information may be limited or incomplete, and our statements should not be read to indicate we have conducted exhaustive inquiry into, or review of, all potentially available relevant information. We anticipate that subsequent events and developments may cause our views to change. Forward-looking statements do not guarantee future performance or development and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors that are in some cases beyond our control. Factors that may cause actual results to differ materially from current expectations include, among other things, those listed under the heading “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this report. We also operate in a rapidly changing environment and new risks emerge from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in, or implied by, any forward-looking statements. As a result, any or all of our forward-looking statements in this report may turn out to be inaccurate. Furthermore, if the forward-looking statements prove to be inaccurate, the inaccuracy may be material.
These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this report. Except as required by law, we assume no obligation to update or revise these forward-looking statements for any reason, even if new information becomes available in the future. We qualify all of our forward-looking statements by these cautionary statements.
Summary of Risk Factors
Investing in our common stock involves risks. See Item 1A. “Risk Factors” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the following principal risks and other risks that make an investment in our common stock speculative or risky:
Business, Financial and Operational Risks
•Our results of operations and future prospects depend on our ability to retain existing, and attract new, members.
•We are, and intend in the future to continue, developing new financial products and services, and our failure to accurately predict their demand or growth could have an adverse effect on our business.
•The success and growth of our business depends upon our ability to continuously innovate and develop new products and technologies.
•If we do not compete effectively in our target markets, our results of operations could be harmed.
•We may not be able to effectively manage our growth.
•Our business may be adversely affected by disruptions in the credit markets and changes to interest rates on our borrowings.
•Our risk management efforts may not be effective, which may expose us to market risks that harm our results of operations.
•We rely extensively on models in managing many aspects of our business. If our models contain errors or are otherwise ineffective, our business could be adversely affected.
•Our results of operations and financial condition have been and may be adversely affected by economic conditions and other factors that we cannot control.
•We have elected the fair value option and we use estimates in determining the fair value of our loans and our asset-backed notes. If our estimates prove incorrect, we may be required to write down the value of these assets or write up the value of these liabilities, which could adversely affect our results of operations.
•Our current level of interest rate spread may decline in the future. Any material reduction in our interest rate spread could adversely affect our results of operations.
•If we are unable to collect payment and service the loans we make to members, our net charge-off rates may exceed expected loss rates, and our business and results of operations may be harmed.
•Our quarterly results are likely to fluctuate significantly and may not fully reflect the underlying performance of our business.
•The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has and may continue to adversely impact our business and results of operations.
•Negative publicity or public perception of our company or our industry could adversely affect our reputation, business, and results of operations.
•Competition for our highly skilled employees is intense, and we may not be able to attract and retain the employees we need to support the growth of our business.
•If we lose the services of any of our key management personnel, our business could suffer.
•Our success and future growth depend on our branding and marketing efforts.
•We may fail to realize all of the anticipated benefits of the Digit acquisition, and the merger or those benefits may take longer to realize than expected.
•Any acquisitions, strategic investments, entries into new businesses, joint ventures, divestitures, and other transactions could fail to achieve strategic objectives, disrupt our ongoing operations or result in operating difficulties, liabilities and expenses, harm our business, and negatively impact our results of operations.
•Fraudulent activity could negatively impact our business, operating results, brand and reputation and require us to take steps to reduce fraud risk.
•Security breaches and incidents may harm our reputation, adversely affect our results of operations, and expose us to liability.
•Any significant disruption in our computer systems and critical third-party vendors may impair the availability of our websites, applications, products or services, or otherwise harm our business.
•We may change our corporate strategies or underwriting and servicing practices, which may adversely affect our business.
•We are, and intend in the future to continue, expanding into new geographic regions, and our failure to comply with applicable laws or regulations, or accurately predict demand or growth, related to these geographic regions could have an adverse effect on our business.
•We are exposed to geographic concentration risk.
•Our proprietary credit risk models rely in part on the use of third-party data to assess and predict the creditworthiness of our members, and if we lose the ability to license or use such third-party data, or if such third-party data contain inaccuracies, it may harm our results of operations
•A deterioration in the financial condition of counterparties, including financial institutions, could expose us to credit losses, limit access to liquidity or disrupt our business.
•Our vendor relationships subject us to a variety of risks, and the failure of third parties to comply with legal or regulatory requirements or to provide various services that are important to our operations could have an adverse effect on our business.
•Our mission to provide inclusive, affordable financial services that empower our members to build a better future may conflict with the short-term interests of our stockholders.
•If we cannot maintain our corporate culture as we grow, we could lose the innovation, collaboration and focus on the mission that contribute to our business.
•Our international operations and offshore service providers involve inherent risks which could result in harm to our business.
Funding and Liquidity Risks
•We have incurred substantial debt and may issue debt securities or otherwise incur substantial debt in the future, which may adversely affect our financial condition and negatively impact our operations.
•A breach of early payment triggers or covenants or other terms of our agreements with lenders could result in an early amortization, default, and/or acceleration of the related funding facilities.
•Our securitizations and structured and whole loan sales may expose us to certain risks, and we can provide no assurance that we will be able to conduct such transactions in the future, which may require us to seek more costly financing.
•We expect to need to raise additional funds in the future, including through equity, debt, or convertible debt financings, to support business growth and those funds may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all.
Intellectual Property Risks
•It may be difficult and costly to protect our intellectual property rights, and we may not be able to ensure their protection.
•We have been, and may in the future be, sued by third parties for alleged infringement of their proprietary rights.
•Our credit risk models, A.I. capabilities, and internal systems rely on software that is highly technical, and if it contains undetected errors, our business could be adversely affected.
•Some aspects of our business processes include open source software, and any failure to comply with the terms of one or more of these open source licenses could negatively affect our business.
Industry and Regulatory Risks
•The financial services industry is highly regulated. Changes in regulations or in the way regulations are interpreted and applied to our business could adversely affect our business.
•Litigation, regulatory actions and compliance issues could subject us to significant fines, penalties, judgments, remediation costs and/or requirements resulting in increased expenses and reputational harm.
•Internet-based and electronic signature-based loan origination processes may give rise to greater risks than paper-based processes.
•The CFPB has broad authority to regulate consumer financial services, creating uncertainty as to how the agency’s actions or the actions of any other new agency could impact our business.
•The collection, storage, use, disclosure, and other processing of personal information is an area of increasing complexity and scrutiny.
•Our business is subject to the regulatory framework applicable to registered investment advisers, including regulation by the SEC.
•Our bank partnership products may lead to regulatory risk and may increase our regulatory burden.
•Anti-money laundering, anti-terrorism financing and economic sanctions laws could have adverse consequences for us.
PART I
Item 1. Business
Company Overview
We are a digital banking platform that puts our members’ financial goals within reach. With intelligent borrowing, savings, budgeting, and spending capabilities, we empower members with the confidence to build a better financial future. By intentionally designing our products to help solve the financial health challenges facing a majority of people in the U.S., we believe our business is well positioned for long-term growth.
Financial Health in America
According to a January 2023 survey by Bankrate, more than half of all Americans do not have enough savings to cover an unplanned expense of $1,000. In 2022, the Financial Health Network ("FHN") reported that more than two-thirds of U.S. households "struggle with spending, saving, borrowing and planning" according to its Financial Health Pulse™ 2022 U.S. Trends Report. In addition, our research shows that while 90% of U.S. consumers believe financial health is important, 57% of those consumers do not want to think about money.
Our digital banking platform is designed to address these societal issues with a comprehensive set of financial services that help people, even those who are not well served by mainstream financial institutions, access credit and automatically budget, save, and invest, without impacting their ability to meet daily spending needs. By applying artificial intelligence ("A.I.") to automate their financial health, we believe we have a compelling suite of products and services that addresses the very real needs of the vast majority of people living in the U.S.
Serving our Members' Financial Needs
Our members are among the hundreds of millions of hardworking Americans who are not well served by mainstream financial products. We take a holistic approach to serving our members and view it as our purpose to responsibly meet their current capital needs, help grow our members’ financial profiles, increase their financial awareness and put them on a path to a financially healthy life. We believe our strong Net Promoter® Score ("NPS"), 81, up from 79 in 2021 for our personal loans demonstrates our success in providing our members with effective and easy to use solutions. Our members access our products primarily through our website, our mobile application, as well as through our partners.
Credit Products—Since our founding in 2005, we have extended more than $15.5 billion in responsible credit through more than 6.3 million loans and credit cards, and helping over 1.1 million people who came to Oportun without a FICO® score to begin establishing a credit history. According to a study commissioned by us on the credit options available to people with little or no credit history, the Financial Health Network found that Oportun loans are, on average, 6 times less expensive than other options and up to 24 times less expensive as compared to online-only installment products. In addition, the study found that our unsecured personal loan product has helped borrowers save more than $2.3 billion in interest and fees. While many of the people who come to us are not well served by mainstream financial institutions due to limited credit history, we use A.I. and billions of proprietary data points to score 100% of our loan applicants and offer our members responsibly designed and affordable credit products that are often otherwise unavailable to them, including personal loans and credit cards.
Digital Banking Products—With our acquisition of Digit on December 22, 2021, we believe we now have a strong competitive advantage over other fintechs and neobanks. As a combined company, we can now offer access to a comprehensive suite of digital banking products, offered either directly or through partners, including savings and investing powered by A.I. and tailored to each member's goals to make achieving financial health automated. Digit began with a savings product with the intent to apply A.I. to make financial health effortless for everyone. Following the success of the initial savings product, Digit expanded its products and services to include bank account and investment products, available through partners. Since 2015, our members have saved over $8.9 billion towards their rainy day fund and other savings goals. See Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and Note 6, Acquisition, in the accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of the Digit acquisition.
Lending as a Service—In addition to reaching members through direct marketing channels, we leverage our proprietary credit scoring and underwriting model to enable us to serve consumers by partnering with other brands. Our first strategic partner for this Lending as a Service model was DolEx Dollar Express, Inc. (“DolEx”). In this partnership, DolEx markets loans and enters borrower applications into Oportun’s system, and Oportun underwrites, originates and services the loans. In October 2021, we launched another Lending as a Service partnership with Barri Financial Group in select locations. In January of 2022, we announced our first all-digital Lending as a Service partnership with Sezzle, a leading provider of Buy Now Pay Later ("BNPL") financing options which launched in the first quarter of 2023. Oportun is now available as a checkout option, through Sezzle, for larger purchases which we believe will allow us to reach more new members. We believe we will be able to offer Lending as a Service to additional partners, and expand our membership base.
Providing our Members with a Seamless Experience
We recently launched a mobile application that integrates our credit and digital banking products into a seamless user experience (“Oportun Mobile App”) that further positions us as a leading fintech with one of the most comprehensive offerings. We believe that by offering our members an integrated experience through the Oportun Mobile App, we can boost member engagement and retention, as well as multi-product adoption.
Our Digital Banking Platform
Consistent with our mission of financial inclusion, we have designed our integrated digital banking platform to provide products and services
that are financially responsible and lower cost compared to market alternatives. Our application of A.I., specifically machine learning, is designed to address the shortcomings of the modern banking system. Since our inception, we have utilized alternative data sets to rapidly build, test and develop our underwriting, pricing, marketing, fraud and servicing models, and with the acquisition of Digit, we now offer machine learning capabilities that help members identify the right amount of money to put towards savings and investments each day. We believe this gives us a strong competitive advantage and an unparalleled suite of digital banking products, which allow us to offer a lower cost option to millions of people in the U.S.
Through the development and utilization of our sophisticated underwriting models, we are able to assess credit risk more effectively compared to other companies and traditional scoring models. We ingest over 9.2 billion data points into our risk model development using traditional (e.g., credit bureau data) and alternative (e.g., transactional information, public records) data. This helps us to score 100% of the applicants who come to us seeking to borrow money, enabling us to serve more people while minimizing risk. In comparison, incumbent financial institutions relying on traditional credit bureau-based and in some cases qualitative underwriting and/or legacy systems and processes either decline or inaccurately underwrite loans due to their inability to properly evaluate applicants' credit.
Our fully centralized and automated digital underwriting platform powers our ability to successfully preapprove borrowers in seconds. As a result, our credit products, including unsecured personal loans, credit cards, and secured personal loans, are a significant differentiator from other lenders and other digital banking companies. Most fintech platforms are focused on borrowers with more established credit histories and higher incomes and are not able to match our ability to effectively manage credit risk among people who may face challenges with aspects of their financial health.
The evolution of our proprietary risk model enables us to underwrite more applicants and make more credit available to new and returning borrowers, while maintaining consistent credit quality. The continuous development and rapid deployment of our credit models enabled by machine learning creates a virtuous cycle that increases our member base and our alternative data set, improving our underwriting tools and ability to grow profitably.
In addition to the challenge of capital access, millions of people in the U.S. have a difficult time trying to save and manage money. Through our digital banking products, we help our members reach their financial goals and improve their financial health by automating away the guess-work and stress of money management. We meet our members where they are, connecting directly to their checking account to analyze spending and income patterns, regardless of whether their bank account is through Digit's partner bank or another bank. We apply algorithms to this data, along with generalized principles of responsible finance and behavioral psychology, to make personalized money allocation decisions on a daily basis for each of our members.
The algorithms behind our digital banking products intelligently utilize the nuances in transaction data to classify income and expenses with up to 95% accuracy. We classify financial obligations, credit, bills and paychecks based on historical data to forecast a future financial picture for each member. We employ continuous learning to update these models with the most recent financial data, so we do not miss new trends in spending habits or income changes (e.g., new employers, subscription services, insurers, side jobs, sales, etc.). With 814 million algorithmic transfers over the last 8+ years based on billions of data points, we have built an A.I. engine with a long track record of making financial health effortless for our members. This serves as a major competitive advantage in delivering new types of personalized but scalable financial services. Our technology, member-centric culture and effective use of data and analytics enable us to efficiently help our members overcome financial challenges.
Our Strategy
We seek to expand our financial services to help a growing number of responsible, hardworking members to borrow, save, bank and invest through our digital banking platform and thus make financial health effortless for them. Our specific objectives are to (1) grow our members, including by organic acquisition, (2) increase the number of products that our members use and drive higher engagement of multi-product relationships, and (3) enhance our platform capabilities across all core functions to better serve our members. Our strategy to achieve these objectives is to (a) invest in our member acquisition channels, especially digital and partner channels, (b) enhance our credit and digital banking products, and (c) provide these complementary product categories with a unified and integrated mobile-first experience powered by A.I. through our Oportun Mobile App. Our ability to comprehensively address our members' most pressing financial needs effortlessly and at attractive pricing will lead to increased lifetime value as members take advantage of our multiple product offerings.
Invest in member acquisition channels – To expand our member base, we plan to invest in scaling our marketing capabilities for our credit products and digital banking services. For example, via brand marketing (including online and broadcast media) and direct marketing (including paid and organic online advertising and social media as well as offers made through our Oportun Mobile App). In addition, our origination partnerships with WebBank for credit cards and Pathward, N.A. (formerly known as "MetaBank, N.A.) for personal loans allow us to reach new members across the nation, mainly through our digital marketing capabilities. We have significant opportunity to gain market share as we increase awareness of Oportun’s superior value proposition to members in markets we entered through these partnerships. In addition to our direct-to-consumer channels, we reach incremental members through our Lending as a Service product offering. By entering Lending as a Service partnerships with other companies, we create new proprietary channels through which to offer our lending products and financial services and acquire new members, multiplying our membership growth potential. We plan to add additional Lending as a Service partners in the future, both with retail origination capabilities, similar to DolEx and Barri Financial, and fully digital platforms such as Sezzle, a leader in the BNPL space. We will also seek to market our digital banking products to former Oportun borrowers who successfully repaid their loans and intend to market our credit products to former Digit members.
Enhance our credit and digital banking products – We leverage machine learning to rapidly build and test strategies across the member lifecycle, including through targeted digital marketing, underwriting, pricing, fraud and member servicing. We believe that as we scale our suite of digital banking products and services, we will further improve member loyalty and increase member lifetime value. We also expect to continue to
derive actionable insights to further drive growth of our secured personal loan and credit card products that are still early in their market adoption lifecycle. Additionally, we will continue to invest significantly in our artificial intelligence capabilities to expand the functionality and efficiency of our products.
Provide a unified and integrated mobile experience – We recently launched our Oportun Mobile App, which brings together all of our products into a seamless user experience. Our Oportun Mobile App will ensure our members and potential members are made aware of and have access to our full range of products, which furthers our vision to make financial health effortless for our members. In addition, we believe this single acquisition funnel will increase member conversion and decrease cost of member acquisition. This affords the broadest possible opportunity to sustain long-term relationships with our members and will enable us to engage with our members more frequently. We plan to invest in increased content and functionality to further increase our members’ engagement. This will strengthen our relationships with our members and enable us to become their preferred provider of credit and digital banking products. We believe this will result in higher member lifetime value as members extend their relationships with us and utilize more of our products. We will continue to invest in further enhancements to serve more of our members’ needs, continue to build lasting and durable relationships with them and improve their financial health.
Our Products
Our financial products allow us to meet our members where they are and assist them with their overall financial health, resulting in opportunities to present multiple relevant products to our members. Our credit products include personal loans, secured personal loans and credit cards. Our digital banking products include, automated savings, as well as a digital bank account and long-term investing and retirement savings available through partners.
Consumers are able to become members and access our products through our mobile application, the Oportun Mobile App and the Oportun.com website, which are our primary channels for onboarding and serving members. Our personal loan products are also available over the phone or through our retail and Lending as a Service partner locations. We help potential and current members become aware of our product offerings through brand marketing (including online and broadcast media and outdoor advertising, including the physical presence of retail locations in some of the communities we serve) and direct marketing (including SMS/text, email, mail and offers made available through our Oportun Mobile App).
Credit Products
Personal Loans - Personal loans allow our consumers a fast and convenient way to address pressing financial needs (for example an unplanned car repair) as well as planned purchases and personal growth opportunities (such as a deposit on a home rental). Our competitive differentiation in personal loans comes from our segment focus, our technology, data, and A.I.-driven approach to delivering personal loans, and the way we tailor our product designs and borrowers experience to meet and exceed the expectations of our target members. This product is currently the majority of our revenue and profitability, and continues to have significant opportunity for growth, benefiting from category growth as well as growth in our brand awareness outside of our historical regional operating footprint (leveraging our partnership with Pathward, N.A.).
Our personal loan is a simple-to-understand, affordable, unsecured, fully amortizing installment loan with fixed payments throughout the life of the loan. We charge fixed interest rates on our loans, which vary based on the amount disbursed and applicable state law, with a cap of 36% annual percentage rate (“APR”) in all cases. As of December 31, 2022, for all active loans in our portfolio and at time of disbursement, the weighted average term and APR at origination was 38 months and 32.0%, respectively. The average loan size for loans we originated in 2022 was $4,189. Our loans do not have prepayment penalties or balloon payments, and range in size from $300 to $12,000 with terms of 12 to 60 months. Generally, loan payments are structured on a bi-weekly or semi-monthly basis to coincide with our members' receipt of their income. As part of our underwriting process, we only approve loans that meet our ability-to-pay criteria. As of December 31, 2022, we originate unsecured personal loans in 12 states through state licenses and in 30 states through our partnership with Pathward, N.A.
Secured Personal Loans - In April 2020, we launched a personal installment loan product secured by an automobile, which we refer to as secured personal loans. This product allows our borrowers to access larger loan sizes than they can with an unsecured loan, which is critical if the need they are facing exceeds our unsecured lending limits for that member. Our secured personal loans business has significant growth potential as we expand geographic and channel availability and make more of our members aware of the product. Our competitive differentiation in secured personal loans comes from leveraging the member base, application flow, and business platform we have already built for unsecured personal loans – we underwrite borrowers seeking a personal loan for both an unsecured and secured loan, allowing them to choose the offer that fits best for them.
Our secured personal loans range in size from $2,525 to $18,000 with terms ranging from 27 to 63 months. The average loan size for secured personal loans we originated in 2022 was $8,304. As of December 31, 2022, for all active loans in our portfolio and at time of disbursement, the weighted average term and APR at origination was 49 months and 28.3%, respectively. As part of our underwriting process, we evaluate the collateral value of the vehicle, verify income for all applicants and only approve loans that meet our ability-to-pay criteria. Our secured personal loans are currently offered in California, Texas, Florida, Arizona and New Jersey and we are in the process of considering expansion into other states.
Credit Cards - We launched the Oportun® Visa® Credit Card, issued by WebBank, Member FDIC, in December 2019, and offer credit cards in 45 states as of December 31, 2022. This product has the advantage of being an “everyday, in your pocket” product, easily usable for small ticket purchases. Credit lines for our credit cards range in size from $300 to $3,000 with an APR between 24.9% to 29.9%. The average APR of the outstanding credit card receivables was 29.8% as of December 31, 2022. The average credit line for credit cards activated in 2022 was $834.
Digital Banking Products
With the acquisition of Digit on December 22, 2021, a digital financial health platform, we now offer a variety of digital banking products, including personalized and automated savings, investing and banking products. Members are able to integrate their existing bank accounts into the platform or they can make us their primary banking relationship through our bank partner. Members set goals for savings or investing through the application or use the application to help manage their debt. Then, our A.I. engine analyzes their income and spending patterns to find the optimal amount that can safely be applied towards their goals and automatically transfers the necessary funds over time to achieve those goals. One proof point of the success of this A.I.-driven approach is the 814 million algorithmic transfers completed in the last 8+ years.
We believe that the mainstream banking industry focuses on serving more affluent borrowers and has not built core deposit products to effectively serve the needs of everyday consumers. Despite the fact that free savings accounts are available at every corner bank, most underserved people in the U.S. have not been successful in their savings goals. We see this market failure as an opening, and our competitive advantage is to leverage A.I. and mobile to deliver better banking products to everyday consumers, to help them actually succeed with their saving, daily budget management, and spend management goals. Additionally, our digital banking platform will allow us to have as frequent as daily engagement with our members through the benefit of our budgeting and money management tools. This will enhance our relationship with our members and allow us to be a preferred provider of other financial services and credit products. The financial result will be higher revenue as members extend their relationships with us, use more credit products and choose to pay for additional financial services. We will continue to invest in and evolve our digital banking platform to further improve our ability to serve our members and continue to build lasting and durable relationships with them.
Savings – Our Savings product is designed to understand a member’s cash flows and save a calculated amount on a regular basis to effortlessly achieve savings goals. Digit's savings product utilizes machine learning to analyze a member’s transaction activity and build forecasts of the member’s future cash flows to make small, frequent savings decisions according to the member’s financial goals in a personalized manner. According to a January 2023 survey by Bankrate, more than half of all Americans do not have enough savings to cover an unplanned expense of $1,000. After one year using the automated savings product, our members have been able to increase their liquid savings by approximately 50% on average. Since 2015 Digit has helped members save over $8.9 billion.
Direct – Our Direct product offers a full checking account, through a bank partner, that intelligently organizes and budgets a member’s money across bills, savings, and spending. The bank account with a brain™, Direct leverages the same A.I. engine used for our savings product to automatically identify and organize recurring bills and guides spending to ensure members' savings goals are met, and that members know exactly what they can safely spend. This is on top of what members can expect from a traditional checking account, including a physical and virtual debit card to use for purchases and ATM withdrawals and checks. Our product allows our busy members to get back to living their lives without stressing about money management.
Investing and Retirement – Our investment and retirement products are a longer-term savings solution via an A.I.-driven portfolio allocation into low-cost investments based upon risk-tolerance. According to Financial Health Network “Financial Health Pulse: 2022 U.S. Trends Report”, 60% of U.S. consumers are not confident about their long-term financial goals. Our long-term investment solutions automatically allocate our members' savings into low-cost risk-adjusted portfolios held in brokerage accounts or tax-advantaged IRAs. Since 2020, Digit members have invested $67 million into long-term goals through low-cost ETF portfolios. The investment accounts, offered through a broker-dealer partner, include a general investing account and a retirement account for our members’ longer term goals, utilizing smart recommendations to invest savings in risk-adjusted portfolios.
Lending as a Service
Beyond our core direct-to-consumer lending business, we believe that we can leverage our proprietary credit scoring and underwriting model to partner with other consumer brands. Our first strategic partner for this Lending as a Service model was DolEx. In this partnership, DolEx markets loans and enters borrower applications into Oportun’s system, and Oportun underwrites, originates and services the loans. In July 2021, we signed Barri Financial Group as a Lending as a Service partner and we launched in several of their locations in October 2021. In January of 2022, we announced our first all-digital Lending as a Service partnership with Sezzle, a leading provider of BNPL financing options which launched in the first quarter of 2023. Oportun is now available as a checkout option, through Sezzle, for larger purchases which we believe will allow us to reach more new members. We believe we will be able to offer Lending as a Service to additional partners and expand our membership base.
Our Competition
In consumer finance, we compete with other consumer finance companies, credit card issuers, financial technology companies and financial institutions, as well as other nonbank lenders serving consumers who do not have access to mainstream credit, including online marketplace lenders, point-of-sale lending, payday lenders, and auto title lenders and pawn shops focused on underserved borrowers. We may also face competition from companies that have not previously competed in the consumer lending market for borrowers with limited credit history. For example, we are already seeing that the companies commonly referred to as “challenger banks” offering low-cost digital-only deposit accounts are beginning to offer lending products catered to underserved borrowers. In addition, it is possible that, in competitive reaction to the challenger banks, traditional banks may introduce new approaches to small-dollar lending. While the consumer lending market is competitive, we believe that we can serve our target market with products that lead to better outcomes for consumers because they cost significantly less than other products used to fulfill similar borrowing needs and their responsible design supports consumer financial health. On the contrary, the offerings of payday, auto title and pawn lenders, for example, are provided at rates that are too expensive relative to the borrowers’ ability to pay, are often structured in a way that forces borrowers to become overextended, and typically lack the personalized touch that is essential to cultivating the trust of our target member base. Few banks or traditional financial institutions lend to individuals who have limited credit history. Those individuals that do have a credit score, but have a relatively limited credit history, also typically face constrained access and low approval rates for credit products.
The principal competitive factors in our sector include member approval parameters (often described informally as “credit box”), price, flexibility of loan terms offered, member convenience and member satisfaction. We believe our technology, responsible construction of our products, A.I.-enabled digital platform and superior member value proposition allow us to compete favorably on each of these factors. Going forward, however, our competition could include large traditional financial institutions that have more substantial financial resources than we do, and which can leverage established distribution and infrastructure channels. Additionally, new companies are continuing to enter the financial technology space and could deploy innovative solutions that compete for our members. See “Risk Factors – If we do not compete effectively in our target markets, our results of operations could be harmed” and “Risk Factors – Competition for our highly skilled employees is intense, and we may not be able to attract and retain the employees we need to support the growth of our business.”
In digital banking, we compete with traditional banks, both large and small, as well as other fintech companies offering mobile-centric digital banking propositions. Currently most consumers continue to bank primarily with traditional banks. However, in the last several years, Fintech companies with digital banking propositions have grown their member bases significantly, especially with underserved consumers. We are already seeing some competitive reactions from traditional banks to this potential disruption. For example a number of larger banks have in the last year introduced more consumer-centric approaches to overdraft, as well as up-to-two-day-early access to payroll deposits. While the digital banking market is competitive, we observe that so far most of the competitive tactics have centered on intuitive low-friction mobile experiences, and reduction or elimination in overdraft fees. Our strategy is to differentiate by harnessing AI to enable members to actually achieve better financing outcomes – to succeed in their savings goals, better manage their monthly budgets, and improve their financial health.
Seasonality
Regulations and Compliance
We are subject to various federal, state and local regulatory regimes related to the financial services that we provide. These laws and regulations, among other things, impose licensing and qualifications requirements; require various disclosures and consents; mandate or prohibit certain terms and conditions for various financial products; prohibit discrimination based on certain prohibited bases; prohibit unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices; require us to submit to examinations by federal, state and local regulatory regimes; and require us to maintain various policies, procedures and internal controls.
We are subject to examination, supervision and regulation by each state in which we are licensed and are regulated by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). In addition to the CFPB, other state and federal agencies have the ability to regulate aspects of our business. For example, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”), as well as many state statutes provide a mechanism for state attorneys general to investigate us. In addition, the Federal Trade Commission (the "FTC") has jurisdiction to investigate aspects of our business. Federal consumer protection laws that these regulators may enforce include laws related to the use of credit reports and credit reporting accuracy, data privacy and security, disclosure of applicable loan terms, anti-discrimination laws, laws protecting members of the military, laws governing payments, including recurring ACH payments and laws regarding electronic signatures and disclosures. Digit Advisors is registered as an investment adviser under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended (the "Advisers Act"), and is subject to regulation by the SEC.
We are also subject to inspections, examinations, supervision and regulation by applicable agencies in each state in which we do business. Many states have laws and regulations that are similar to the federal consumer protection laws referred to above, but the degree and nature of such laws and regulations vary from state to state. State laws also further dictate what state licenses we need to conduct business and also regulate how we conduct our business activities.
In addition, as a result of our bank partnerships, prudential bank regulators with supervisory authority over our partners have the ability to regulate aspects of our business.
We are subject to the USA PATRIOT Act, Office of Foreign Assets Control, Bank Secrecy Act, Anti-Money Laundering laws, and Know-Your-Customer requirements and certain state money transmitter laws.
The laws and regulations applicable to us are continuing to evolve through legislative and regulatory action and judicial and regulatory interpretation and we monitor these areas closely. We regularly review our consumer contracts, consumer-facing content, policies, procedures and processes to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations. We have built our systems and processes with controls in place in order to ensure compliance with applicable laws. In addition to ensure proper controls are in place, we have a compliance management system that leverages the five key control components of governance, compliance program risk assessments, policies, procedures and training, member complaint monitoring and internal compliance audits.
For more information with respect to the regulatory framework affecting our business, see "Risk Factors – Risks Related to our Industry and Regulation."
Our Technology Infrastructure
Our applications, including our proprietary workflow management system that handles loan and credit card application, document verification, loan disbursement and servicing, as well as our systems that handle that our automated savings, investing and banking tools are architected to be highly available, resilient, scalable, and secure. Critical services in the cloud are deployed across multiple availability zones within a region to ensure that we have the necessary scalability and availability to support our service-level objectives. Service design is vetted against current industry best practices to ensure that as the cloud evolves, we are taking advantage of current feature sets surrounding availability and scalability.
To safeguard the confidentiality, integrity and availability of our data and systems, we maintain a comprehensive program of cybersecurity and privacy policies and procedures, management oversight, accountability structures, and technology design processes. Senior management regularly provides the Board's audit and risk committee with updates to our program. This program also includes a cyber incident response plan that provides controls and procedures for timely and accurate reporting of any material cybersecurity incident. To ensure organization-wide attention to cybersecurity issues, we conduct mandatory employee training on cybersecurity and provide ongoing cybersecurity education and awareness, such as mock phishing attacks and cybersecurity awareness materials. We continuously monitor our environment in real-time using tools designed to detect security events and engage with third parties to audit our information security program and to perform regular penetration tests of our web applications and cloud environments. We remain vigilant in staying ahead of new and emerging risks utilizing our tools and security teams and continue to review and make strategic investments in our information security program to keep our data and systems secure.
Infrastructure is in place and designed to support redundancy across our mission critical systems. Disaster recovery and business continuity plans, and tests have been completed, which help to ensure our ability to recover in the event of a disaster or other unforeseen event. In the event of database restores, we perform data consistency checks to validate the integrity of the data recovery process. A comprehensive business impact analysis is performed annually detailing the maximum tolerable downtime for all mission critical functions. Across our infrastructure, a robust and holistic monitoring-and-alerting practice allows for awareness and detection capabilities ensuring faster incident response and resolution time, limiting the risk of unplanned events, such as downtime or security threats.
Our Intellectual Property
We protect our intellectual property through a combination of trademarks, trade dress, domain names, copyrights and trade secrets, as well as contractual provisions, confidentiality procedures, non-disclosure agreements with third parties, employee disclosure and invention assignment agreements and other contractual rights. We currently have no patent applications on our proprietary risk model, underwriting process or loan approval decision making process because applying for a patent would require us to publicly disclose such information, which we regard as trade secrets. We may pursue such protection in the future to the extent we believe it will be beneficial.
We have trademark rights in our name, our logo, and other brand indicia, and have trademark registrations for select marks in the United States and many other jurisdictions around the world. We will pursue additional trademark registrations to the extent we believe it will be beneficial. We also have registered domain names for websites that we use in our business. We may be subject to third party claims from time to time with respect to our intellectual property. See "Item 3. Legal Proceedings" for more information.
In addition to the protection provided by our intellectual property rights, we enter into confidentiality and intellectual property rights agreements with our employees, consultants, contractors and business partners. Under such agreements, our employees, consultants and contractors are subject to invention assignment provisions designed to protect our proprietary information and ensure our ownership in intellectual property developed pursuant to such agreements.
Our People
At Oportun, we are building a community of employees, partners, and members who support each other on the path to new opportunities, because we believe that when we work together, we can make life better. Our welcoming and inclusive company culture is grounded in our core values - service, excellence, care, innovation, courage, and empowerment – and our people strategies are committed to fostering a culture which encourages and empowers our employees to live our core values every day.
•Employee Engagement – We conduct an annual engagement survey as a means of measuring employee engagement and satisfaction, as well as a tool for improving our people strategies for the year ahead. Approximately 82% of our employees participated in our 2022 employee engagement survey, of which 85% reported that they were satisfied with Oportun as a place to work and 89% reported that they were proud to work at Oportun. Survey results are evaluated and shared across the organization, including our Board’s compensation and leadership committee, to identify areas of progress and areas for improvement. Based on feedback received this year, management
implemented several initiatives to improve the employee experience through rewards and recognition, increased communication transparency, and streamlining processes and collaboration tools. We have been recognized as a Greater Bay Area’s Top Workplace for the past four years and in 2022 we were named one of Comparably’s Companies with Happiest Employees, which is a list derived from top sentiment ratings anonymously provided by employees.
•Diversity and Inclusion – We believe that innovation starts with inclusion. Our focus on diversity and inclusion is reflected throughout our organization, starting at the highest level. Currently, 70% of our Board identifies as women or members of an underrepresented group and the majority of our leadership team identifies as either women or members of an underrepresented group. The majority of Oportun employees identify as women or members of an underrepresented group and the majority of Oportun’s leadership team identifies as either women or members of an underrepresented group. We define the leadership team as Directors, Senior Directors, Vice Presidents and above, inclusive of the Board. We have nine employee resource groups focused on our Asian, Black, Hispanic/Latinx, LGBTQ+, early career individuals, disability/accessibility, South Asian, veteran, and women communities. We are committed to fostering a culture of diversity, equity and inclusion; providing comprehensive training and leadership development programs; and continuing to increase diverse representation at every level of the Company.
•Total Rewards - We continue to focus on the total wellness of our people, anchored by the pursuit of our mission, creation of career opportunities and promotion of employee well-being. We benchmark market practices, and regularly review our compensation against the market to ensure it remains competitive. In addition to salaries, our benefits programs include annual bonuses, equity awards, a 401(k) plan, healthcare and insurance benefits, flexible spending accounts, paid time off, family leave, paid time off for volunteering, matching gifts, employee assistance programs, family care resources, and tools to promote mental health and wellness. In 2021, we transitioned to a remote-first policy and we believe that our remote-first culture gives our employees more flexibility to choose where and how to work, while allowing us to engage with a wider pool of talent. To support our remote-first culture, we actively encourage personal well-being through initiatives, including wellness days for employees to take time to rest and recharge, engagement programs (speaker events, employee resource groups, virtual events, etc.), and recognition programs.
We had 3,000 full-time and 235 part-time employees worldwide as of December 31, 2022. This includes 875 corporate employees in the United States, of which 274 employees are dedicated to technology, risk, analytics, A.I. and data science. On February 9, 2023, we announced that we were reducing our corporate employees by 10% in the United States, India and Mexico, or approximately 155 employees.
Available Information
Our website address is www.oportun.com. Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to reports filed pursuant to Section 13(a) and 15(d) of the Exchange Act, are filed with the SEC. The SEC maintains a website that contains our filings at www.sec.gov.
These reports are also available free of charge through our website, www.investor.oportun.com, as soon as reasonably practicable after we file them with, or furnish them to, the SEC.
We announce material information to the public through a variety of means, including filings with the SEC, press releases, public conference calls, our websites (www.oportun.com and www.digit.co), the investor relations section of our website (investor.oportun.com), as well as social media, including our LinkedIn pages (https://www.linkedin.com/company/oportun/ and https://www.linkedin.com/company/digit-co/), Twitter accounts (@Oportun and @hellodigit) and Instagram account (@hellodigit). The information on our website is not incorporated by reference into this report. The website addresses listed above are provided for the information of the reader and are not intended to be active links.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. Any of the following risks could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. The following risks could cause the trading price of our common stock to decline, which would cause you to lose all or part of your investment. You should carefully consider these risks, all of the other information in this report, including our consolidated financial statements, the notes thereto and the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and general economic and business risks before making a decision to invest in our common stock. While we believe the risks described below include all material risks currently known by us, it is possible that these may not be the only ones we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also impair our business operations.
Business, Financial and Operational Risks
Our results of operations and future prospects depend on our ability to retain existing, and attract new, members.
We operate in a rapidly changing and highly competitive industry and our results of operations and future prospects depend on, among other things, continued growth of our member base, our ability to increase the activity of our members, including by using additional products or services we offer, and our ability to attract members in a cost-effective manner. Our member retention rates may decline or fluctuate due to pricing changes, our expansion into new products and markets, our members' ability to obtain alternative funding sources based on their credit history with us, and new members we acquire in the future may be less loyal than our current member base.
In particular, it is important that we continue to ensure that our members with loans remain loyal to us and we continue to extend loans to members who have successfully repaid their previous loans. As of December 31, 2022 and 2021, members with repeat loans comprised 78% and 76%, respectively, of our Owned Principal Balance at End of Period. If our repeat loan rates decline, we may not realize consistent or improved operating results from our existing member base.
We are, and intend in the future to continue, developing new financial products and services, and our failure to accurately predict their demand or growth could have an adverse effect on our business.
We are, and intend in the future to continue, developing new financial products and services. We intend to continue investing significant resources in developing new tools, features, services, products and other offerings. New initiatives are inherently risky, as each involves unproven business strategies and new financial products and services with which we have limited or no prior development or operating experience.
We can provide no assurance that we will be able to develop, commercially market and achieve acceptance of our new products and services. Our development efforts with respect to these initiatives could distract management from current operations and could divert capital and other resources from other growth initiatives important to our business. In addition, our investment of resources to develop new products and services may either be insufficient, result in expenses that are excessive considering revenue originated from these new products and services, or may not be able to attract new members or retain existing members. We have previously invested resources to develop and launch new products and services and subsequently decided to discontinue these products and services in order to strategically realign our resources. If we are not able to effectively implement new technology-driven products and services as quickly as our competitors or be successful in marketing these products and services to our members and strategic partners, demand for our products and services may decrease. In addition, the borrower profile of members using our new products and services may not be as attractive as existing members with credit products, which may lead to higher levels of delinquencies or defaults than we have historically experienced. Failure to accurately predict demand or growth with respect to our new products and services could adversely impact our business, and these new products and services may not become profitable, and even if they are profitable, operating margins of some new products may not be as high as the margins we have experienced historically or we may not be able to achieve target margins.
The success and growth of our business depends upon our ability to continuously innovate and develop new products and technologies.
The financial services industry is undergoing rapid technological changes, with frequent introductions of new technology-driven products and services. Developing and incorporating new technologies, including A.I., into our products and services may require significant investment, take considerable time, and ultimately may not be successful. We may not be able to effectively implement new technology-driven products and services as quickly as competitors or be successful in marketing these products and services to our members. Furthermore, our technology may become obsolete or uncompetitive, and there is no guarantee that we will be able to successfully develop, obtain or use new technologies to adapt our models and systems.
As with many disruptive innovations, new technologies present risks and challenges that could affect their adoption, and therefore our business. A.I. and related technologies are subject to public debate and heightened regulatory scrutiny. Any negative publicity or negative public perception of A.I. could negatively impact demand for our products and services or hinder our ability to attract new members and strategic partners. The regulatory framework for A.I. and machine learning technologies is evolving and remains uncertain. It is possible that new laws and regulations will be adopted, or existing laws and regulations may be interpreted in new ways, that would affect our business, products and services and the way in which we use A.I., including with respect to fair lending laws. Our success will depend on our ability to develop and incorporate new technologies and adapt to technological changes and evolving industry standards. If we are unable to do so in a timely or cost-effective manner, our business could be harmed.
If we do not compete effectively in our target markets, our results of operations could be harmed.
The industries in which we compete are highly competitive, continuously changing, highly innovative, and increasingly subject to regulatory scrutiny and oversight. Our current and potential future competition primarily includes other consumer finance companies, credit card issuers, financial technology companies, technology platforms, neobanks, challenger banks, and financial institutions, as well as payday lenders and pawn shops. We may compete with others in the market who may in the future provide offerings similar or are competitive with ours, particularly companies who may provide lending, money management and other services though a platform similar to our platform.
Many of our current or potential competitors have significantly more financial, technical, marketing, access to low-cost capital, and other resources than we do and may be able to devote greater resources to the development, promotion, sale and support of their platforms and distribution channels. As such, many of our competitors can leverage their size, robust networks, financial wherewithal, brand awareness, pricing power and technological assets to compete with us. In addition, our potential competitors also include, smaller, earlier-stage companies with more versatile technology platforms, increased operational efficiencies, and greater brand recognition than us. To the extent new entrants gain market share, the use of our products and services would decline. Our long-term success depends on our ability to compete effectively against existing and potential competitors that seek to provide banking and financial technology products and services. If we fail to compete effectively against these competitors, our revenues, results of operations, prospects for future growth and overall business will be materially and adversely affected.
We may not be able to effectively manage the growth of our business.
Although we have experienced rapid growth in our business and operations in recent years, we cannot assure you that our business will continue to grow at our historical growth rates. The growth and expansion of our business has placed significant demands on our management, operational, risk management, technology, marketing, compliance and finance and accounting infrastructure, and has resulted in increased expenses, a trend that we expect to continue as our business continues to grow. In addition, we are required to continuously develop and adapt our systems and infrastructure in response to the increasing sophistication of the consumer financial services market, evolving fraud and information security landscape, and regulatory developments relating to existing and planned business operations. Overall revenue growth depends on a number of factors, including on our ability to increase the origination volume of our products and services, attract new and retain existing members, build our brand, achieve the anticipated benefits and synergies from the Digit acquisition, expand and manage our remote-first workforce, all while managing our business systems, operations and expenses. If we are unable to accomplish these tasks, our future growth may be harmed.
Further, many economic and other factors outside of our control, including general economic and market conditions, pandemics, consumer and commercial credit availability, inflation, unemployment, and consumer debt levels, may adversely affect our ability to sustain revenue growth consistent with recent history. Since 2022, we have engaged in a series of cost-saving measures in response to challenging macroeconomic conditions and such decisions to save costs in certain ways may adversely affect our business and future growth.
Our business may be adversely affected by disruptions in the credit markets and changes to interest rates on our borrowings.
We depend on securitization transactions, warehouse facilities and other forms of debt financing, as well as whole loan and structured loan sales, in order to finance the principal amount of most of the loans we make to our members. See more information about our outstanding debt in Note 9, Borrowings to the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report. However, there is no assurance that these sources of capital will continue to be available in the future on terms favorable to us or at all. The availability of debt financing and other sources of capital depends on many factors, some of which are outside of our control. Conditions in the credit markets may continue to experience disruption or deterioration, including as a result of rising interest rates, which could make it difficult for us to extend the maturity of or refinance our existing indebtedness or obtain new indebtedness with similar terms. The debt capital available to us in the future, if available at all, may bear a higher interest rate and may be available only on terms and conditions less favorable than those of our existing debt and such debt may need to be incurred in a rising interest rate environment. Events of default or breaches of financial, performance or other covenants, as a result of the underperformance of certain pools of loans underpinning our securitizations or other debt facilities, could reduce or terminate our access to funding from institutional investors. Such events could also result in default rates at a higher interest rate and therefore increase our cost of capital. In addition, our ability to access future capital may be impaired because our interests in our financed pools of loans are “first loss” interests and so these interests will only be realized to the extent all amounts owed to investors or lenders and service providers under our securitizations and debt facilities are paid in full. In the event of a sudden or unexpected shortage or restriction on the availability of funds, we cannot be sure that we will be able to maintain the necessary levels of funding to retain current levels of originations without incurring higher funding costs, a reduction in the term of funding instruments or increasing the rate of whole loan sales, or be able to access funding at all. If we are unable to arrange financing on favorable terms, our business may be adversely affected and we may not be able to grow our business as planned and we may have to curtail new originations and reduce credit lines to cardholders.
In July 2017, the United Kingdom’s Financial Conduct Authority, which regulates LIBOR, announced that it will no longer persuade or compel banks to submit LIBOR rates after 2021. At the end of 2021, the ICE Benchmark Administration, the administrator for LIBOR, ceased publishing one-week and two-month U.S. dollar LIBOR and will cease publishing all remaining U.S. dollar LIBOR tenors in mid-2023. Other regulators have suggested reforming or replacing other benchmark rates. These may be replaced by SOFR or other benchmark rates over the next several years. Uncertainty as to the nature of such phase out and selection of an alternative reference rate, together with disruption in the financial markets, could increase in the cost of our credit facilities that are currently tied to LIBOR. Our management continues to monitor the status and discussions regarding LIBOR. Changes in interest rates on our variable rate debt could adversely affect our interest expense, results of operations, and cash flows.
We have elected the fair value option and we use estimates in determining the fair value of our loans and our asset-backed notes. If our estimates prove incorrect, we may be required to write down the value of these assets or write up the value of these liabilities, which could adversely affect our results of operations.
Our ability to measure and report our financial position and results of operations is influenced by the need to estimate the impact or outcome of future events on the basis of information available at the time of the issuance of the financial statements. We use estimates, assumptions, and judgments when certain financial assets and liabilities are measured and reported at fair value. Fair values and the information used to record valuation adjustments for certain assets and liabilities are based on quoted market prices and/or other observable inputs provided by independent third-party sources, when available. During periods of market disruption, including periods of significantly rising or high interest rates, rapidly widening credit spreads or illiquidity, it may be difficult to value certain assets if trading becomes less frequent or market data becomes less observable. In such cases, certain asset valuations may require significant judgment, and may include inputs and assumptions that require greater estimation, including credit quality, liquidity, interest rates, and other relevant inputs. If actual results differ from our judgments and assumptions, then it may have an adverse impact on the results of operations and cash flows. Management has processes in place to monitor these judgments and assumptions, including review by our internal valuation committee, but these processes may not ensure that our judgments and assumptions are correct.
We use estimates and assumptions in determining the fair value of our loans receivable held for investment and asset-backed notes. Our Loans Receivable at Fair Value represented 87% of our total assets and our asset-backed notes represented 78% of our total liabilities as of December 31, 2022. The fair value of our loans receivable held for investment are determined using Level 3 inputs and the fair value of our asset-backed notes are determined using Level 2 inputs. Changes to these inputs could significantly impact our fair value measurements. Valuations are highly dependent upon the reasonableness of our assumptions and the predictability of the relationships that drive the results of our valuation methodologies. In addition, a variety of factors such as changes in the interest rate environment and the credit markets, changes in average life, higher than anticipated delinquency and default levels or financial market illiquidity, may ultimately affect the fair values of our loans receivable and asset-backed notes. Material differences in these ultimate values from those determined based on management’s estimates and assumptions may require us to adjust the value of certain assets and liabilities, including in a manner that is not comparable to others in our industry, which could adversely affect our results of operations.
Our current level of interest rate spread may decline in the future. Any material reduction in our interest rate spread could adversely affect our results of operations.
We earn over 90% of our revenue from interest payments on the loans we make to our members. Financial institutions and other funding sources provide us with the capital to fund a substantial portion of the principal amount of our loans to members and charge us interest on funds that we borrow. In the event that the spread between the interest rate at which we lend to our members and the rate at which we borrow from our lenders decreases, our Net Revenue will decrease. We have capped the APR for newly originated loans at 36% since August 2020. Interest rates have recently risen and may continue to rise, which increases our interest expense and cost of funds and may result in lower operating margins. The interest rates we charge to our members and pay to our lenders could each be affected by a variety of factors, including our ability to access capital markets, the volume of loans we make to our members, product mix, competition and regulatory limitations.
Market interest rate changes may adversely affect our business forecasts and expectations and are highly sensitive to many macroeconomic factors beyond our control, such as inflation, recession, the state of the credit markets, global economic disruptions, unemployment and the fiscal and monetary policies of the federal government and its agencies. Factors outside our control, including interest rate changes and widening credit spreads, may require us to make adjustments to the fair value of our loans receivable held for investment or our asset-backed notes, which may in turn adversely affect our results of operations or lead to volatility in our Net Revenue. For example, rising interest rates decrease the fair value of our loans receivable held for investment, which decreases Net Revenue, but also decreases the fair value of our asset-backed notes, which increases Net Revenue. Because the duration and fair value of our loans and asset-backed notes are different, the respective changes in fair value may not fully offset each other resulting in a negative impact on Net Revenue and increasing the volatility of our results of operations. Any reduction in our interest rate spread could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations, cash flows, and financial condition. We do not currently hedge our interest rate exposure associated with our debt financing or fair market valuation of our loans.
Our risk management efforts may not be effective, which may expose us to market risks that harm our results of operations.
We could incur substantial losses and our business operations could be disrupted if we are unable to effectively identify, monitor and mitigate financial risks, such as credit risk, interest rate risk, prepayment risk and liquidity risk, as well as operational risks. Our risk management policies, procedures and models may not be sufficient to identify all of the risks we are exposed to, mitigate the risks we have identified or identify additional risks that arise in the future.
As our loan mix changes and as our product offerings evolve, our risk management strategies may not always adapt to such changes. Some of our methods of managing risk are based upon our use of observed historical market behavior and management’s judgment. Other of our methods for managing risk depend on the evaluation of information regarding markets, members or other matters that are publicly available or otherwise accessible to us. While we employ a broad and diversified set of risk monitoring and risk mitigation techniques, those techniques and the judgments that accompany their application cannot anticipate every economic and financial outcome or the timing of such outcomes. If our risk management efforts are ineffective, we could suffer losses that could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We rely extensively on models in managing many aspects of our business. If our models contain errors or are otherwise ineffective, our business could be adversely affected.
Our ability to attract members and to build trust in our credit products is significantly dependent on our ability to effectively evaluate a member’s creditworthiness and likelihood of default. In deciding whether to extend credit to prospective members, we rely heavily on our proprietary credit risk models, which are statistical models built using third-party alternative data, credit bureau data, application data and our credit experience gained through monitoring the performance of our members over time. These models are built using forms of A.I., such as machine learning. If our credit risk models fail to adequately predict the creditworthiness of our members or their ability to repay their loans due to programming or other errors, or if any portion of the information pertaining to the potential member is incorrect, incomplete or becomes stale (whether by fraud, negligence or otherwise), and our systems do not detect such errors, inaccuracies or incompleteness, or any of the other components of our credit decision process described herein fails, we may experience higher than forecasted loan losses. Also, if we are unable to access certain third-party data used in our credit risk models, or access to such data is limited, our ability to accurately evaluate potential members may be compromised. Credit and other information that we receive from third parties about a member may also be inaccurate or may not accurately reflect the member’s creditworthiness, which may adversely affect our loan pricing and approval process, resulting in mispriced loans, incorrect approvals or denials of loans. In addition, this information may not always be complete, up-to-date or properly evaluated. As a result, these methods may not predict future risk exposures, which could be significantly greater than the historical measures or available information indicate.
Our reliance on our credit risk models and other models in other aspects of our business, including valuation, pricing, collections management, marketing targeting models, fraud prevention, liquidity and capital planning, direct mail and telesales, and savings and investing algorithms may prove in practice to be less predictive than we expect for a variety of reasons, including as a result of errors in constructing, interpreting or using the models or the use of inaccurate assumptions (including failures to update assumptions appropriately in a timely manner). We rely on our credit risk models and other models to develop and manage new products and services, including our digital banking platform, with which we have limited development or operating experience, as well as new geographies. Our assumptions may be inaccurate, and our models may not be as predictive as expected for many reasons, in particular because they often involve matters that are inherently difficult to predict and beyond our control, such as macroeconomic conditions, credit market volatility and interest rate environment, and human behavior, and they often involve complex interactions between a number of dependent and independent variables and factors. In particular, even if the general accuracy of our valuation models is validated, valuations are highly dependent upon the reasonableness of our assumptions and the predictability of the relationships that drive the results of the models. The errors or inaccuracies in our models may be material and could lead us to make wrong or sub-optimal decisions in managing our business.
Additionally, if we make errors in the development, validation or implementation of any of the models or tools we use to underwrite the loans that we then securitize or sell to investors, those investors may experience higher delinquencies and losses. We may also be subject to liability to those investors if we misrepresented the characteristics of the loans sold because of those errors. Moreover, future performance of our members’ loans could differ from past experience because of macroeconomic factors, policy actions by regulators, lending by other institutions or reliability of data used in the underwriting process. To the extent that past experience has influenced the development of our underwriting procedures and proves to be inconsistent with future events, delinquency rates and losses on loans could increase. Errors in our models or tools and an inability to effectively forecast loss rates could also inhibit our ability to sell loans to investors or draw down on borrowings under our warehouse and other debt facilities, which could limit new origination growth and harm our financial performance. Additionally, the use of A.I. is relatively new and the regulatory framework is evolving and remains uncertain. Any negative regulatory or public scrutiny based upon this could adversely affect our business and reputation.
Our results of operations and financial condition have been and may be adversely affected by economic conditions and other factors that we cannot control.
Key macroeconomic conditions historically have affected our business, results of operations and financial condition and are likely to affect them in the future. Poor economic conditions reduce the demand and usage of our credit products and adversely affect the ability and willingness of members to pay amounts owed to us, increasing delinquencies, bankruptcies, and charge-offs and negatively impacting the fair value of our loans. They may also impact our ability to make accurate credit assessments or lending decisions. Many of these factors are outside our control and include: general economic conditions or outlook, unemployment levels, housing markets, immigration patterns and policies, energy costs, inflation, government shutdowns, delays in tax refunds, volatility or disruption in the capital markets, and changes in interest rates, as well as events such as natural disasters, acts of war, terrorism, pandemics or adverse health developments, social unrest, and catastrophes. The United States has recently experienced historically high levels of inflation, which may increase our expenses and adversely impact our borrowers' ability to make payments on their loans. Additionally, the United States is experiencing an acute workforce shortage, which, in turn has created a hyper-competitive wage environment that may further increase employee compensation. From March 2022 through December 2022, the Federal Reserve raised the target range for the federal funds rate on seven separate occasions and signaled that it anticipates additional increases in the target range will be appropriate to lower inflation. Further adverse changes in inflation and interest rates could negatively impact consumer and business confidence, and adversely affect the economy as well as our business and results of operations. There can be no assurance that our forecasts of economic conditions, our assessments and monitoring of credit risk, and our efforts to mitigate credit risk through risk-based pricing, appropriate loan underwriting, management of loan delinquencies and charge-off rates are, or will be, sufficient to prevent an adverse impact to our business and financial results.
As our business grows and we increase our product and service offerings, we intend to continue to expend significant funds, and we may not be able to generate sufficient revenue to offset our higher operating expenses. We recorded a net loss of $77.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, primarily due to the goodwill impairment, increased operating expenses, increased interest expense and a net decrease in fair value. Our business was adversely impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic and we recorded a net loss of $45.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. We also experienced net losses prior to 2017.
On February 9, 2023, we announced that we were taking a series of measures to streamline our operations, including reducing the size of the corporate staff by 10%. These cost reduction efforts may adversely affect us in unforeseen ways, including interfering with our ability to achieve our business objectives; challenging our ability to effectively manage all aspects of our business operations; causing concerns from current and potential employees, vendors, partners and other third parties with whom we do business; and increasing the likelihood of turnover of other key employees, all of which may have an adverse impact on our business. Our plans may also change as we continue to refocus on reducing operating costs and streamlining operations. These actions may take more time than we currently estimate and we may not be able to achieve the cost-efficiencies sought.
Our members with credit products may be particularly negatively impacted by worsening economic conditions that place financial stress on these members resulting in loan defaults or charge-offs. In addition, major medical expenses, divorce, death, or other issues that affect our members could affect our members’ willingness or ability to make payments on their loans. Our business is currently heavily concentrated on consumer lending and, as a result, we are more susceptible to fluctuations and risks particular to U.S. consumer credit than a company with a more diversified lending portfolio. If our members default under a loan receivable held directly by us, we will experience loss of principal and anticipated interest payments. Our servicing costs may also increase without a corresponding increase in our interest on loans.
Decreases in consumer demand for automobiles and declining values of vehicles securing outstanding secured personal loans would weaken collateral coverage for secured personal loans and increase the amount of loss in the event of default. Significant increases in the inventory of used vehicles may also depress the prices at which repossessed vehicles may be sold or delay the timing of these sales. Consequently, if a vehicle securing a secured personal loan is repossessed while the used car auction market is depressed, the sale proceeds for such vehicle may be lower than expected, resulting in higher than expected losses.
If we are unable to collect payment and service the loans we make to members, our net charge-off rates may exceed expected loss rates, and our business and results of operations may be harmed.
Our unsecured personal loans and credit card receivables, which comprise a significant portion of our overall portfolio, are not secured by any collateral, not guaranteed or insured by any third party and not backed by any governmental authority in any way. We are therefore limited in our ability to collect on these loans if a member is unwilling or unable to repay them for any reason.
Our ability to adequately service our loans is dependent on our ability to grow and appropriately train our customer service and collections staff, our ability to expand our servicing capabilities as the number of our loans increase, our ability to contact our members when they default, and our ability to leverage technologies to service and collect amounts owed with respect to loans. Additionally, our customer service and collections staff are dependent upon maintaining adequate information technology, telephony, and internet connectivity such that they can complete their job functions. Since the onset of the pandemic, the majority of our contact center staff has worked remotely and we will continue to operate the contact centers in this manner. If our contact center operations become constrained for any reason, the effectiveness of our collection activities may be reduced.
In November 2021 we voluntarily implemented certain provisions of the call limitations set forth in Regulation F, the CFPB’s Debt Collection Rule that took effect at that time, which is not applicable to creditors such as us who are collecting their own debts. If we did not correctly estimate the impact of a reduced calling strategy, the effectiveness of our efforts to collect on defaulted loans may be impacted. Additionally, in August 2020, we changed our small claims filing practices, including dismissing all pending small claims court filings and suspending all new legal collection actions. We temporarily suspended our legal collections process, which may be resumed in the future. If we are unable to employ alternative means of engaging severely delinquent members and collecting on defaulted loans, the effectiveness of our efforts to collect on defaulted loans may be impacted. Because our net charge-off rate depends on the collectability of the loans, if we experience an unexpected significant increase in the number of members who fail to repay their loans or an increase in the principal amount of the loans that are not repaid, our revenue and results of operations could be adversely affected. Furthermore, personal unsecured loans and credit card debt are generally dischargeable in bankruptcy. If we experience an unexpected, significant increase in the number of members who successfully discharge their debt in a bankruptcy action, our results of operations could be adversely affected.
We incorporate our estimate of lifetime loan losses in our measurement of fair value for our loans receivable held for investment. While this evaluation process uses historical and other objective information, the classification of loans and the forecasts and establishment of loan losses and fair value are also dependent on our subjective assessment based upon our experience and judgment. Given the unprecedented nature of the COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on the economy, the amount of subjective assessment and judgment applied to develop our forecasts has increased materially, since no directly corresponding historical data set exists. Our methodology for establishing our fair value is based on the guidance in Accounting Standards Codification, 820 and 825, and, in part, on our historic loss experience. If member behavior changes as a result of economic conditions and if we are unable to predict how economic conditions and other factors impacting collectability may affect our estimate of lifetime loan losses, the fair value may be reduced for our Loans Receivable at Fair Value, which will decrease Net Revenue. Our calculations of fair value are estimates, and if these estimates are inaccurate, our results of operations could be adversely affected. Neither state regulators nor federal regulators regulate our calculations of fair value, and unlike traditional banks, we are not subject to periodic review by bank regulatory agencies of our loss estimates or our calculations of fair value. In addition, because our debt financings include delinquency triggers as predictors of losses, increased delinquencies or losses may reduce or terminate our access to debt financing.
Our quarterly results are likely to fluctuate significantly and may not fully reflect the underlying performance of our business.
Our quarterly results of operations are likely to vary significantly in the future and period-to-period comparisons of our results of operations may not be meaningful, due to factors such as our election of the fair value option and the evolving and uncertain duration of the COVID-19 pandemic. Accordingly, the results for any one quarter are not necessarily an indication of future performance. Our quarterly financial results may fluctuate due
to a variety of factors, some of which are outside of our control and, as a result, may not fully reflect the underlying performance of our business. Factors that may cause fluctuations in our quarterly financial results include:
•loan volumes, product and loan mix and the channels through which our loans are originated;
•the number and extent of prepayments of loans;
•the effectiveness of our direct marketing and other marketing channels;
•the effectiveness of our proprietary credit risk models;
•the timing and success of new products and origination channels;
•the amount and timing of operating expenses and capital expenditures, including those related to member acquisition, development of new products and services, and maintenance and expansion of our business, operations and infrastructure;
•net charge-off rates;
•adjustments to the fair value of assets and liabilities on our balance sheet;
•our involvement in litigation or regulatory enforcement efforts (or the threat thereof) or those that impact our industry generally;
•changes in laws and regulations that impact our business;
•our borrowing costs and access to the capital markets; and
•general economic, industry, and market conditions, including economic slowdowns, recessions, rising interest and inflation rates, and tightening of credit markets.
In addition, we experience significant seasonality in demand for our loans, which is generally lower in the first quarter. The seasonal slowdown is primarily attributable to high loan demand around the holidays in the fourth quarter and the general increase in our members’ available cash flows in the first quarter, including cash received from tax refunds, which temporarily reduces their borrowing needs. While our growth has obscured this seasonality from our overall financial results, we expect our results of operations to continue to be affected by such seasonality in the future.
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has and may continue to adversely impact our business and results of operations.
The COVID-19 pandemic and health and safety measures taken by governments and private industry in response to the pandemic have significantly impacted worldwide economic activity and consumer behavior and continue to create economic uncertainty. Worker shortages, supply chain issues, inflationary pressures, vaccine and testing requirements, the emergence of new variants and the reinstatement and subsequent lifting of restrictions and health and safety related measures in response to the emergence of new variants have occurred in the past and may occur in the future. In 2020 through 2022, we offered payment relief options to members impacted by COVID-19, including hardship programs, reduced payment plans, late fee waivers and other borrower accommodations. In the future, we may offer additional payment relief options and may cease offering some options when the federal state of emergency ends.
We are unable to predict the future path or impact of any global or regional COVID-19 resurgences, including existing or future variants, or other public health crises. An extended period of disruption as a result of a health epidemic or pandemic, including COVID-19, may negatively impact us, as well as our members, vendors, and partners.
Negative publicity or public perception of our company or our industry could adversely affect our reputation, business, and results of operations.
Negative publicity about our industry or our company, including the terms of the consumer loans, effectiveness of the proprietary credit risk model, privacy and security practices, originations, marketing, servicing and collections, use of A.I, and other business practices or initiatives, litigation, regulatory compliance and the experience of members, even if inaccurate, could adversely affect our reputation and the confidence in our brands and business model or lead to changes in our business practices. We regularly engage with media outlets and consumer advocates and have previously, and in the future, may respond to inquiries by modifying our business practices or policies to better align with our mission. Despite our responsiveness to the inquiries, certain media outlets and consumer advocates chose to and have continued to highlight the very past practices that we had already modified. The proliferation of social media may increase the likelihood that negative public opinion will impact our reputation and business. Our reputation is very important to attracting new members and retaining existing members. While we believe that we have a good reputation and that we provide members with a superior experience, there can be no assurance that we will continue to maintain a good relationship with members.
In addition, negative perception may result in our being subject to more restrictive laws and regulations and potential investigations, enforcement actions and lawsuits. If there are changes in the laws affecting any of our products, or our marketing and servicing, or if we become subject to such investigations, enforcement actions and lawsuits, our financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected. Entry into new products, as well as into the banking business or new origination channels, such as bank partnerships and other partnerships could lead to negative publicity or draw additional scrutiny.
Harm to our reputation can also arise from many other sources, including employee or former employee misconduct, misconduct by outsourced service providers or other counterparties, failure by us or our partners to meet minimum standards of service and quality, and inadequate protection of member information and compliance failures and claims. Our reputation may also be harmed if we fail to maintain our certification as a Community Development Financial Institution (CDFI).
Competition for our highly skilled employees is intense, and we may not be able to attract and retain the employees we need to support the growth of our business.
Competition for highly skilled personnel, particularly engineering and data analytics personnel, is extremely intense across the country and is likely to continue to increase, as more companies are offering remote or hybrid working arrangements. We have experienced and expect to continue to face difficulty identifying and hiring qualified personnel in many areas, especially as we pursue our growth strategy. We may not be able to hire or
retain such personnel at compensation levels consistent with our existing compensation and salary structure. Many of the companies with which we compete for experienced employees have greater resources than we have and may be able to offer more attractive terms of employment. In particular, employee candidates, specifically in high-technology industries, often consider the value of any equity they may receive in connection with their employment, so significant volatility or a further decline in the price of our stock may adversely affect our recruitment strategies. Additionally, changes to U.S. immigration policies, as well as restrictions on global travel due to public health crises requiring quarantines or other precautions to limit exposure to infectious diseases, may limit our ability to hire and/or retain talent. In February 2023, we announced a 10% reduction in our corporate workforce. This reduction could make it more difficult to attract, retain and hire new talent. Our failure to attract and retain suitably qualified individuals could have an adverse effect on our ability to operate our business and achieve our corporate strategies.
In addition, we invest significant time and expense in training our employees, which increases their value to competitors who may seek to recruit them. If we fail to retain our employees, we could incur significant expenses in hiring and training their replacements and the quality of our services and our ability to serve our members could be adversely affected.
If we lose the services of any of our key management personnel, our business could suffer.
Our future success significantly depends on the continued service and performance of our key management personnel. Competition for these employees is intense and we may not be able to replace, attract and retain key personnel. We do not maintain key-man insurance for every member of our senior management team. The loss of the service of our senior management team or key team members, and the process to replace any of them, or the inability to attract additional qualified personnel as needed, all of which would involve significant time and expense, could harm our business.
Our success and future growth depend on our branding and marketing efforts.
If our marketing efforts are not successful or if we are unsuccessful in developing our brand marketing campaigns, our ability to attract and retain members, attract new strategic partners and grow our business may be negatively impacted. In the future, we intend to continue to dedicate significant resources to our marketing efforts, particularly as we develop our brand. If any of our current marketing channels becomes less effective, if we are unable to continue to use any of these channels, if the cost of using these channels significantly increases or if we are not successful in generating new channels, we may not be able to attract new members in a cost-effective manner or increase the activity of our existing members, including by using additional products or services we offer. If we are unable to recover our marketing costs through increases in the size, value or overall number of credit products we originate, or other product selection and utilization, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects.
We may fail to realize all of the anticipated benefits of the Digit acquisition, and the merger or those benefits may take longer to realize than expected.
We believe that there are significant benefits and synergies that may be realized through combining the platform, product and service offerings of Oportun and Digit. As we continue to integrate the businesses and seek to realize anticipated benefits and synergies, we will continue to be required to devote significant attention and resources to successfully align our business practices and operations, which may disrupt both companies' businesses. The full benefits of the acquisition, including anticipated growth opportunities, may not be realized as expected or may not be achieved within the anticipated time frame, or at all. Failure to achieve the anticipated benefits of the acquisition could adversely affect our results of operations or cash flows, cause dilution to our earnings per share, decrease or delay any accretive effect of the acquisition and negatively impact the price of our common stock.
Any acquisitions, strategic investments, entries into new businesses, joint ventures, divestitures, and other transactions could fail to achieve strategic objectives, disrupt our ongoing operations or result in operating difficulties, liabilities and expenses, harm our business, and negatively impact our results of operations.
Our success will depend, in part, on our ability to grow our business. In some circumstances, we may determine to do so through the acquisition of complementary businesses and technologies rather than through internal development. The identification of suitable acquisition candidates can be difficult, time-consuming, and costly, and we may not be able to successfully complete identified acquisitions. We have previously acquired, and in the future, may acquire, complementary assets or businesses. The risks we face in connection with acquisitions include:
•diversion of management time and focus from operating our business to addressing acquisition integration challenges;
•utilization of our financial resources for acquisitions or investments that may fail to realize the anticipated benefits;
•inability of the acquired technologies, products or businesses to achieve expected levels of revenue, profitability, productivity or other benefits;
•coordination of technology, product development and sales and marketing functions and integration of administrative systems;
•transition of the acquired company’s members to our systems;
•retention of employees from the acquired company;
•regulatory risks, including maintaining good standing with existing regulatory bodies or receiving any necessary approvals, as well as being subject to new regulators with oversight over an acquired business;
•acquisitions could result in dilutive issuances of equity securities or the incurrence of debt;
•cultural challenges associated with integrating employees from the acquired company into our organization;
•the need to implement or improve controls, procedures and policies at a business that prior to the acquisition may have lacked effective controls, procedures and policies;
•potential write-offs of loans or intangibles or other assets acquired in such transactions that may have an adverse effect on our results of operations in a given period;
•liability for activities of the acquired company before the acquisition, including patent and trademark infringement claims, violations of laws, commercial disputes, security weaknesses and incidents, tax liabilities and other known and unknown liabilities;
•assumption of contractual obligations that contain terms that are not beneficial to us, require us to license or waive intellectual property or increase our risk for liability; and
•litigation, claims or other liabilities in connection with the acquired company.
Our failure to address these risks or other problems encountered in connection with our future acquisitions and investments could cause us to fail to realize the anticipated benefits of these acquisitions or investments, cause us to incur unanticipated liabilities and harm our business generally.
Fraudulent activity could negatively impact our business, brand and reputation and require us to continue to take steps to reduce fraud risk.
Third parties have, and we expect that they will likely continue to attempt to commit fraud by, among other things, fraudulently obtaining credit products or creating fictitious accounts using stolen identities or personal information and making transactions with stolen financial instruments, Third parties may also seek to engage in abusive schemes or fraud attacks that are often difficult to detect and may be deployed at a scale that would otherwise not be possible in physical transactions. Risks associated with each of these include theft of funds and other monetary loss, the effects of which could be compounded if not detected quickly. Fraudulent activity may not be detected until well after it occurs and the severity and potential impact may not be fully known for a substantial period of time after it has been discovered. Measures to detect and reduce the risk of fraud and abusive behavior are complex, require continuous monitoring and enhancements, and may not be effective in detecting and preventing fraud, particularly new and continually evolving forms of fraud or in connection with new or expanded product offerings. If these measures do not succeed, our business could be materially adversely impacted.
Despite our efforts, the possibility of fraudulent or other malicious activities and human error or malfeasance cannot be eliminated entirely and will evolve as new and emerging technology is deployed, including the increasing use of personal mobile and computing devices that are outside of our network and control environments. Additionally, increasing our product and service offerings may introduce opportunities for fraudulent activity that we have not previously experienced. Numerous and evolving fraud schemes and misuse of our products and services could subject us to significant costs and liabilities, require us to change our business practices, cause us to incur significant remediation costs, lead to loss of member confidence in, or decreased use of, our products and services, damage our reputation and brands, divert the attention of management from the business, result in litigation (including class action litigation), and lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and possibly regulatory investigations and intervention, any of which could have a material adverse impact on our business.
Security breaches and incidents may harm our reputation, adversely affect our results of operations, and expose us to liability.
Our reputation and ability to attract, retain and serve our members is dependent upon the reliable performance and security of our technology infrastructure and those of third parties that we utilize in our operations. These systems may be subject to damage or interruption from, among other things, earthquakes, adverse weather conditions, other natural disasters, terrorist attacks, rogue employees, power loss, telecommunications failures, and cybersecurity risks. We have been and continue to be the subject of actual or attempted unauthorized access, mishandling or misuse of information, computer viruses or malware, and cyber-attacks that could obtain confidential information, destroy data, disrupt or degrade service, threaten the integrity and availability of our systems, distributed denial of service attacks, social engineering, security breaches and incidents, and other infiltration, exfiltration or other similar events. The automated nature of our business may make us attractive targets for hacking and potentially vulnerable to computer malware, physical or electronic break-ins and similar disruptions. Further, our adoption of remote working arrangements for our corporate and many of our contact center employees may result in increased consumer or employee privacy, IT security, and fraud concerns arising from the increased electronic transfer and other online activity. Techniques used in cybersecurity attacks to obtain unauthorized access, disable or sabotage information technology systems change frequently, as data breaches and other cybersecurity events have become increasingly commonplace, including as a result of the intensification of state-sponsored cybersecurity attacks during periods of geopolitical conflict, such as the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. We have seen, and will continue to see, industry-wide vulnerabilities, which could affect our or other parties’ systems.
We also face indirect technology, cybersecurity and operational risks relating to the members and other third parties with whom we do business or upon whom we rely on to facilitate or enable our business activities, including vendors, payment processors, and other parties who have access to confidential information due to our agreements with them. The use of bank partnerships could leave us exposed to additional information security risks arising from the interaction between our and any partners' information technology infrastructure, and the sharing between us of member information. We cannot guarantee that our or our systems and networks, or those of any third parties with whom we do business, have not been breached or that they do not contain exploitable defects or bugs that could result in a breach of or disruption to any of our systems and networks. Potential vulnerabilities can be exploited from inadvertent or intentional actions of our employees, contractors, third-party vendors, business partners, or by malicious third parties.
Any failure or perceived failure by us, or the third parties with whom we do business, to comply with our privacy, confidentiality, or data security-related legal or other obligations to third parties, or any security breaches impacting us, our third-party providers or partners, may result in governmental investigations, enforcement actions, regulatory fines, litigation, or public statements against us by advocacy groups or others. In addition, a data security incident could cause third parties, to lose trust in us or subject us to claims by third parties that we have breached our
privacy- and confidentiality-related obligations. Any belief by members or others that a security breach or other incident has affected us, even if a security breach or other incident has not affected us or any of our third-party providers or partners, could have any or all of the foregoing impacts on us, including harm to our reputation. Even the perception of inadequate security may harm our reputation and negatively impact our ability to attract and retain members.
We incur significant costs to detect and prevent security breaches and other security-related incidents, and we expect our costs will increase as we work to continuously improve our systems and processes to prevent future breaches and incidents. Any event that leads, or is believed to have led, to unauthorized access, to, or use, access, loss, corruption, disclosure or other processing of our data could disrupt our business; harm our reputation; compel us to comply with applicable federal and/or state breach notification laws and foreign law equivalents; subject us to litigation, regulatory investigation and oversight, or mandatory corrective action; require us to verify the correctness of database contents; or otherwise subject us to liability under laws and contractual obligations, including those that protect the privacy and security of personal information. This could result in increased costs for us to address the incident and in an effort to prevent further breaches or incidents, and result in significant legal and financial exposure and/or reputational harm. These mandatory disclosures regarding a security breach are costly to implement and often lead to widespread negative publicity.
We cannot ensure that any limitations of liability provisions in any agreements with third parties would be enforceable or adequate or would otherwise protect us from any liabilities or damages with respect to any particular cybersecurity claim. We maintain errors, omissions, and cyber liability insurance policies covering certain security and privacy damages. However, we cannot be certain that our coverage will continue to be available on economically reasonable terms or will be available in sufficient amounts to cover one or more large claims, or that the insurer will not deny coverage as to any future claim. The successful assertion of one or more large claims against us that exceed available insurance coverage, or the occurrence of changes in our insurance policies, including premium increases or the imposition of large deductible or co-insurance requirements, could have an adverse effect on our business and financial condition.
Our retail locations also process physical member loan documentation that contain confidential information about our members, including financial and personally identifiable information. We retain physical records in various storage locations outside of our retail locations. The loss or theft of, or other unauthorized access to or use of, member information and data from our retail locations or other storage locations could subject us to additional regulatory scrutiny, possible civil litigation and possible financial liability and losses.
Any significant disruption in our computer systems and critical third-party vendors may impair the availability of our websites, applications, products or services, or otherwise harm our business.
Our ability to deliver products and services, and otherwise operate our business and comply with applicable laws, depends on the efficient and uninterrupted operation of our computer systems and third-party data centers, as well as third-party providers. Our computer systems, including those provided by third-party providers and partners, may encounter service interruptions at any time due to system or software failure, natural disasters, severe weather conditions, health epidemics or pandemics, terrorist attacks, cyber-attacks, computer viruses, physical or electronic break-ins, technical errors, insider threats, power outages or other events. Any of these occurrences may interrupt the availability, or reduce or adversely affect the functionality of our websites, applications, products or services, including our ability to service our loans, process loan applications, and provide digital banking services to our members. Our disaster recovery plan has not been tested under actual disaster conditions, and we may not have sufficient capacity to recover all data and services in the event of an outage. Additionally, our reliance on third-party providers may mean that we are not able to resolve operational problems internally or on a timely basis, as our operations will depend upon such third-party providers communicating appropriately and responding swiftly to their own service disruptions.
The implementation of technology changes and upgrades to maintain current and integrate new systems may cause service interruptions, transaction processing errors or system conversion delays and may cause us to fail to comply with applicable laws, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business. We expect that new technologies and business processes applicable to the financial services industry will continue to emerge and that these new technologies and business processes may be better than those we currently use. There is no assurance that we will be able to successfully adopt new technology as critical systems and applications become obsolete and better ones become available. A failure to maintain and/or improve current technology and business processes, address capacity constraints, upgrade our systems and continually develop our technology and infrastructure, could disrupt our operations or cause our products and services to be less competitive.
In addition, the software that we have developed to use in our daily operations is highly complex and may contain undetected technical errors that could cause our computer systems to fail. For example, each loan that we make involves our proprietary automated underwriting process and depends on the efficient and uninterrupted operation of our computer systems. Any failure of our computer systems involving our automated underwriting process and any technical or other software errors pertaining to this automated underwriting process could compromise our ability to accurately evaluate potential members, which could result in significant claims and liability and negative publicity. Additionally, in the event of damage or interruption, our insurance policies may not adequately compensate us for any of our losses.
We may change our corporate strategies or underwriting and servicing practices, which may adversely affect our business.
As our business grows and evolves, we have, and may in the future, change certain aspects of our corporate strategies or any of our underwriting guidelines without notice to our stockholders. Any changes in strategy or our underwriting or servicing practices could impact our business in any number of ways, including impacting our member mix, product and service offerings, risk profile of our loan portfolio, and operational and regulatory compliance requirements. We may also decide to modify our strategy with respect to whole loan sales, including increasing or decreasing the number of loans sold. We continue to evaluate our business strategies and underwriting and servicing practices and will continue to make changes
to adapt to changing economic conditions, regulatory requirements and industry practices. Additionally, a change in our underwriting and servicing practices may reduce our credit spread and may increase our exposure to interest rate risk, default risk and liquidity risk.
We are, and intend in the future to continue, expanding into new geographic regions, and our failure to comply with applicable laws or regulations, or accurately predict demand or growth, related to these geographic regions could have an adverse effect on our business.
We intend to continue expanding into new geographic regions, including through strategic partnerships or a national bank charter. In addition, each of the new states where we do not currently operate may have different laws and regulations that apply to our products and services. As such, we expect to be subject to significant additional legal and regulatory requirements, including various federal and state consumer lending laws. We have limited experience in managing risks and the compliance requirements attendant to these additional legal and regulatory requirements in new geographies or related to strategic partnerships. The costs of compliance and any failure by us to comply with such regulatory requirements in new geographies could harm our business. If our partners decide to or are no longer able to provide their services, we could incur temporary disruptions in our loan transactions or we may be unable to do business in certain states or certain locations.
We are exposed to geographic concentration risk.
The geographic concentration of our loan originations may expose us to an increased risk of loss due to risks associated with certain regions. Certain regions of the United States from time to time will experience weaker economic conditions and higher unemployment and, consequently, will experience higher rates of delinquency and loss than on similar loans nationally. In addition, natural, man-made disasters or health epidemics or pandemics in specific geographic regions may result in higher rates of delinquency and loss in those areas. A significant portion of our outstanding receivables originated in certain states, and within the states where we operate, originations are generally more concentrated in and around metropolitan areas and other population centers. Therefore, economic conditions, natural, man-made disasters, health epidemics or pandemics, public policies that have the effect of drawing financial-services companies into contentious political or social issues, or other factors affecting these states or areas in particular could adversely impact the delinquency and default experience of the receivables and could adversely affect our business. Further, the concentration of our outstanding receivables in one or more states would have a disproportionate effect on us if governmental authorities in any of those states take action against us or take action affecting how we conduct our business.
As of December 31, 2022, 45%, 26%, 9%, 5% and 4% of our Owned Principal Balance at End of Period related to members from California, Texas, Florida, Illinois and New Jersey, respectively. If any of the events noted in these risk factors were to occur in or have a disproportionate impact in regions where we operate or plan to commence operations, it may negatively affect our business in many ways, including increased delinquencies and loan losses or a decrease in future originations.
Our proprietary credit risk models rely in part on the use of third-party data to assess and predict the creditworthiness of our members, and if we lose the ability to license or use such third-party data, or if such third-party data contain inaccuracies, it may harm our results of operations.
We rely on our proprietary credit risk models, which are statistical models built using third-party alternative data, credit bureau data, application data and our credit experience gained through monitoring the payment performance of our members over time. If we are unable to access certain third-party data used in our credit risk models, or our access to such data is limited, our ability to accurately evaluate potential members will be compromised, and we may be unable to effectively predict probable credit losses inherent in our loan portfolio, which would negatively impact our results of operations. Third-party data sources, including credit bureau data and other alternative data sources, are aggregated by our risk engine to be used in our credit risk models to score applicants, make credit decisions, and in our verification processes to confirm member-reported information. If the information that we receive from third parties about a member is inaccurate or does not accurately reflect the member’s creditworthiness, this may cause us to provide loans to higher risk members than we intended through our underwriting process and/or inaccurately price the loans we make. We use numerous third-party data sources and multiple credit factors within our proprietary credit risk models, which helps mitigate, but does not eliminate, the risk of an inaccurate individual report. In addition, there are risks that the costs of our access to third-party data may increase or our terms with such third-party data providers could worsen. In recent years, well-publicized allegations involving the misuse or inappropriate sharing of personal information have led to expanded governmental scrutiny of practices relating to the safeguarding of personal information and the use or sharing of personal data by companies in the U.S. and other countries. That scrutiny has in some cases resulted in, and could in the future lead to, the adoption of stricter laws and regulations relating to the use and sharing of personal information. These types of laws and regulations could prohibit or significantly restrict our third-party data sources from sharing information, or could restrict our use of personal data when developing our proprietary credit risk models, or for fraud prevention purposes. These restrictions could also inhibit our development or marketing of certain products or services, or increase the costs of offering them to members or reduce the effectiveness of credit models at predicting credit outcomes or preventing fraud.
We follow procedures to verify a member’s identity and address which are designed to minimize fraud. These procedures may include visual inspection of applicant identification documents to ensure authenticity, review of paystubs or bank statements for proof of income and employment, and review of analysis of information from credit bureaus, fraud detection databases and other alternative data sources for verification of identity, employment, income and other debt obligations. If any of the information that is considered in the loan review process is inaccurate, whether intentional or not, and such inaccuracy is not detected prior to loan funding, the loan may have a greater risk of default than expected. If any of our procedures are not followed, or if these procedures fail, fraud may occur. Additionally, there is a risk that following the date of the loan application, a member may have defaulted on, or become delinquent in the payment of, a pre-existing debt obligation, taken on additional debt, lost his or her job or other sources of income or experienced other adverse financial events. Fraudulent activity or significant increases in fraudulent activity could also lead to regulatory intervention, negatively impact our results of operations, brand and reputation and require us to take additional steps to reduce fraud risk, which could increase our costs.
A deterioration in the financial condition of counterparties, including financial institutions, could expose us to credit losses, limit access to liquidity or disrupt our business.
We have entered into, and may in the future enter into, financing and derivative transactions with counterparties in the financial services industry, including brokers and dealers, commercial banks, investment banks, hedge funds, and other financial institutions. Furthermore, the operations of U.S. and global financial services institutions are interconnected, and a decline in the financial condition of one or more financial services institutions, or the perceived lack of creditworthiness of such financial institutions, may expose us to credit losses or defaults, limit access to liquidity or otherwise disrupt our business. As such, our financing and derivative transactions expose us to the risk of counterparty default, which can be exacerbated during periods of market illiquidity.
Our vendor relationships subject us to a variety of risks, and the failure of third parties to comply with legal or regulatory requirements or to provide various services that are important to our operations could have an adverse effect on our business.
We have vendors that, among other things, provide us with key services, including financial, technology and other services to support our loan origination, servicing and other activities. Our expansion into new channels, products or markets may introduce additional third-party service providers, strategic partners and other third parties on which we may become reliant. For example, in connection with the secured personal loan product, we work with third parties that provide information and/or services in connection with valuation, title management and title processing, repossessions, and remarketing. These types of third-party relationships are subject to increasingly demanding regulatory requirements and attention by our partner banks' federal bank regulators (the Federal Reserve Board, the Office of Comptroller of the Currency and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) and our consumer financial services regulators, including state regulators and the CFPB, which could increase the scope of management involvement and decreasing the benefit that we receive from using third-party vendors. We could be adversely impacted to the extent our vendors and partners fail to comply with the legal requirements applicable to the particular products or services being offered. Moreover, if our bank partners or their regulators conclude that we have not met the heightened standards for oversight of our third-party vendors, we could be subject to enforcement actions, civil monetary penalties, supervisory orders to cease and desist or other remedial actions.
In some cases, third-party vendors are the sole source, or one of a limited number of sources, of the services they provide to us. Most of our vendor agreements are terminable on little or no notice, and if our current vendors were to stop or were unable to continue providing services to us on acceptable terms, we may be unable to procure alternatives from other vendors in a timely and efficient manner on acceptable terms or at all. If any third-party vendor fails to provide the services we require, due to factors outside our control, we could be subject to regulatory enforcement actions, suffer economic and reputational harm and incur significant costs to resolve any such disruptions in service.
Our mission to provide inclusive, affordable financial services that empower our members to build a better future may conflict with the short-term interests of our stockholders.
Our mission is to provide inclusive, affordable financial services that empower our members to build a better future. We have made and will continue to make decisions that we believe will benefit our members and therefore provide long-term benefits for our business, even if our decision negatively impacts our short-term results of operations. For example, we constrain the maximum rates we charge in order to further our goal of making our loans affordable for our target members. Our decisions may negatively impact our short-term financial results or not provide the long-term benefits that we expect and may adversely impact our business operations, results of operations, and financial condition.
If we cannot maintain our corporate culture as we grow, we could lose the innovation, collaboration and focus on the mission that contribute to our business.
We believe that a critical component of our success is our corporate culture and our deep commitment to our mission. We believe this mission-based culture fosters innovation, encourages teamwork and cultivates creativity. Our mission defines our business philosophy as well as the emphasis that we place on our members, our people and our culture and is consistently reinforced to and by our employees. As we continue to grow, including from the integration of employees and businesses acquired in connection with previous or future acquisitions, we may find it difficult to maintain these valuable aspects of our corporate culture and our long-term mission. Operating as a remote-first company may make it difficult for us to preserve our corporate culture and could negatively impact on workforce morale and productivity. Any failure to preserve our culture could negatively impact our future success, including our ability to attract and retain employees, encourage innovation and teamwork, and effectively focus on and pursue our mission and corporate objectives.
We are dependent on hiring an adequate number of hourly bilingual employees to run our business and are subject to government regulations concerning these and our other employees, including minimum wage laws.
Our workforce is comprised primarily of bilingual employees who work on an hourly basis. In certain areas where we operate, there is significant competition for hourly bilingual employees and the lack of availability of an adequate number of hourly bilingual employees could adversely affect our operations. In addition, we are subject to applicable rules and regulations relating to our relationship with our employees, including minimum wage and break requirements, health benefits, unemployment and sales taxes, overtime and working conditions and immigration status. We are from time to time subject to employment-related claims, including wage and hour claims. Further, legislated increases in minimum wage, as well as increases in additional labor cost components, such as employee benefit costs, workers’ compensation insurance rates, and compliance costs and fines, would increase our labor costs.
Misconduct by our employees could harm us by subjecting us to monetary loss, significant legal liability, regulatory scrutiny and reputational harm.
Our reputation is critical to maintaining and developing relationships with our existing and potential members and third parties with whom we do business. There is a risk that our employees could be accused of or engage in misconduct that adversely affects our business, including fraud, redirection, misappropriation of member funds, improper execution of loan transactions, embezzlement and theft, disclosure of personal and business information and the failure to follow protocol when interacting with members that could lead us to suffer direct losses from the activity as well as serious reputational harm. Employee misconduct could also lead to regulatory sanctions and prompt regulators to allege or to determine based upon such misconduct that we have not established adequate supervisory systems and procedures to inform employees of applicable rules or to detect and deter violations of such rules. Misconduct by our employees, or even unsubstantiated allegations of misconduct, could harm our reputation and our business.
Our international operations and offshore service providers involve inherent risks which could result in harm to our business.
As of December 31, 2022, we had 1,553 employees related to three contact centers in Mexico. These employees provide certain English/Spanish bilingual support related to member-facing contact center activities, administrative and technology support of the contact centers and back-office support services. We have also engaged outsourcing partners in the United States that provide offshore member-facing contact center activities in Colombia, Jamaica and the Philippines, and may in the future include additional locations in other countries. In addition, our technology development center in India is staffed through outsourcing partners and our own employees. We have engaged vendors that utilize employees or contractors based outside of the United States. As of December 31, 2022, our outsourcing partners have provided us, on an exclusive basis, the equivalent of 807 full-time equivalents in Colombia, Jamaica, Philippines and India. These international activities are subject to inherent risks that are beyond our control, including:
•risks related to government regulation or required compliance with local laws;
•local licensing and reporting obligations;
•difficulties in developing, staffing and simultaneously managing a number of varying foreign operations as a result of distance, language and cultural differences;
•different, uncertain, overlapping or more stringent local laws and regulations;
•political and economic instability, tensions, security risks and changes in international diplomatic and trade relations;
•state or federal regulations that restrict offshoring of business operational functions or require offshore partners to obtain additional licenses, registrations or permits to perform services on our behalf;
•natural disasters, public health issues, epidemics or pandemics, acts of war, and terrorism, and other events outside our control;
•compliance with applicable U.S. laws and foreign laws related to consumer protection, intellectual property, privacy, data security, corruption, money laundering, and export/trade control;
•misconduct by our outsourcing partners and their employees or even unsubstantiated allegations of misconduct;
•risks due to lack of direct involvement in hiring and retaining personnel; and
•potentially adverse tax developments and consequences.
Violations of the complex foreign and U.S. laws, rules and regulations that apply to our international operations and offshore activities of our service providers may result in reputational harm, heightened regulatory scrutiny, fines, criminal actions or sanctions against us, our directors or our employees, as well as restrictions on the conduct of our business.
If we discover a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting that we are unable to remedy or otherwise fail to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting or disclosure controls and procedures, our ability to report our financial results on a timely and accurate basis and the market price of our common stock may be adversely affected.
We have developed our disclosure controls, internal control over financial reporting and other procedures to ensure information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we will file with the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms, and information required to be disclosed in reports under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our principal executive and financial officers. To maintain and improve the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting, we have expended and anticipate we will continue to expend significant resources, including accounting-related costs and significant management oversight. Any failure to maintain the adequacy of our internal controls, or consequent inability to produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis, could increase our operating costs and could materially impair our ability to operate our business. Our current controls and any new controls that we develop may become inadequate because of changes in conditions in our business. If our internal controls are perceived as inadequate or we are unable to produce timely or accurate financial statements, investors may lose confidence in our operating results and our stock price could decline. In addition, if we are unable to continue to meet these requirements, we may not be able to remain listed on Nasdaq.
Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires our management to certify financial and other information in our quarterly and annual reports and provide an annual management report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. We are also required to have our independent registered public accounting firm attest to, and issue an opinion on, the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. If we are unable to assert that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, or if, when required, our independent registered public accounting firm is unable to express an opinion on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting, we could lose investor confidence in the accuracy and completeness of our financial reports, which could subject us to sanctions or investigations by the SEC or other regulatory
authorities, adversely affect our ability to access the credit markets and sell additional equity and commit additional financial and management resources to remediate deficiencies.
Because we receive a significant amount of cash in our retail locations through member loan repayments, we may be subject to theft and cash shortages due to employee errors.
Since our business requires us to receive a significant amount of cash in each of our retail locations, we are subject to the risk of theft (including by or facilitated by employees) and cash shortages due to employee errors. We have experienced theft and attempted theft in the past. Although we have implemented various procedures and programs to reduce these risks, maintain insurance coverage for theft and provide security measures for our facilities, we cannot make assurances that theft and employee error will not occur.
Our business is subject to the risks of natural disasters, public health crises and other catastrophic events, and to interruption by man-made problems.
A significant natural disaster, such as an earthquake, fire, hurricanes, flood or other catastrophic event (many of which are becoming more acute and frequent as a result of climate change), or interruptions by strikes, crime, terrorism, social unrest, cyber-attacks, pandemics or other public health crises, power outages, geopolitical unrest or other man-made problems, could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. For example, a significant natural disaster in Northern California or any other location in which we have offices or facilities or employees working remotely, could adversely affect our business operations, financial condition and prospects, and our insurance coverage may be insufficient to compensate us for losses that may occur.
Our IT systems are backed up regularly to highly available, alternate data centers in a different region, and we have conducted disaster recovery testing of our mission critical systems. Despite any precautions we may take, however, the occurrence of a natural disaster or other unanticipated problems at our data centers could result in lengthy interruptions in our services. In addition, acts of war, terrorism, and other geopolitical unrest could cause disruptions in our business and lead to interruptions, delays or loss of critical data.
In addition, a large number of members make payments and apply for loans at our retail locations. If one or more of our retail locations becomes unavailable for any reason or other public health crisis, localized weather events, or natural or man-made disasters, our ability to conduct business and collect payments from members on a timely basis may be adversely affected, which could result in lower loan originations, higher delinquencies and increased losses. For example, during parts of the COVID-19 pandemic, we temporarily closed a few of our retail locations due to public health orders or other concerns, which we believe resulted in lower Aggregate Originations. While all of our retail locations are currently open, it is possible that we will have to temporarily close retail locations as necessary due to public health orders or other concerns relating to any public health crisis. The closure of retail locations could further adversely affect our loan originations, member experience, results of operations and financial condition.
The aforementioned risks may be further increased if our business continuity plans prove to be inadequate and there can be no assurance that both personnel and non-mission critical applications can be fully operational after a declared disaster within a defined recovery time. If our personnel, systems, or primary data center facilities are impacted, we may suffer interruptions and delays in our business operations. In addition, if these events impact our members or their ability to timely repay their loans, our business could be negatively affected.
In addition, the impacts of climate change on the global economy and our industry are rapidly evolving. We may be subject to increased regulations, reporting requirements, standards or expectations regarding the environmental impacts of our business. While we seek to mitigate our business risks associated with climate change, there are inherent climate-related risks wherever business is conducted. Any of our primary locations may be vulnerable to the adverse effects of climate change. For example, our Bay Area headquarters have experienced and may continue to experience, climate-related events and at an increasing frequency, including floods, drought, water scarcity, heat waves, wildfires and resultant air quality impacts and power shutoffs associated with the wildfires. Changing market dynamics, global policy developments and increasing frequency and impact of extreme weather events on critical infrastructure in the United States and elsewhere have the potential to disrupt our business, the business of our critical vendors, partners and members, and may cause us to experience higher attrition, losses and additional costs to maintain or resume operations. In addition, current and emerging legal and regulatory requirements with respect to climate change (e.g., carbon pricing) and other aspects of ESG (e.g., disclosure requirements) may result in increased compliance requirements on our business, which may increase our operating costs and disrupt our business.
We may not maintain sufficient business interruption or property insurance to compensate us for potentially significant losses, including potential harm to our business that may result from interruptions in our ability to provide our financial products and services.
Unfavorable outcomes in legal proceedings may harm our business and results of operations.
We have been, and may in the future become, subject to litigation, claims, investigations, legal and administrative cases and proceedings, whether civil or criminal, or lawsuits by governmental agencies or private parties. If the results of any pending or future legal proceedings are unfavorable to us or if we are unable to successfully defend against third-party lawsuits, we may be required to pay monetary damages or fulfill our indemnification obligations or we may be subject to fines, penalties, injunctions or other censure. Even if we adequately address the issues raised by an investigation or proceeding or successfully defend a third-party lawsuit or counterclaim, we may have to devote significant financial and management resources to address these issues.
Funding and Liquidity Risks
We amended our Corporate Financing, as a result of which certain tranches of additional loans are available on an uncommitted basis, and our business could be adversely affected if we were unable to access such additional capital.
On March 10, 2023 (the “Second Amendment Closing Date”), Oportun Financial Corporation (the “Company”) entered into an Amendment No. 2 to Credit Agreement (the ”Second Amendment”), by and among the Company, as borrower, the subsidiaries of the Company party thereto as guarantors, certain affiliates of Neuberger Berman Specialty Finance as lenders, and Wilmington Trust, National Association, as administrative agent and collateral agent (the “Agent”), which amended the Credit Agreement, dated as of September 14, 2022 (as amended, supplemented or otherwise modified, including by the Second Amendment, the “Amended Credit Agreement”), by and among the Company, the lenders from time to time party thereto and the Agent.
On the Second Amendment Closing Date, the Company borrowed $20.8 million of incremental term loans (the “Incremental Tranche A-1 Loans”) and intends to borrow an additional $4.2 million of incremental term loans (the “Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans”) on or about March 27, 2023, which amount has been committed by the applicable lenders. Under the Amended Credit Agreement, the Company may borrow up to an aggregate additional amount of $50.0 million on an uncommitted basis, in two $25.0 million tranches (the “Incremental Tranche B Loans” and the “Incremental Tranche C Loans”) expected to be available, if provided by the applicable lenders, on or about April 21, 2023 and June 23, 2023, respectively.
The loans (the “Loans”) and other obligations under the Amended Credit Agreement are secured by the assets of the Company and certain of its subsidiaries guaranteeing the Loans, including pledges of the equity interests of certain subsidiaries that are directly or indirectly owned by the Company, subject to customary exceptions.
On the Second Amendment Closing Date, pursuant to the Second Amendment, the Company issued warrants (the “Warrants”) to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche A-1 Loans to purchase 1,980,242 shares of the Company’s common stock at an exercise price of $0.01 per share. In addition, (a) in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans to purchase 116,485 shares of the Company’s common stock, (b) in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche B Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche B Loans to purchase 1,048,363 shares of the Company’s common stock, and (c) in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche C Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche C Loans to purchase 1,048,363 shares of the Company’s common stock, in each case, at an exercise price of $0.01 per share. The Company also entered into a Registration Rights Agreement with the applicable lenders on the Second Amendment Closing Date (the “Registration Rights Agreement”), which stipulates that the Company will file a registration statement with the Securities and Exchange Commission with respect to the shares underlying the Warrants.
Given the uncommitted nature of the Incremental Tranche B and Incremental Tranche C Loans, there can be no assurance that the Company will be able to access such additional capital. If we do not have sufficient capital, we may have to take additional actions to decrease expenses, curtail the origination of loans, and our ability to continue to support our growth and to respond to challenges could be impaired.
In addition, if we do not have sufficient capital, we may need to engage in equity, debt or convertible debt financings to secure additional funds. If we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities or securities convertible into equity securities, those securities may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to the rights of our common stock and our stockholders may experience dilution. Debt financing, if available, may have a high cost of funds and may involve covenants restricting our operations or our ability to incur additional debt. Lenders may also require warrants to boost their return, the issuance of which would be dilutive to our stockholders. Any debt or additional equity financing that we raise may contain terms that are not favorable to us or our stockholders and could also negatively impact our stock price. A number of factors, including market volatility or depressed valuations, trading prices in the equity markets, our financial condition and capital market conditions will impact our ability to obtain equity or debt financing. We may not be able to engage in any of these activities or engage in these activities on desirable terms, which could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operation and financial condition.
We have incurred substantial debt and may issue debt securities or otherwise incur substantial debt in the future, which may adversely affect our financial condition and negatively impact our operations.
We have a substantial amount of indebtedness, which requires significant interest payments. From time to time, we may seek to obtain additional capital. We depend on securitization transactions, warehouse facilities and other forms of debt financing, as well as whole loan and structured loan sales, in order to finance the growth of our business and the origination of most of the loans we make to our members. Our outstanding borrowings or any additional indebtedness we may incur, could require us to divert funds identified for other purposes for debt service and impair our liquidity position. If we cannot generate sufficient cash flow from operations to service our debt, we may need to adopt one or more alternatives to refinance our debt, dispose of assets or obtain necessary funds, including obtaining additional equity capital which could be on terms that may be onerous or highly dilutive.
We do not know whether we will be able to take any of these actions on a timely basis, on terms satisfactory to us or at all.
Our substantial level of indebtedness and the current constraints on our liquidity could have important consequences, including the following:
•we must use a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations to pay interest and principal on our debt, which reduces or will reduce funds available to us for other purposes such as working capital, capital expenditures, other general corporate purposes, execution of growth strategies, and potential acquisitions;
•our ability to refinance such indebtedness or to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions or general corporate purposes may be impaired;
•default and foreclosure on our and our subsidiaries’ assets if asset performance and our operating revenue are insufficient to repay debt obligations;
•mandatory repurchase obligations for any loans conveyed or sold into a debt financing or under a whole loan purchase facility if the representations and warranties we made with respect to those loans were not correct when made;
•acceleration of obligations to repay the indebtedness (or other outstanding indebtedness to the extent of cross default triggers), even if we make all principal and interest payments when due, if we breach any covenants that require the maintenance of certain financial ratios with respect to us or the loan portfolio securing our indebtedness or the maintenance of certain reserves or tangible net worth and do not obtain a waiver for such breach or renegotiate such covenant;
•inability to obtain necessary additional financing if the debt security contains covenants restricting our ability to obtain such financing while the debt security is outstanding;
•inability to obtain necessary additional financing if changes in the characteristics of our loans or our collection and other loan servicing activities change and cease to meet conditions precedent for continued or additional availability under our debt financings;
•limitations on our flexibility in planning for and reacting to changes in our business and in the industry in which we operate;
•place us at a disadvantage compared to our competitors that have less debt;
•defaults based on loan portfolio performance or default in our collection and loan servicing obligations could result in our being replaced by a third-party or back-up servicer and notification to our members to redirect payments;
•downgrades or revisions of agency ratings for our debt financing;
•monitoring, administration and reporting costs and expenses, including legal, accounting and other monitoring reporting costs and expenses, required under our debt financings; and
•we may be more vulnerable to economic downturn and adverse developments in our business, including potential economic recession, inflation, and other factors outside our control.
Our ability to meet our expenses, to remain in compliance with our covenants under our debt instruments and to make future principal and interest payments in respect of our debt depends on, among other factors, our operating performance, competitive developments and financial market conditions, all of which are significantly affected by financial, business, economic and other factors. We are not able to control many of these factors. Given current industry and economic conditions, our cash flow may not be sufficient to allow us to pay principal and interest on our debt and meet our other obligations.
To the extent our relationship with lenders is negatively affected by disputes that may arise from time to time, it may be more difficult to seek covenant relief, if needed, or to raise additional funds in the future.
A breach of early payment triggers or covenants or other terms of our agreements with lenders could result in an early amortization, default, and/or acceleration of the related funding facilities.
The primary funding sources available to support the maintenance and growth of our business include, among others, asset-backed securitizations, revolving debt facilities (including the Secured Financing), Corporate Financing, and structured and whole loan sales. If we are unable to comply with various conditions precedent to availability under these facilities (including the eligibility of our loans), covenants and other specified requirements set forth in our agreements with our lenders, this could result in the early amortization, default and/or acceleration of our existing facilities. Such covenants and requirements include financial covenants, portfolio performance covenants and other events. The Corporate Financing contains financial covenants requiring a minimum liquidity maintenance covenant, minimum asset coverage ratio, together with other customary affirmative and negative covenants, and events of default. The obligations are secured by assets of the Company and its subsidiaries. Compliance with these covenants may limit our ability to take actions that might be to our advantage or to the advantage of our stockholders.
Our securitizations contain collateral performance threshold triggers related to the three-month average annualized gross charge-off or net charge-off rate which, if exceeded, would lead to early amortization. To support our collateral requirements under our financing agreements, we use a random selection process to take loans off our warehouse line to pledge to our securitizations. An inability to originate enough loans to meet the collateral requirements in our financing arrangements, could result in the early amortization, default and/or acceleration of our existing facilities. Moreover, we currently act as servicer with respect to the unsecured consumer loans held by our subsidiaries. If we default in our servicing obligations or fail to meet certain financial covenants, an early amortization event or event of default could occur, and/or we could be replaced by our back-up servicer or another successor servicer. If the back-up servicer or successor servicer is not adequate, the collection and processing of repayments may be impaired.
During an early amortization period or if an event of default exists, principal and interest collections from the loans in our asset-backed facilities would be applied to repay principal under such facilities and principal collections would no longer be available on a revolving basis to fund purchases of newly originated loans. If an event of default exists under our revolving debt or loan sale facilities, the applicable lenders or purchasers’ commitments to extend further credit or purchase additional loans under the related facility would terminate. If collections were insufficient to repay
the amounts due under our securitizations and our revolving debt facilities, the applicable lenders, trustees and noteholders could seek remedies, including against the collateral pledged under such facilities. Any of these events would negatively impact our liquidity, including our ability to originate new loans, and require us to rely on alternative funding sources. If we were unable to arrange new or alternative methods of financing on favorable terms, we might have to curtail the origination of loans, and we may be replaced by our back-up servicer or another successor servicer.
Various risks, uncertainties and events beyond our control could affect our ability to comply with these covenants and maintain these financial ratios. Failure to comply with any of the covenants in our existing or future financing agreements could result in a default under those agreements and under other agreements containing cross-default provisions. A default would permit lenders to accelerate the maturity for the debt under these agreements and to foreclose upon any collateral securing the debt. Under these circumstances, we might not have sufficient funds or other resources to satisfy all of our obligations. In addition, the limitations imposed by financing agreements on our ability to incur additional debt and to take other actions might significantly impair our ability to obtain other financing. For more information on covenants, requirements and events, see Note 9, Borrowings of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report.
Our securitizations and structured and whole loan sales may expose us to certain risks, and we can provide no assurance that we will be able to conduct such transactions in the future, which may require us to seek more costly financing.
We have securitized, and may in the future securitize, certain of our loans to generate cash to originate new loans or pay our outstanding indebtedness. In each such transaction and in connection with our warehouse facilities, we sell and convey a pool of loans to a special purpose entity ("SPE"). Concurrently, each SPE issues notes or certificates pursuant to the terms of an indenture. The securities issued by the SPE are secured by the pool of loans owned by the SPE. In exchange for the sale of a portion of the pool of loans to the SPE, we receive cash, which are the proceeds from the sale of the securities. We also contribute a portion of the pool of loans in consideration for the equity interests in the SPE. Subject to certain conditions in the indenture governing the notes issued by the SPE (or the agreement governing the SPE’s revolving loan), the SPE is permitted to purchase additional loans from us or distribute to us residual amounts received by it from the loan pool, which residual amounts are the cash amounts remaining after all amounts payable to service providers and the noteholders have been satisfied. We also have the ability to swap pools of loans with the SPE. Our equity interest in the SPE is a residual interest in that it entitles us as the equity owner of the SPE to residual cash flows, if any, from the loans and to any assets remaining in the SPE once the notes are satisfied and paid in full (or in the case of a revolving loan, paid in full and all commitments terminated). As a result of challenging credit and liquidity conditions, the value of the subordinated securities we retain in our securitizations might be reduced or, in some cases, eliminated.
The securitization market is subject to changing market conditions, and we may not be able to access this market when we would otherwise deem appropriate. Further, other matters, such as (i) accounting standards applicable to securitization transactions and (ii) capital and leverage requirements applicable to banks and other regulated financial institutions holding asset-backed securities, could result in decreased investor demand for securities issued through our securitization transactions, or increased competition from other institutions that undertake securitization transactions. In addition, compliance with certain regulatory requirements may affect the type of securitizations that we are able to complete.
Asset-backed securities and the securitization markets were heavily affected by the Dodd-Frank Act and have also been a focus of increased regulation by the SEC. For example, the Dodd-Frank Act mandates the implementation of rules requiring securitizers or originators to retain an economic interest in a portion of the credit risk for any asset that they securitize or originate. Furthermore, sponsors are prohibited from diluting the required risk retention by dividing the economic interest among multiple parties or hedging or transferring the credit risk the sponsor is required to maintain. Rules relating to securitizations rated by nationally-recognized statistical rating agencies require that the findings of any third-party due diligence service providers be made publicly available at least five business days prior to the first sale of securities, which has led and will continue to lead us to incur additional costs in connection with each securitization. In addition, some of the regulations to be implemented under the Dodd-Frank Act relating to securitization have not yet been finalized. Any new rules or changes to the Dodd-Frank Act (or the current rules thereunder) could adversely affect our ability and our cost to access the asset-backed securities market.
If it is not possible or economical for us to securitize our loans in the future, we would need to seek alternative financing to support our operations and to meet our existing debt obligations, which may not be available on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. If the cost of such alternative financing were to be higher than our securitizations, we would likely reduce the fair value of our loans receivable held for investment, which would negatively impact our results of operations.
The gain on sale generated by any of our structured or whole loan sales and servicing fees earned on sold loans represents a significant source of our earnings. Demand for our loans at the current premiums may be impacted by factors outside our control, including availability of loan pools, demand by investors for loan assets and attractiveness of returns offered by competing investment alternatives offered by other loan originators with more attractive characteristics than our loan pools and loan purchaser interest. In March 2022, we participated in a securitization through which we issued amortizing asset-backed notes secured by a pool of its unsecured and secured personal installment loans and may do additional structured loan sales in the future. See Note 5, Loans Held for Sale and Loans Sold of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report. If we are unable to sell additional loans or obtain other financing, our revenue and liquidity may be negatively impacted and we may not be able to grow our business as planned and we may have to further curtail our originations.
Our results of operations are affected by our ability to sell our loans for a premium over their net book value. Potential loan purchasers might reduce the premiums they are willing to pay, or even require a discount to principal balance, for the loans that they purchase during periods of economic slowdown or recession to compensate for any increased risks. A reduction in the sale price of the loans we sell under any future whole loan sale program would likely result in a reduction in the fair value of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value, which would negatively impact our results of operations. Any sustained decline in demand for our loans or increase in delinquencies, defaults or foreclosures may reduce the price we receive on future loan sales below our loan origination cost.
We may need to raise additional funds in the future, including through equity, debt, or convertible debt financings, to support business growth and those funds may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all.
We intend to continue to make investments to support our business growth and may require additional funds to respond to business challenges, including the need to develop new financial products and services, enhance our risk management model, improve our operating infrastructure, or acquire complementary businesses and technologies. Additionally, increases in our cost of funds and charge-offs may reduce our margins and require us to raise more capital to support our existing business and execute our corporate strategies. Accordingly, we may need to engage in equity, debt or convertible debt financings to secure additional funds. If we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities or securities convertible into equity securities, those securities may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to the rights of our common stock and our stockholders may experience dilution. Any large equity or equity-linked offering could also negatively impact our stock price. A number of factors, including market volatility or depressed valuations, trading prices in the equity markets, our financial condition and capital market conditions will impact our ability to obtain equity or debt financing.
Debt financing, if available, may involve covenants restricting our operations or our ability to incur additional debt. Lenders may also require warrants to boost their return, the issuance of which would be dilutive to our stockholders. Any debt or additional equity financing that we raise may contain terms that are not favorable to us or our stockholders.
If we do not have sufficient capital, we may be unable to pursue certain opportunities and our ability to continue to support our growth and to respond to challenges could be impaired.
Intellectual Property Risks
It may be difficult and costly to protect our intellectual property rights, and we may not be able to ensure their protection.
Our ability to offer our products and services to our members depends, in part, upon our proprietary technology. We may be unable to protect our proprietary technology effectively which would adversely affect our ability to compete with them. We rely on a combination of copyright, trade secret, trademark laws and other rights, as well as confidentiality procedures and contractual provisions to protect our proprietary technology, processes and other intellectual property and do not have patent protection. However, the steps we take to protect our intellectual property rights may be inadequate. For example, a third party may attempt to reverse engineer or otherwise obtain and use our proprietary technology without our consent. The pursuit of a claim against a third party for infringement of our intellectual property could be costly, and there can be no guarantee that any such efforts would be successful. Our failure to secure, protect and enforce our intellectual property rights could adversely affect our brand and business.
We have been, and may in the future be, sued by third parties for alleged infringement of their proprietary rights.
Our proprietary technology, including our credit risk models and A.I. algorithms, may infringe upon claims of third-party intellectual property, and we may face intellectual property challenges from such other parties. The expansion of our suite of financial products and services may create additional trademark risk. We may not be successful in defending against any such challenges or in obtaining licenses to avoid or resolve any intellectual property disputes. If we are unsuccessful, such claim or litigation could result in a requirement that we pay significant damages or licensing fees, which would negatively impact our financial performance. We may also be obligated to indemnify parties or pay substantial legal settlement costs, including royalty payments, and to modify applications or refund fees. Even if we were to prevail in such a dispute, any litigation regarding our intellectual property could be costly and time consuming, and may divert the attention of our management and key personnel from our business operations.
Moreover, it has become common in recent years for individuals and groups to purchase intellectual property assets for the sole purpose of making claims of infringement and attempting to extract settlements from companies such as ours. Even in instances where we believe that claims and allegations of intellectual property infringement against us are without merit, defending against such claims is time consuming and expensive and could result in the diversion of time and attention of our management and employees. In addition, although in some cases a third party may have agreed to indemnify us for such costs, such indemnifying party may refuse or be unable to uphold its contractual obligations. In other cases, our insurance may not cover potential claims of this type adequately or at all, and we may be required to pay monetary damages, which may be significant.
Our credit risk models, A.I. capabilities, and internal systems rely on software that is highly technical, and if it contains undetected errors, our business could be adversely affected.
Our credit risk models, A.I. capabilities, and internal systems rely on internally developed software that is highly technical and complex. In addition, our models, A.I. capabilities, and internal systems depend on the ability of such software to store, retrieve, process and manage immense amounts of data. The software on which we rely has contained, and may now or in the future contain, undetected errors, bugs or other defects. Some errors may only be discovered after the code has been released for external or internal use. Errors, bugs or other defects within the software on which we rely may result in a negative experience for our members, result in errors or compromise our ability to protect member data or our intellectual property. Specifically, any defect in our credit risk models could result in the approval of unacceptably risky loans. Such defects could also result in reputational harm, loss of members, loss of revenue, adjustments to the fair value of our loans receivable held for investment or our asset-backed notes, challenges in raising capital, or liability for damages.
Some aspects of our business processes include open source software, and any failure to comply with the terms of one or more of these open source licenses could negatively affect our business.
We incorporate open source software into processes supporting our business. Such open source software may include software covered by licenses like the GNU General Public License and the Apache License. The terms of various open source licenses have not been interpreted by U.S. courts, and there is a risk that such licenses could be construed in a manner that limits our use of the software, inhibits certain aspects of our systems and negatively affects our business operations.
Some open source licenses contain requirements that we make source code available at no cost for modifications or derivative works we create based upon the type of open source software we use. We may face claims from third parties claiming ownership of, or demanding the release or license of, such modifications or derivative works (which could include our proprietary source code or credit risk models) or otherwise seeking to enforce the terms of the applicable open source license. If portions of our proprietary credit risk models are determined to be subject to an open source license, or if the license terms for the open source software that we incorporate change, we could be required to publicly release the affected portions of our source code, re-engineer all or a portion of our model or change our business activities, any of which could negatively affect our business and our intellectual property rights.
In addition to risks related to license requirements, the use of open source software can lead to greater risks than the use of third-party commercial software, as open source licensors generally do not provide warranties or controls on the origin of the software. Use of open source software may also present additional security risks because the public availability of such software may make it easier for hackers and other third parties to determine how to breach our website and systems that rely on open source software.
Industry and Regulatory Risks
The financial services industry is highly regulated. Changes in regulations or in the way regulations are interpreted and applied to our business could adversely affect our business.
We are subject to various federal, state and local regulatory regimes related to the financial services that we provide. The principal policy objectives of these regulatory regimes are to provide meaningful disclosures to consumers, to protect against unfair, deceptive and abusive acts or practices and to prevent discrimination. Laws and regulations, among other things, impose licensing and qualifications requirements; require various disclosures and consents; mandate or prohibit certain terms and conditions for various financial products; prohibit discrimination based on certain prohibited bases; prohibit unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices; require us to submit to examinations by federal and state regulatory regimes; and require us to maintain various policies, procedures and internal controls.
Federal and state agencies have broad enforcement powers over us, including powers to periodically examine and continuously monitor our operations and to investigate our business practices and broad discretion to deem particular practices unfair, deceptive, abusive or otherwise not in accordance with the law. State attorneys general have a variety of legal mechanisms at their disposal to enforce state and federal consumer financial laws. For example, Section 1042 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the "Dodd-Frank Act") grants state attorneys general the ability to enforce the Dodd-Frank Act and regulations promulgated under the Dodd-Frank Act’s authority and to secure remedies against entities within their jurisdiction. State attorneys general also have a variety of legal mechanisms at their disposal to enforce state and federal consumer financial laws have enforcement authority under state law with respect to unfair or deceptive practices. Generally, under these statutes, state attorneys general may conduct investigations, bring actions, and recover civil penalties or obtain injunctive relief against entities engaging in unfair, deceptive, or fraudulent acts. Attorneys general may also coordinate among themselves or with other regulators to enter into coordinated actions or settlements. Finally, several consumer financial laws like the Truth in Lending Act and Fair Credit Reporting Act grant enforcement or litigation authority to state attorneys general.
Changes in laws or regulations, or the regulatory application or interpretation of the laws and regulations applicable to us, could adversely affect our ability to operate in the manner in which we currently conduct business, and may also make it more difficult or costly for us to originate additional loans, or for us to collect payments on our loans to members or otherwise operate our business by subjecting us, our service providers, or strategic partners, to additional licensing, registration and other regulatory requirements in the future.
Failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations could result in additional compliance requirements, limitations on our ability to collect or retain all or part of the principal of or interest on loans, fines or penalties, an inability to continue operations, modification in business practices, regulatory actions, loss of required licenses or registrations, potential impairment, voiding, or voidability of loans, rescission of contracts, civil and criminal liability and damage to our reputation. It could also result in a default or early amortization event under certain of our debt facilities and reduce or terminate availability of debt financing to us to fund originations. To the extent it is determined that any loan we make was not originated in accordance with all applicable laws as we are required to represent under our securitization and other debt facilities and in loan sales to investors, we could be obligated to repurchase for cashor swap for qualifying assets, any such loan determined not to have been originated in compliance with legal requirements. We may not have adequate liquidity and resources to make such cash repurchases or swap for qualifying assets.
Litigation, regulatory actions and compliance issues could subject us to significant fines, penalties, judgments, remediation costs and/or requirements resulting in increased expenses and reputational harm.
In the ordinary course of business, we have been named as a defendant in various legal actions, including class actions and other litigation. Generally, this litigation arises from the claims of violation of do-not-call, credit reporting, collection, and bankruptcy laws. The complexity of the laws related to secured personal loans regarding vehicle titling, lien placement and repossession may enhance the risk of consumer litigation. Further, the origination of loans through bank partnerships may increase the risk of litigation or regulatory scrutiny including based on the "true lender" theory that seeks to recharacterize a lending transaction. State legislation requiring licensure and state restrictions including fee and rate limits on bank partner loans may also reduce profitability and/or increase regulatory and litigation risk. Additionally, platforms offering banking services and products through partners have also been challenged by federal and state regulators on a variety of claims.
Regulatory bodies may enact new laws or promulgate new regulations or view matters or interpret laws and regulations differently than they have in the past, or commence investigations or inquiries into our business practices. For example, in April 2022, the CFPB announced that it intends to examine nonbank financial companies that pose risks to consumers, and in November 2022, the Treasury Department issued a report encouraging the CFPB to increase its supervisory activity with respect to larger nonbank lenders. If the CFPB decides to subject us to its supervisory process, it could significantly increase the level of regulatory scrutiny of our business practices. In addition, the Biden Administration recently announced a government-wide effort to eliminate “junk fees” which could subject our business practices to even further scrutiny. The CFPB’s action on junk fees thus far has largely focused on fees associated with deposit products, such as “surprise” overdraft fees and not-sufficient-funds fees, that are not within scope of our products or services. However, what constitutes a “junk fee” remains undefined. The CFPB has called out other fees, such as pay-to-pay fees charged by debt collectors, and is actively soliciting consumer input on fee practices associated with other consumer financial products or services, signaling that the “junk fee” initiative is likely to continue to broaden in scope. In February 2023, the CFPB published a proposed rule, which is currently subject to public comment, amending Regulation Z to mandate significant decreases to credit card late fees and eliminate annual inflation adjustments for late fee safe harbor amounts. All such legal and regulatory actions are inherently unpredictable and, regardless of the merits of the claims, legal and regulatory actions are often expensive, time-consuming, disruptive to our operations and resources, and distracting to management. In addition, certain of those actions include claims for indeterminate amounts of damages. Our involvement in any such matter also could cause significant harm to our reputation and divert management attention from the operation of our business, even if the matters are ultimately determined in our favor. If resolved against us, legal actions could result in excessive verdicts and judgments, injunctive relief, equitable relief, and other adverse consequences that may affect our financial condition and how we operate our business. We have in the past chosen to settle (and may in the future choose to settle) certain matters in order to avoid the time and expense of litigating them. Although none of the settlements has been material to our business, there is no assurance that, in the future, such settlements will not have a material adverse effect on our business.
In addition, a number of participants in the consumer financial services industry have been the subject of putative class action lawsuits, state attorney general actions and other state regulatory actions, federal regulatory enforcement actions, including actions relating to alleged unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices, violations of state licensing and lending laws, including state usury laws, actions alleging violations of the Americans with Disabilities Act, discrimination on the basis of race, ethnicity, gender or other prohibited bases, and allegations of noncompliance with various state and federal laws and regulations relating to originating and servicing consumer finance loans and other consumer financial services and products. The current regulatory environment, increased regulatory compliance efforts, and enhanced regulatory enforcement have resulted in significant operational and compliance costs and may prevent us from providing certain products and services. There is no assurance that these regulatory matters or other factors will not, in the future, affect how we conduct our business or adversely affect our business. In particular, legal proceedings brought under state consumer protection statutes or under several of the various federal consumer financial services statutes subject to the jurisdiction of the CFPB may result in a separate fine for each violation of the statute, which, particularly in the case of class action lawsuits, could result in damages substantially in excess of the amounts we earned from the underlying activities.
Some of our consumer financing agreements include arbitration clauses. If our arbitration agreements were to become unenforceable for any reason, we could experience an increase to our consumer litigation costs and exposure to potentially damaging class action lawsuits.
In addition, from time to time, through our operational and compliance controls, we identify compliance issues that require us to make operational changes and, depending on the nature of the issue, result in financial remediation to impacted members. These self-identified issues and voluntary remediation payments could be significant, depending on the issue and the number of members impacted, and could generate litigation or regulatory investigations that subject us to additional risk.
Internet-based and electronic signature-based loan origination processes may give rise to greater risks than paper-based processes.
We use internet-based loan processes to obtain application information, distribute certain legally required notices to applicants and borrowers, and to obtain electronically signed loan documents in lieu of paper documents with wet borrower signatures obtained in person. These processes may entail greater risks than would paper-based loan origination processes, including risks regarding the sufficiency of notice for compliance with consumer protection laws, risks that borrowers may challenge the authenticity of their signature or of the loan documents, risks that a court of law may not enforce electronically signed loan documents and risks that, despite controls, unauthorized changes are made to the electronic loan documents. If any of those factors were to cause any loans, or any of the terms of the loans, to be unenforceable against the borrowers, or impair our ability to service our loans, the value of our loan assets would decrease significantly to us and to our whole loan purchasers, securitization investors and warehouse lenders. In addition to increased default rates and losses on our loans, this could lead to the loss of whole loan purchasers and securitization investors and trigger terminations and amortizations under our debt warehouse facilities, each of which would materially adversely impact our business.
The CFPB has broad authority to regulate consumer financial services, creating uncertainty as to how the agency’s actions or the actions of any other new agency could impact our business.
The CFPB has broad authority to create and modify regulations under federal consumer financial protection laws and regulations, such as the Truth in Lending Act and Regulation Z, the Equal Credit Opportunity Act and Regulation B, the Fair Credit Reporting Act and Regulation V, the Electronic Funds Transfer Act and Regulation E, and to enforce compliance with those laws. The CFPB is charged with the examination and supervision of certain participants in the consumer financial services market, including short-term, small dollar lenders, and larger participants in other areas of financial services. While historically, we have not been subject to CFPB supervisory authority, it is possible that we may become subject to additional regulatory scrutiny and compliance costs going forward through supervision by the CFPB. In recent publications, the CFPB has indicated that the agency is significantly increasing its oversight and scrutiny over consumer finance and on April 25, 2022, the CFPB announced that it was invoking a previously unused legal provision to examine nonbank financial companies that it believes pose risk to consumers. The CFPB may also request, through examination or investigation, reports concerning our organization, business conduct, markets and activities and if the CFPB were to determine that we were engaging in activities that pose risks to consumers, may conduct on-site examinations of our business on a periodic basis. On October 19, 2022, in Community Financial Services Association of America v. Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit found that the CFPB's independent funding through the Federal Reserve violated the U.S. Constitution’s appropriations clause and invalidated the remaining portions of the CFPB’s restrictions on the lenders offering payday, auto title and other short-term, high-interest loans. The CFPB has appealed the decision to the Supreme Court of the United States and we are unable to predict the timing, outcome, and impact of this litigation.
In addition, the CFPB maintains an online complaint system that allows consumers to log complaints with respect to various consumer finance products, including the credit products we offer. This system could inform future CFPB decisions with respect to its regulatory, enforcement or examination focus. The CFPB also may issue requests for public input in certain areas of concern that may lead to increased regulatory scrutiny on us, our products and consumer finance industry and impose restrictions on fees and charges, thereby impacting results of our business. For example, in March 2022, it requested public input on fees for financial products and has indicated that it plans to ramp up enforcement actions against lenders that illegally charge credit card late-payment fees and may rewrite its rules that set thresholds for such fees. Further, in February 2023, the CFPB proposed a rule that would amend regulations to limit credit card late-payment fees to $8 or 25% of the minimum payment due, whichever is greater.
On March 3, 2021, we received a Civil Investigative Demand (CID) from the CFPB. The stated purpose of the CID is to determine whether small-dollar lenders or associated persons, in connection with lending and debt-collection practices, have failed to comply with certain federal consumer protection laws over which the CFPB has jurisdiction. We have received additional information requests related to the CID. The information requests are focused on our legal collection practices from 2019 to 2021 and hardship treatments offered to members during the COVID-19 pandemic. On September 15, 2022, we received a Notice and Opportunity to Respond and Advise (“NORA”) letter from the staff of the CFPB in connection with the CID, stating that it is considering whether to recommend that the CFPB take legal action against us based on alleged violations focused on our failure to timely dismiss certain lawsuits and the hardship treatments offered during the COVID-19 pandemic, including credit reporting related thereto. On October 14, 2022, we provided the CFPB with a written response to the NORA letter disputing the allegations. The Company is cooperating fully with the CFPB with respect to this matter and we believe that our business practices have been in full compliance with applicable laws. Because the CFPB has broad authority to determine what it views as potentially unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices, at this time, the Company is unable to predict the ultimate outcome of this matter.
Digit received a CID from the CFPB in June 2020. The CID was disclosed and discussed during the acquisition process. The stated purpose of the CID is to determine whether Digit, in connection with offering its products or services, misrepresented the terms, conditions, or costs of the products or services in a manner that is unfair, deceptive, or abusive. While the Company believes that the business practices of the Company, including Digit, have been in full compliance with applicable laws, in the interest of resolving this matter, on August 11, 2022, Digit agreed to a consent order with the CFPB resolving such CID. In connection with such consent order, Digit agreed to implement a redress and compliance plan to pay at least $68,145 in consumer redress to consumers who may have been harmed and paid a $2.7 million civil penalty to the CFPB in the third quarter of 2022.
Other federal or state regulators could launch similar investigations or join the CFPB in its investigation. In addition, actions by the CFPB could result in requirements to alter or cease offering affected financial products and services, making them less attractive and restricting our ability to offer them. The CFPB could also implement rules that restrict our effectiveness in servicing our financial products and services. Future actions by the CFPB (or other regulators) against us or our competitors that discourage the use of our or their services or restrict our business activities could result in reputational harm and adversely affect our business. If the CFPB changes regulations that were adopted in the past by other regulators and transferred to the CFPB by the Dodd-Frank Act, or modifies through supervision or enforcement past regulatory guidance or interprets existing regulations in a different or stricter manner than they have been interpreted in the past by us, the industry or other regulators, our compliance costs and litigation exposure could increase materially. The current presidential administration has appointed and is expected to continue to appoint consumer-oriented regulators at federal agencies such as the CFPB, FTC, OCC and FDIC, and the government’s focus on enforcement of federal consumer protection laws is expected to increase. It is possible that these regulators could promulgate rulemakings and bring enforcement actions that materially impact our business and the business of our lending partners.
The collection, storage, use, disclosure, and other processing of personal information is an area of increasing complexity and scrutiny.
We collect, store, use, disclose, and otherwise process a large volume of personal information about individuals (including members and employees). New laws and regulations concerning the processing of personal information continue to be vigorously debated and enacted at all levels of government across the United States and around the globe while existing laws, such as the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, are being amended or reinterpreted to account for the rapidly evolving data economy. The California Consumer Privacy Act (the "CCPA"), including the California Privacy Rights Act of 2020 ("CPRA") amendments imposes significant requirements on businesses processing consumer personal information – principally
around enabling and honoring consumer choices related to such processing. Violations of the CCPA can result in civil penalties assessed by the Attorney General or the California Privacy Protection Agency and individual plaintiffs may pursue statutory damages in a private right of action for certain data breaches. Several U.S. states have already followed California’s lead in enacting comprehensive privacy legislation and others are likely to do so in the future. At the federal level, regulators, including the CFPB and FTC, have adopted, or are considering adopting, laws and regulations concerning personal information and data privacy and security. The FTC, for example, released its updated Standards for Safeguarding Customer Information (Safeguards Rule), effective June 9, 2023, which raises the bar for covered financial institutions’ information security programs through proscriptive requirements for things like accountability and oversight, performing risk assessments, encryption, and enabling multi-factor authentication to protect all forms of customer information. This patchwork of legislation and regulation may give rise to conflicts or differing views of personal privacy rights.
The rapidly evolving privacy and data protection regulatory environment, along with increased scrutiny from consumers and their advocates and increased complexity in Oportun’s organizational structure, demands careful attention to our own processing of personal information and processing by third parties acting on our behalf. For example, we’ve seen an increase in third-party arrangements, including, for example, with lead aggregators, bank partners, Lending as a Service partners and affiliate relationships through our subsidiary Digit. Our failure, or a failure by third parties with whom we do business, to comply with applicable privacy laws or regulations and contractual obligations required by our business partners, and even a perceived failure, could damage our reputation, harm our ability to obtain market adoption, discourage existing and prospective members from using our products and services, require us to change our business practices, business partners or operational structure, or result in investigations, claims, or fines by governmental agencies and private plaintiffs. Even in the absence of a challenge to our practices, we may incur substantial costs to implement new systems to comply with regulatory requirements, such as consumer requests concerning the processing of their personal information and to honor any choices that may be available to them by law.
Our business is subject to the regulatory framework applicable to registered investment advisers, including regulation by the SEC.
We offer investment management services through Digit Advisors, LLC which provides automated investment advice regarding the selection of a portfolio of exchange traded funds through our mobile application. Digit Advisors is registered as an investment adviser under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended (the "Advisers Act"), and is subject to regulation by the SEC.
Investment advisers are subject to the anti-fraud provisions of the Advisers Act and to fiduciary duties derived from these provisions, which apply to our relationships with our members who are advisory clients, as well as the funds we manage. These provisions and duties impose restrictions and obligations on us with respect to our dealings with our members, including for example restrictions on transactions with our affiliates. Our investment adviser has in the past and will in the future be subject to periodic SEC examinations. Our investment adviser is also subject to other requirements under the Advisers Act and related regulations primarily intended to benefit advisory clients. These additional requirements relate to matters including maintaining effective and comprehensive compliance programs, record-keeping and reporting and disclosure requirements. The Advisers Act generally grants the SEC broad administrative powers, including the power to limit or restrict an investment adviser from conducting advisory activities in the event such investment adviser fails to comply with federal securities laws. Additional sanctions that may be imposed for failure to comply with applicable requirements include the prohibition of individuals from associating with an investment adviser, the revocation of registrations and other censures and fines. Even if an investigation or proceeding did not result in a sanction or the sanction imposed against us or our employees were small in monetary amount, the adverse publicity relating to the investigation, proceeding or imposition of these sanctions could harm our reputation and ability to gain or retain members.
Our bank partnership products may lead to regulatory risk and may increase our regulatory burden.
We provide our credit card products through a bank partnership program with WebBank and we have bank partnership programs with Pathward, N.A., to offer unsecured installment loans and provide deposit accounts, debit card services and other transaction services to our members. State and federal agencies have broad discretion in their interpretation of laws and their interpretation of requirements related to bank partnership programs and may elect to alter standards or the interpretation of the standards applicable to these programs. In addition, as a result of our bank partnerships, prudential bank regulators with supervisory authority over our partners have the ability to regulate aspects of our business. There has also been significant recent government enforcement action and litigation challenging the validity of such arrangements for lending products, including disputes seeking to recharacterize lending transactions on the basis that the non-bank party rather than the bank is the “true lender” or “de facto lender”, and in case law challenging the “valid when made” doctrine, which holds that based on federal preemption, state interest rate limitations are not applicable in the context of certain bank-non-bank partnership arrangements.
The uncertainty of the federal and state regulatory environments around bank partnership programs means that our efforts to launch products and services through bank partners may not ultimately be successful, or may be challenged by legislation or regulatory action. If the legal structure underlying our relationship with our bank partners were to be successfully challenged, we may be found to be in violation of state licensing requirements and state laws regulating interest rates and fees. In the event of such a challenge or if our arrangements with our bank partners were to change or end for any reason, we would need to rely on an alternative bank relationship, find an alternative bank relationship, rely on existing state licenses, obtain new state licenses, pursue a national bank charter, and/or be subject to the interest rate limitations of certain states. In addition, adverse orders or regulatory enforcement actions against our bank partners, even if unrelated to our business, could impose restrictions on their ability to continue to extend credit or on current terms. Regulation by federal and state regulators may also subject us to increased compliance, legal and operational costs, and could subject our business model to scrutiny and otherwise increase our regulatory burden, or may adversely affect our ability to expand our business.
Anti-money laundering, anti-terrorism financing and economic sanctions laws could have adverse consequences for us.
We maintain a compliance program designed to enable us to comply with all applicable anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing laws and regulations, including the Bank Secrecy Act and the USA PATRIOT Act and U.S. economic sanctions laws administered by the Office of Foreign Assets Control. This program includes policies, procedures, processes and other internal controls designed to identify, monitor, manage and mitigate the risk of money laundering and terrorist financing and engaging in transactions involving sanctioned countries persons and entities. These controls include procedures and processes to detect and report suspicious transactions, perform member due diligence, respond to requests from law enforcement, and meet all recordkeeping and reporting requirements related to particular transactions involving currency or monetary instruments. Our failure to comply with anti-money laundering, economic and trade sanctions regulations, and similar laws could subject us to substantial civil and criminal penalties, or result in the loss or restriction of our state licenses, or liability under our contracts with third parties, which may significantly affect our ability to conduct some aspects of our business. Changes in this regulatory environment, including changing interpretations and the implementation of new or varying regulatory requirements, may significantly affect or change the manner in which we currently conduct some aspects of our business.
We may have to constrain our business activities to avoid being deemed an investment company under the Investment Company Act.
The Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the "Investment Company Act") contains substantive legal requirements that regulate the way “investment companies” are permitted to conduct their business activities. We believe we have conducted, and we intend to continue to conduct, our business in a manner that does not result in our company being characterized as an investment company, including by relying on certain exemptions from registration as an investment company. We rely on guidance published by the SEC staff or on our analyses of such guidance to determine our qualification under these and other exemptions. To the extent that the SEC staff publishes new or different guidance with respect to these matters, we may be required to adjust our business operations accordingly. If we are deemed to be an investment company, we may attempt to seek exemptive relief from the SEC, which could impose significant costs and delays on our business. We may not receive such relief on a timely basis, if at all, and such relief may require us to modify or curtail our operations. If we are deemed to be an investment company, we may also be required to institute burdensome compliance requirements and our activities may be restricted.
We are subject to governmental export and import controls that could subject us to liability, impair our ability to compete in international markets and adversely affect our business.
Although our business does not involve the commercial sale or distribution of hardware, software or technology, in the normal course of our business activities we may from time to time ship general commercial equipment outside the United States to our subsidiaries or affiliates for their internal use. In addition, we may export, transfer or provide access to software and technology to non-U.S. persons such as employees and contractors, as well as third-party vendors and consultants engaged to support our business activities. In all cases, the sharing of software and/or technology is solely for the internal use of the company or for the use by business partners to provide services to us, including software development. However, such shipments and transfers may be subject to U.S. and foreign regulations governing the export and import of goods, software and technology. If we fail to comply with these laws and regulations, we and certain of our employees could be subject to significant sanctions, fines, penalties and reputational harm. Further, any change in applicable export, import or economic sanctions regulations or related legislation, shift in approach to the enforcement or scope of existing regulations or change in the countries, persons or technologies targeted by these regulations could adversely affect our business.
General Risk Factors
You may be diluted by the future issuance of additional common stock in connection with our equity incentive plans, acquisitions or otherwise.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation authorizes us to issue shares of common stock authorized but unissued and rights relating to common stock for the consideration and on the terms and conditions established by our Board in its sole discretion, whether in connection with acquisitions or otherwise. We have authorized 9,072,159 shares for issuance under our 2019 Equity Incentive Plan, 1,593,052 shares for issuance under our 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, and 563,955 shares for issuance under our 2021 Inducement Equity Incentive Plan, each subject to adjustment in certain events. Any common stock that we issue, including under our existing equity incentive plans or other equity incentive plans that we may adopt in the future, could dilute your percentage ownership.
The issuance of shares of our Common Stock upon exercise of our outstanding Warrants issued in connection with the Amended Credit Agreement would increase the number of shares eligible for future resale in the public market and result in dilution to our stockholders.
As of March 10, 2023, the Warrants to purchase 1,980,242 shares of our Common Stock issued in connection with the Amended Credit Agreement were outstanding and exercisable. The exercise price of these Warrants is $0.01 per share. In addition, pursuant to the Amended Credit Agreement, in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans to purchase 116,485 shares of the Company’s common stock, in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche B Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche B Loans to purchase 1,048,363 shares of the Company’s common stock, and in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche C Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche C Loans to purchase 1,048,363 shares of the Company’s common stock, in each case, at an exercise price of $0.01 per share. The Company also entered into the Registration Rights Agreement, which stipulates that the Company will file a registration statement with the Securities and Exchange Commission with respect to the shares underlying the Warrants. To the extent such warrants are exercised, additional shares of common stock will be issued, which will result in dilution to holders of our common stock and increase the number of shares
eligible for resale in the public market. Sales of substantial numbers of such shares in the public market or the fact that such warrants may be exercised could adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
The price of our common stock may be volatile, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
The trading price of our common stock has been and may continue to be volatile and will depend on a number of factors, including those described in this “Risk Factors” section, many of which are beyond our control and may not be related to our operating performance. These fluctuations could cause you to lose all or part of your investment in our common stock, because you might be unable to sell your shares at or above the price you paid. Factors that could cause fluctuations in the trading price of our common stock include the following:
•failure to meet quarterly or annual guidance with regard to revenue, margins, earnings or other key financial or operational metrics;
•fluctuations in the trading volume of our share or the size of our public float;
•price and volume fluctuations in the overall stock market from time to time;
•changes in operating performance and market valuations of similar companies;
•failure of financial analysts to maintain coverage of us, changes in financial estimates by any analysts who follow our company, or our failure to meet these estimates or the expectations of investors;
•speculation in the press or investment community;
•any major change in our management;
•sales of shares of our common stock by us or our stockholders;
•actual or anticipated fluctuations in our results of operations;
•actual or perceived data security breaches or incidents impacting us or our third-party service providers;
•changes in prevailing interest rates;
•quarterly fluctuations in demand for our loans;
•actual or anticipated developments in our business or our competitors’ businesses or the competitive landscape generally;
•developments or disputes concerning our intellectual property or other proprietary rights;
•litigation, government investigations and regulatory actions;
•passage of legislation or other regulatory developments that adversely affect us or our industry;
•general economic conditions, such as rising interest and inflation rates; and
•other risks and uncertainties described in these risk factors.
Broad market and industry factors may seriously affect the market price of our common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance. In the past, following periods of volatility in the overall market and the market prices of particular companies’ securities, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against these companies. Such litigation could result in substantial costs and a diversion of our management’s attention and resources, which could harm our business. We may be the target of additional litigation of this type in the future as well.
If financial or industry analysts do not publish research or reports about our business, or if they issue an adverse or misleading opinion regarding our stock, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock is influenced by the research and reports that industry or financial analysts publish about us or our business. We do not control these analysts or the content and opinions included in their reports. If any of the analysts who cover us issue an adverse or misleading opinion regarding our stock price, our stock price would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease coverage of our company or fail to publish reports on us regularly, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause our stock price or trading volume to decline.
The enactment of tax reform legislation could adversely impact our financial position and results of operations.
Legislation or other changes in U.S. and international tax laws could increase our liability and adversely affect our after-tax profitability. For example, the United States recently enacted the Inflation Reduction Act, which implemented, among others, a 15% alternative minimum tax on adjusted financial statement income for certain large companies and a 1% excise tax on certain stock buybacks. In addition, many countries and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development have reached an agreement to implement a 15% global minimum tax. Such proposed changes, as well as regulations and legal decisions interpreting and applying these changes, may have significant impacts on our effective tax rate, cash tax expenses and net deferred taxes in the future.
Our directors, officers, and principal stockholders have substantial control over our company, which could limit your ability to influence the outcome of key transactions, including a change of control.
Our directors, executive officers, and each of our 5% stockholders and their affiliates, in the aggregate, beneficially own a significant number of the outstanding shares of our common stock. As a result, these stockholders, if acting together, will be able to influence or control matters requiring approval by our stockholders, including the election of directors and the approval of mergers, acquisitions or other extraordinary transactions. They
may also have interests that differ from yours, and they may vote in a way with which you disagree or which may be adverse to your interests. This concentration of ownership may have the effect of delaying, preventing or deterring a change of control of our company, could deprive our stockholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their common stock as part of a sale of our company and might ultimately affect the market price of our common stock.
The requirements of being a public company may strain our resources, divert management’s attention and affect our ability to attract and retain qualified Board members.
As a public company, we are subject to the reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended ( the "Exchange Act"), the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Dodd-Frank Act, the listing standards of the Nasdaq Stock Market, and other applicable securities rules and regulations, including changes in corporate governance practices and the establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls. Compliance with these rules and regulations increases our legal and financial compliance costs, makes some activities more difficult, time-consuming or costly and increases demand on our systems and resources.
In addition, changing laws, regulations and standards or interpretations thereof relating to corporate governance and public disclosure are creating uncertainty for public companies, increasing legal and financial compliance costs and making some activities more time-consuming. We intend to invest resources to comply with evolving laws, regulations and standards, and this investment may result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management’s time and attention. If our efforts to comply with new laws, regulations and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies due to ambiguities related to their application and practice, regulatory authorities may initiate legal proceedings against us.
Certain of our market opportunity estimates, growth forecasts, and key metrics could prove to be inaccurate, and any real or perceived inaccuracies may harm our reputation and negatively affect our business.
Market opportunity estimates, growth forecasts and key metrics, including those we have generated ourselves, are subject to significant uncertainty and are based on assumptions and estimates that may not prove to be accurate. The estimates and forecasts relating to the size and expected growth of our market opportunity may prove to be inaccurate. It is impossible to offer every loan product, term or feature that every member wants, and our competitors may develop and offer products, terms or features that we do not offer. The variables that go into the calculation of our market opportunity are subject to change over time, and there is no guarantee that any particular number or percentage of the individuals covered by our market opportunity estimates will generate any particular level of revenues. Even if the markets in which we compete meet our size estimates and growth forecasts, our business could fail to grow at expected rates, if at all, for a variety of reasons outside of our control. Furthermore, in order for us to successfully address this broader market opportunity, we will need to successfully expand into new geographic regions where we do not currently operate.
Our key metrics are calculated using internal company data, including Members and Products, and have not been validated by an independent third-party. We have in the past implemented, and may in the future implement, new methodologies for calculating these metrics which may result in the metrics from prior periods changing, decreasing or not being comparable to prior periods. As our business develops, we may revise or cease reporting metrics if we determine that such metrics are no longer appropriate measures of our performance. Our key metrics may also differ from estimates published by third parties or from similarly titled metrics of our competitors due to differences in methodology. If investors or analysts do not perceive our metrics to be sufficient or accurate representations of our business, or if we discover material inaccuracies in our metrics, our stock price, reputation and prospects would be adversely affected.
Certain provisions in our charter documents and under Delaware law could limit attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our Board, delay or prevent an acquisition of our company, and adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
Provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, and amended and restated bylaws may have the effect of delaying or preventing a change of control or changes in our Board. These provisions include the following:
•a classified Board with three-year staggered terms, which may delay the ability of stockholders to change the membership of a majority of our Board;
•our Board has the right to elect directors to fill a vacancy created by the expansion of the Board or the resignation, death or removal of a director, which prevents stockholders from being able to fill Board vacancies;
•our stockholders may not act by written consent or call special stockholders’ meetings;
•our amended and restated certificate of incorporation prohibits cumulative voting in the election of directors, which limits the ability of minority stockholders to elect director candidates;
•stockholders must provide advance notice and additional disclosures in order to nominate individuals for election to the Board or to propose matters that can be acted upon at a stockholders’ meeting, which may discourage or deter a potential acquiror from conducting a solicitation of proxies to elect the acquiror’s own slate of directors or otherwise attempting to obtain control of our company; and
•our Board may issue, without stockholder approval, shares of undesignated preferred stock, which may make it possible for our Board to issue preferred stock with voting or other rights or preferences that could impede the success of any attempt to acquire us.
As a Delaware corporation, we are also subject to certain Delaware anti-takeover provisions. Under Delaware law, a corporation may not engage in a business combination with any holder of 15% or more of its capital stock unless the holder has held the stock for three years or, among other things, the Board has approved the transaction. Such provisions could allow our Board to prevent or delay an acquisition of our company.
Certain of our executive officers may be entitled, pursuant to the terms of their employment arrangements, to accelerated vesting of their stock options following a change of control of our company under certain conditions. In addition to the arrangements currently in place with some of our executive officers, we may enter into similar arrangements in the future with other officers. Such arrangements could delay or discourage a potential acquisition.
Any provision of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or amended and restated bylaws or Delaware law that has the effect of delaying or deterring a potential acquisition could limit the opportunity for our stockholders to receive a premium for their shares of our common stock in connection with such acquisition, and could also affect the price that some investors are willing to pay for our common stock.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware or the U.S. federal district courts will be the exclusive forums for substantially all disputes between us and our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers or other employees.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware is the sole and exclusive forum for the following types of actions or proceedings under Delaware statutory or common law: (1) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (2) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers or other employees to us or our stockholders, (3) any action asserting a claim against us or any of our directors, officers or other employees arising pursuant to any provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or our amended and restated bylaws, (4) any action to interpret, apply, enforce or determine the validity of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or our amended and restated bylaws, or (5) any action asserting a claim against us or any of our directors, officers or other employees that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine. This provision would not apply to suits brought to enforce a duty or liability created by the Exchange Act or the rules and regulations thereunder. Furthermore, Section 22 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (“Securities Act”), creates concurrent jurisdiction for federal and state courts over all such Securities Act actions. Accordingly, both state and federal courts have jurisdiction to entertain such claims. To prevent having to litigate claims in multiple jurisdictions and the threat of inconsistent or contrary rulings by different courts, among other considerations, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation further provides that U.S. federal district courts will be the exclusive forum for resolving any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under the Securities Act. While the Delaware courts have determined that such choice of forum provisions are facially valid, a stockholder may nevertheless seek to bring a claim in a venue other than those designated in the exclusive forum provisions. In such instance, we would expect to vigorously assert the validity and enforceability of the exclusive forum provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation. This may require significant additional costs associated with resolving such action in other jurisdictions, which could adversely affect our business and financial condition, and there can be no assurance that the provisions will be enforced by a court in those other jurisdictions.
These exclusive forum provisions may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers, or other employees, which may discourage lawsuits against us and our directors, officers and other employees. If a court were to find either exclusive-forum provision in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation to be inapplicable or unenforceable in an action, we may incur further significant additional costs associated with resolving the dispute in other jurisdictions, all of which could seriously harm our business.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 2. Properties
Our corporate headquarters is located in San Carlos, California pursuant to a lease expiring in February 2026. We are currently subleasing a portion of our headquarters space to third parties. As of December 31, 2022, we leased additional facilities and office space in California, Texas, Mexico, and India. We also operate retail locations and co-locations throughout the United States.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
The information set forth under Note 16, Leases, Commitments and Contingencies, in the accompanying Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements is incorporated herein by reference. From time to time, we may bring or be subject to other legal proceedings and claims in the ordinary course of business, including legal proceedings with third parties asserting infringement of their intellectual property rights, consumer litigation, and regulatory proceedings. Other than as described in this report, we are not presently a party to any legal proceedings that, if determined adversely to us, we believe would individually or taken together have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, cash flows or results of operations.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
None.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market Information and Stockholders
Oportun's common stock has been listed for trading on the Nasdaq Global Select Market since September 26, 2019 under the symbol "OPRT". As of March 8, 2023, we had 132 registered stockholders of our common stock. This figure does not reflect the beneficial ownership of shares held in nominee name or held in trust by other entities. Therefore, the actual number of stockholders is greater than this number of registered stockholders of record.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our capital stock, and we do not currently intend to pay any cash dividends on our capital stock in the foreseeable future. We currently intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings to support operations and to finance the growth of our business. Any future determination to pay dividends will be made at the discretion of our Board.
Stock Performance
As a “Smaller Reporting Company” as defined by Item 10 of Regulation S-K, the Company is not required to provide this information.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
None.
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities
None.
Use of Proceeds
None.
Item 6. Reserved
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
For more information about terms and abbreviations used in this report see the “Glossary” at the end of Part II of this report.
An index to our management's discussion and analysis follows:
The following Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (this “MD&A”) is intended to help the reader understand our results of operations and financial condition. This MD&A is provided as a supplement to, and should be read together with, our audited consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto and other disclosures included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Some of the information contained in this MD&A, including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should review the information contained in Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in this MD&A.
Overview
We are a digital banking platform that puts our members’ financial goals within reach. With intelligent borrowing, savings, budgeting, and spending capabilities, we empower members with the confidence to build a better financial future. By intentionally designing our products to help solve the financial health challenges facing a majority of people in the U.S., we believe our business is well positioned for significant growth. We take a holistic approach to serving our members and view it as our purpose to responsibly meet their current capital needs, help grow our members’ financial profiles, increase their financial awareness and put them on a path to a financially healthy life. In our 16-year lending history, we have extended more than $15.5 billion in responsible credit through more than 6.3 million loans and credit cards. We have been certified as a Community Development Financial Institution ("CDFI") by the U.S. Department of the Treasury since 2009.
With our acquisition of Digit in 2021, we believe we now have a strong competitive advantage over other fintechs and neobanks. As a combined company, we can now offer access to a comprehensive suite of digital banking products, offered either directly or through partners, including lending, savings and investing powered by A.I. and tailored to each member's goals.
Our financial products allow us to meet our members where they are and assist them with their overall financial health, resulting in opportunities to present multiple relevant products to our members. Our credit products include personal loans, secured personal loans and credit cards. Our digital banking products include digital banking, automated savings, long-term investing and retirement savings. Consumers are able to become members and access our products through our digital banking app—the Oportun Mobile app—and the Oportun.com website, which are our primary channels for onboarding and serving members. Our personal loan products are also available over the phone or through over 700 retail locations, which includes 590 of our Lending as a Service partner locations.
Credit Products
Personal Loans - Our personal loan is a simple-to-understand, affordable, unsecured, fully amortizing installment loan with fixed payments throughout the life of the loan. We charge fixed interest rates on our loans, which vary based on the amount disbursed and applicable state law, with a cap of 36% annual percentage rate (“APR”) in all cases. As of December 31, 2022, for all active loans in our portfolio and at time of disbursement, the weighted average term and APR at origination was 38 months and 32.0%, respectively. The average loan size for loans we originated in 2022 was $4,189. Our loans do not have prepayment penalties or balloon payments, and range in size from $300 to $12,000 with terms of 12 to 60 months. Generally, loan payments are structured on a bi-weekly or semi-monthly basis to coincide with our members' receipt of their income. As part of our underwriting process, we verify income for all applicants and only approve loans that meet our ability-to-pay criteria. As of December 31, 2022, we originate unsecured personal loans in 12 states through state licenses and in 30 states through our partnership with Pathward, N.A. (formerly known as MetaBank, N.A.).
Secured Personal Loans - In April 2020, we launched a personal installment loan product secured by an automobile, which we refer to as secured personal loans. Our secured personal loans range in size from $2,525 to $18,000 with terms ranging from 27 to 63 months. The average loan size for secured personal loans we originated in 2022 was $8,304. As of December 31, 2022, for all active loans in our portfolio and at time of disbursement, the weighted average term and APR at origination was 49 months and 28.3%, respectively. As part of our underwriting process, we
evaluate the collateral value of the vehicle, verify income for all applicants and only approve loans that meet our ability-to-pay criteria. Our secured personal loans are currently offered in California, Texas, Florida, Arizona and New Jersey and we are in the process of considering expansion into other states.
Credit Cards - We launched Oportun® Visa® Credit Card, issued by WebBank, Member FDIC, in December 2019, and offer credit cards in 45 states as of December 31, 2022. Credit lines on our credit cards range in size from $300 to $3,000 with an APR between 24.9% to 29.9%. The average APR of the outstanding credit card receivables was 29.8% as of December 31, 2022. The average credit line for credit cards activated in 2022 was $834.
Digital Banking Products
Savings – Our Savings product is designed to understand a member’s cash flows and save the right amount on a regular basis to effortlessly achieve savings goals. Our savings product utilizes machine learning to analyze a member’s transaction activity and build forecasts of the member’s future cash flows to make small, frequent savings decisions according to the member’s financial goals in a personalized manner. Members integrate their existing bank accounts into the platform or they can make Digit their primary banking relationship through a bank partner. After one year using the automated savings product, members have been able to increase their liquid savings by approximately 50%. Since 2015 Digit has helped members save more than $8.9 billion.
Direct – Our Direct product offers a full checking account, through a bank partner, that intelligently organizes and budgets a member’s money across bills, savings, and spending. The bank account with a brain™, Direct leverages the same A.I. engine used for our savings product to automatically identify and organize recurring bills and guides spending to ensure members' savings goals are met, and that members know exactly what they can safely spend. This is on top of what members can expect from a traditional checking account, including a physical and virtual debit card to use for purchases and ATM withdrawals and checks.
Investing and Retirement – Our investment and retirement products are a longer-term savings solution via an A.I.-driven portfolio allocation into low-cost investments based upon risk-tolerance. Our long-term investment solutions automatically allocates our members' savings into low-cost risk-adjusted portfolios held in brokerage accounts or tax-advantaged IRAs. Since 2020, our members have invested $66.6 million into long-term goals through low-cost ETF portfolios. The investment products include a general investing account and a retirement account for our members’ longer term goals, utilizing smart recommendations to invest savings in risk-adjusted portfolios.
The funds in these savings, checking, investing and retirement accounts are owned by members of our digital banking products and are not the assets of the Company. Therefore, these funds are not included in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Lending as a Service
Beyond our core direct-to-consumer lending business, we believe that we can leverage our proprietary credit scoring and underwriting model to partner with other consumer brands and expand our member base. With our Lending as a Service model, our partner markets loans and enters borrower applications into our system and Oportun underwrites, originates and services the loans. Our first lending as a service partner was DolEx Dollar Express, Inc. with an initial launch in December 2020. In October of 2021, we launched another Lending as a Service partnership with Barri Financial Group in select locations. In January of 2022, we announced our first all-digital Lending as a Service partnership with Sezzle, a leading provider of Buy Now Pay Later ("BNPL") financing options which launched in the first quarter of 2023. Oportun is now available as a checkout option, through Sezzle, for larger purchases which we believe will allow us to reach more new members. We believe we will be able to offer Lending as a Service to additional partners, and expand our membership base.
Capital Markets Funding
To fund our growth at a low and efficient cost, we have built a diversified and well-established capital markets funding program, which allows us to partially hedge our exposure to rising interest rates or credit spreads by locking in our interest expense for up to three years. Over the past eight years, we have executed 20 bond offerings in the asset-backed securities market, the last 17 of which include tranches that have been rated investment grade. We have issued two- and three-year fixed rate bonds which have provided us committed capital to fund future loan originations at a fixed Cost of Debt. On July 22, 2022, we issued $400.0 million of amortizing asset-backed notes. On September 14, 2022, we entered into a credit agreement for a $150.0 million senior secured term loan, which was upsized and amended on March 10, 2023 to provide the ability to be able to borrow up to an additional $75.0 million. On March 10, 2023, we borrowed $20.8 million of Incremental Tranche A-1 Loans and intend to borrow an additional $4.2 million of Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans on or about March 27, 2023, which amount has been committed by the applicable lenders. We may borrow up to an aggregate additional amount of $50.0 million on an uncommitted basis, in two $25.0 million tranches, expected to be available, if provided by the applicable lenders, on or about April 21, 2023 and June 23, 2023, respectively. On November 3, 2022, we issued $300.0 million of amortizing asset-backed notes.
Through March 4, 2022, we were also party to a whole loan sale program whereby we sold a percentage of our loans to a third-party financial institution. We allowed the whole loan sale program agreement to expire on its own terms. In March 2022, we participated in a securitization and sold loans through the issuance of amortizing asset-backed notes secured by a pool of our unsecured and secured personal installment loans. We also sold our share of the residual interest in the pool. The sold loans had an aggregate unpaid principal balance of approximately $227.6 million ("2022-1 transaction"). During 2022, we sold certain populations of our personal loans and credit card receivables that had an aggregate unpaid principal balance, including unpaid interest and fees, of approximately $66.2 million. In addition to possible future whole loan, structured or other loan sales, we also have a $600.0 million Personal Loan Warehouse facility with a term through September 2024 and a $150.0 million Credit Card Warehouse facility with a term through December 2023 which also helps to fund our receivables growth. On March 8, 2023, the Credit Card Warehouse facility
was amended, extending its term through December 2024 and reducing its commitment from $150.0 million to $120.0 million.
Streamlining Operations
On February 9, 2023, we announced that we are taking a series of measures to streamline our operations, including reducing the size of our corporate staff by 10%, impacting approximately 155 employees, and reducing our expenditures on external contractors. In relation to these and other personnel related activities, we expect to incur non-recurring, pre-tax charges of $6 to $7 million in the first quarter of 2023. These reductions are anticipated to result in annualized run-rate savings in compensation and benefits of approximately $38 million beginning in 2023. We have also identified certain non-personnel related operational efficiencies that are anticipated to result in annualized run-rate savings of $10 to $15 million beginning in 2023.
Retail Network Optimization
During the first quarter of 2022, we closed an additional 27 retail locations in April 2022 and reduce a portion of the workforce who manage and operate these retail locations. The income statement impact for the twelve months ended December 31, 2022 was $1.9 million, and was recorded through General, administrative and other on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. This amount included expenses related to the retail location closures and all severance and benefits-related costs. While we do not expect any significant additional expenses to be incurred related to these closures, we are continually evaluating the performance of retail and partner locations. During the first quarter of 2021, pursuant to our retail network optimization plan we closed 136 retail locations and reduced a portion of the employee workforce who managed and operated these retail locations. The income statement impact for the twelve months ended December 31, 2021 was $12.8 million, and was recorded through General, administrative and other on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. This amount included expenses related to the retail location closures and all severance and benefits-related costs.
Key Financial and Operating Metrics
We monitor and evaluate the following key metrics in order to measure our current performance, develop and refine our growth strategies, and make strategic decisions.
The following table and related discussion set forth key financial and operating metrics for our operations as of and for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021. For similar financial and operating metrics and discussion of our 2021 results compared to our 2020 results, refer to Part II. Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021 as filed with the SEC on March 1, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of or for the Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
Key Financial and Operating Metrics | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
Members (1) | | 1,877,260 | | | 1,479,660 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
Products (1) | | 2,006,245 | | | 1,545,463 | | | |
| Aggregate Originations | | $ | 2,922,871 | | | $ | 2,295,012 | | | |
| 30+ Day Delinquency Rate | | 5.6 | % | | 3.9 | % | | |
| Annualized Net Charge-Off Rate | | 10.1 | % | | 6.8 | % | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Return on Equity | | (13.5) | % | | 8.9 | % | | |
| Adjusted Return on Equity | | 12.1 | % | | 14.7 | % | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Other Metrics | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
Managed Principal Balance at End of Period | | $ | 3,406,981 | | | $ | 2,583,462 | | | |
Owned Principal Balance at End of Period | | $ | 3,098,609 | | | $ | 2,272,864 | | | |
Average Daily Principal Balance | | $ | 2,740,318 | | | $ | 1,756,170 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
(1) The 1,479,660 Members and 1,545,463 Products reported as of December 31, 2021 reflect our previously defined and disclosed "Members" and "Products" metrics. Beginning January 1, 2022, we modified our definition of Members to reflect the long-term nature of our relationship with our members and modified our definition of Products to reflect multiproduct adoption by our members.
See “Glossary” at the end of Part II of this report for formulas and definitions of our key performance metrics.
Members
We define Members as borrowers with an outstanding or successfully paid off loan, originated by us or under a bank partnership program that we service, or individuals who have been approved for a credit card issued under a bank partnership program. Members also include individuals who have signed-up to use or are using any of our Savings, Direct, Investing and/or Retirement products. We view Members as an indication of growth of our business and our ability to establish long term relationships with the users of our products. Member growth is generally an indicator of future revenue, but is not directly correlated with revenue, since not all Members who sign up for one of our products fully utilize or continue to use our products.
Members as of December 31, 2022 grew to 1.9 million, as compared to 1.5 million as of December 31, 2021. This increase was due to the success in our marketing efforts during the year.
Products
Products refers to the aggregate number of personal loans and/or credit card accounts that our Members have had or been approved for that have been originated by us or through one of our bank partners. Products also include the aggregate number of digital banking products we offer as a result of our acquisition of Digit, including Savings, Direct, Investing and Retirement, that our Members use or have signed-up to use. We view Products as an indicator of the effectiveness of our member acquisition efforts and multiproduct adoption.
Products as of December 31, 2022, grew to 2.0 million, compared to the 1.5 million Products we had as of December 31, 2021. This increase was due to growth in both our credit products and our digital banking products.
Aggregate Originations
Aggregate Originations increased to $2.92 billion for the year ended December 31, 2022 from $2.30 billion for the year ended December 31, 2021, representing a 27.4% increase. The increase is primarily driven by a growth in average loan size due to a focus on returning members with historically lower credit risk and a larger number of loans originated. We originated 764,516 and 753,474 loans for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. The increase is primarily driven by an increased number of applications due to higher demand, partially offset by a reduction in our approval rate as we tightened credit.
30+ Day Delinquency Rate
Our 30+ Day Delinquency Rate increased to 5.6% as of December 31, 2022 from 3.9% as of December 31, 2021. The increase reflects the higher mix of first-time borrowers and the return to pre-pandemic underwriting criteria later in 2021. In mid-2022, we took numerous actions to improve the credit performance on newly originated loans; including significantly tightening our underwriting standards for all borrowers, particularly for higher risk digital marketing channels, and adjusting loan size based on member free cash flow. We also focused lending towards existing and returning members to address rising delinquencies.
Annualized Net Charge-Off Rate
Annualized Net Charge-Off Rate for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 was 10.1% and 6.8%, respectively. The increase is primarily driven by a higher mix of first-time borrowers in 2022 compared to 2021. In mid-2022, we took numerous actions to improve the credit performance on newly originated loans; including significantly tightening our underwriting standards for all borrowers, particularly for higher risk digital marketing channels, and adjusting loan size based on member free cash flow. We also focused lending towards existing and returning members to improve credit outcomes as existing and returning members historically have had lower loss rates. Further, due to credit tightening in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and government stimulus payments our Annualized Net Charge-Off Rate was lower in 2021. We anticipate that this rate may increase in 2023 due to the impact of inflation and other macroeconomic factors on members.
Return on Equity and Adjusted Return on Equity
For the year ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, Return on Equity was (13.5)% and 8.9%, respectively. The decrease in Return on Equity is primarily due to lower net income, primarily as a result of the goodwill impairment.
For the year ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, Adjusted Return on Equity was 12.1% and 14.7%, respectively. The decrease in Adjusted Return on Equity is primarily due to lower Adjusted Net Income. Adjusted Net Income was lower due to higher credit losses, higher cost of funds and decreased fair value of our loan portfolio as a result of higher loss and discount rate assumptions. For a reconciliation of Return on Equity to Adjusted Return on Equity, see “Non–GAAP Financial Measures.”
Historical Credit Performance
Our Annualized Net Charge-off Rate ranged between 7% and 9% from 2011 to 2019 and was 9.8% in 2020, a modest variance above this range during the pandemic. Due to credit tightening in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and government stimulus payments our Annualized Net Charge-Off Rate decreased to 6.8% in 2021. Our Annualized Net Charge-off Rate increased to 10.1% in 2022 primarily due to a higher mix of first-time borrowers in 2021 and the first half of 2022. In response to this increase, we tightened our credit underwriting standards and focused lending towards existing and returning members to improve credit outcomes. Consistent with our charge-off policy, we evaluate our loan portfolio and charge a loan off at the earlier of when the loan is determined to be uncollectible or when loans are 120 days contractually past due and charge-off a credit
card account when it is 180 days contractually past due.
In addition to monitoring our loss and delinquency performance on an owned portfolio basis, we also monitor the performance of our loans by the period in which the loan was disbursed, generally years or quarters, which we refer to as a vintage. We calculate net lifetime loan loss rate by vintage as a percentage of original principal balance. Net lifetime loan loss rates equal the net lifetime loan losses for a given year through December 31, 2022 divided by the total origination loan volume for that year.
The below chart and table shows our net lifetime loan loss rate for each annual vintage of our personal loan product since we began lending in 2006, excluding loans originated from July 2017 to August 2020 under a loan program for borrowers who did not meet the qualifications for our core loan origination program. 100% of those loans were sold pursuant to a whole loan sale agreement. We have managed to stabilize cumulative net loan losses since the financial crisis that started in 2008. We even achieved a net lifetime loan loss rate of 5.5% during the peak of the recession in 2009. The evolution of our credit models has allowed us to increase our average loan size and commensurately extend our average loan terms. Cumulative net lifetime loan losses for the 2015, 2016, 2017, and 2018 vintages increased partially due to the delay in tax refunds in 2017 and 2019, the impact of natural disasters such as Hurricane Harvey, and the longer duration of the loans. The 2018 and 2019 vintages are increasing due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The 2021 vintage is running higher than prior vintages primarily due to a higher percentage of loan disbursements to new members. We have tightened credit and began reducing loan volumes to new and returning members in the third quarter of 2021 and reduced further in the second half of 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year of Origination |
| | 2007 | | 2008 | | 2009 | | 2010 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | 2013 | | 2014 | | 2015 | | 2016 | | 2017 | | 2018 | | 2019 | | 2020 | | 2021 |
| Dollar weighted average original term for vintage in months | | 9.3 | | | 9.9 | | | 10.2 | | | 11.7 | | | 12.3 | | | 14.5 | | | 16.4 | | | 19.1 | | | 22.3 | | | 24.2 | | | 26.3 | | | 29.0 | | | 30.0 | | | 32.0 | | | 33.3 | |
| Net lifetime loan losses as of December 31, 2022 as a percentage of original principal balance | | 7.7 | % | | 8.9 | % | | 5.5 | % | | 6.4 | % | | 6.2 | % | | 5.6 | % | | 5.6 | % | | 6.1 | % | | 7.1 | % | | 8.0 | % | | 8.2 | % | | 9.8 | % | | 10.6 | %* | | 7.5 | %* | | 8.7 | %* |
| Outstanding principal balance as of December 31, 2022 as a percentage of original amount disbursed | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 2.2 | % | | 14.5 | % | | 50.6 | % |
* Vintage is not yet fully mature from a loss perspective.
Seasonality
Our quarterly results of operations may not necessarily be indicative of the results for the full year or the results for any future periods. Our business is highly seasonal, and the fourth quarter is typically our strongest quarter in terms of loan originations. For the three months ended December 31, 2022, our business exhibited lower than typical originations due to our credit tightening. Prior to the pandemic, we historically experienced a seasonal decline in credit performance in the fourth quarter primarily attributable to competing demand of our borrowers' available cash flow around the holidays. General increases in our borrowers’ available cash flow in the first quarter, including from cash received from tax refunds, temporarily reduces our borrowers’ borrowing needs. We experienced this seasonal trend in 2022, consistent with years prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Results of Operations
The following tables and related discussion set forth our Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021. For a discussion regarding our operating and financial data for the year ended December 31, 2021, as compared to the same period in 2020, refer to Part II, Item 7. “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021, as filed with the SEC on March 1, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Revenue | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | $ | 876,114 | | | $ | 575,839 | | | |
| Non-interest income | | 76,431 | | | 50,943 | | | |
| Total revenue | | 952,545 | | | 626,782 | | | |
| Less: | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | 93,046 | | | 47,669 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Total net decrease in fair value | | (218,842) | | | (48,632) | | | |
| Net revenue | | 640,657 | | | 530,481 | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Technology and facilities | | 216,120 | | | 139,564 | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | 110,033 | | | 116,882 | | | |
| Personnel | | 154,850 | | | 115,833 | | | |
| Outsourcing and professional fees | | 67,630 | | | 57,931 | | | |
| General, administrative and other | | 58,838 | | | 37,480 | | | |
| Goodwill impairment | | 108,472 | | | — | | | |
| Total operating expenses | | 715,943 | | | 467,690 | | | |
| Income (loss) before taxes | | (75,286) | | | 62,791 | | | |
| Income tax expense | | 2,458 | | | 15,377 | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (77,744) | | | $ | 47,414 | | | |
Total revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Revenue | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | $ | 876,114 | | | $ | 575,839 | | | | | $ | 300,275 | | | 52.1 | % | | | | |
| Non-interest income | | 76,431 | | | 50,943 | | | | | 25,488 | | | 50.0 | % | | | | |
| Total revenue | | $ | 952,545 | | | $ | 626,782 | | | | | $ | 325,763 | | | 52.0 | % | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | 92.0 | % | | 91.9 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-interest income | | 8.0 | % | | 8.1 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total revenue | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest income. Total interest income increased by $300.3 million, or 52.1%, from $575.8 million for 2021 to $876.1 million for 2022. The increase is primarily attributable to growth in our Average Daily Principal Balance, which grew from $1.76 billion for 2021 to $2.74 billion for 2022, an increase of 56.0%. The increase was partially offset by a decrease in portfolio yield of 82 basis points in the year ended December 31, 2022 compared to the year ended December 31, 2021 driven by our tightening of credit underwriting standards and focusing lending towards existing and returning members in the second half of 2022. Existing and returning members generally receive lower APRs, but historically have lower loss rates compared to new members.
Non-interest income. Total non-interest income increased by $25.5 million, or 50.0%, from $50.9 million for 2021 to $76.4 million for 2022. This increase is primarily due to $37.5 million attributable to Digit subscription income and $6.7 million increase in servicing revenue. This was partially offset by decreased gain on loans sold of $21.5 million under our whole loan sale programs due to the expiration of our whole loan sale agreement on March 4, 2022.
Interest expense
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Interest expense | | $ | 93,046 | | | $ | 47,669 | | | | | $ | 45,377 | | | 95.2 | % | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue | | 9.8 | % | | 7.6 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of Debt | | 3.7 | % | | 3.1 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leverage as a percentage of Average Daily Principal Balance | | 91.2 | % | | 88.5 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense. Interest expense increased by $45.4 million, or 95.2%, from $47.7 million for 2021 to $93.0 million for 2022. We financed approximately 91.2% of our loans receivable through debt for 2022 as compared to 88.5% for 2021, and our Average Daily Debt Balance increased from $1.55 billion to $2.50 billion for 2022, an increase of 60.9%. Our Cost of Debt has increased due to increases in interest rates and wider credit spreads on our new asset-backed securitization issuances. We expect our interest expense to increase as benchmark interest rates rise and as we continue to fund our portfolio growth through debt.
Total net decrease in fair value
Net increase (decrease) in fair value reflects changes in fair value of loans receivable held for investment and asset-backed notes on an aggregate basis and is based on a number of factors, including benchmark interest rates, credit spreads, remaining cumulative charge-offs and borrower payment rates. Increases in the fair value of loans increase Net Revenue. Conversely, decreases in the fair value of loans decrease Net Revenue. Increases in the fair value of asset-backed notes decrease Net Revenue. Decreases in the fair value of asset-backed notes increase Net Revenue. We also have derivative instruments related to our bank partnership program with Pathward, N.A. Changes in the fair value of the derivative instrument are reflected in the total fair value mark-to-market adjustment below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Fair value mark-to-market adjustment: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value mark-to-market adjustment on Loans Receivable at Fair Value | | $ | (68,897) | | | $ | 57,044 | | | | | $ | (125,941) | | | * | | | | |
| Fair value mark-to-market adjustment on asset-backed notes | | 184,906 | | | 15,408 | | | | | 169,498 | | | * | | | | |
| Fair value mark-to-market adjustment on derivatives | | 3,702 | | | (3,097) | | | | | 6,799 | | | | | | | |
| Total fair value mark-to-market adjustment | | 119,711 | | | 69,355 | | | | | 50,356 | | | * | | | | |
| Charge-offs, net of recoveries on loans receivable at fair value | | (276,796) | | | (119,413) | | | | | (157,383) | | | * | | | | |
| Net settlements on derivative instruments | | (15,688) | | | 1,426 | | | | | (17,114) | | | * | | | | |
Fair value mark on loans sold (1) | | (46,069) | | | — | | | | | (46,069) | | | * | | | | |
| Total net decrease in fair value | | $ | (218,842) | | | $ | (48,632) | | | | | $ | (170,210) | | | * | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value mark-to-market adjustment | | 12.6 | % | | 11.1 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Charge-offs, net of recoveries on loans receivable at fair value | | (29.1) | % | | (19.1) | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total net decrease in fair value | | (16.5) | % | | (8.0) | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Discount rate | | 11.48 | % | | 6.94 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remaining cumulative charge-offs | | 10.38 | % | | 9.60 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Average life in years | | 1.00 | | | 0.86 | | | | | | | | | | | |
* Not meaningful
(1) The fair value mark-to-market adjustment on loans receivable at fair value shown for the year ended December 31, 2022, excludes $(46.1) million related to the cumulative fair value mark on loans sold as part of the structured and other loan sales in 2022. For details regarding the structured and other loan sales in 2022, refer to Note 5, Loans Held for Sale and Loans Sold of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report.
Net decrease in fair value. Net decrease in fair value for 2022 was $218.8 million. This amount represents a total fair value mark-to-market increase of $119.7 million, and $276.8 million of charge-offs, net of recoveries on Loans Receivable at Fair Value. The total fair value mark-to-market adjustment consists of a $(68.9) million mark-to-market adjustment on Loans Receivable at Fair Value due to (a) an increase in remaining cumulative charge-offs from 9.60% as of December 31, 2021 to 10.38% as of December 31, 2022, (b) an increase in the discount rate from 6.94% as of December 31, 2021 to 11.48% as of December 31, 2022, partially offset by (c) an increase in average life from 0.86 years as of December 31, 2021 to 1.00 years as of December 31, 2022. The $184.9 million mark-to-market adjustment on asset-back notes is due to rising rates and widening asset-backed securitization spreads. The total net increase (decrease) in fair value for the year ended December 31, 2022 includes a $(46.1) million adjustment related to the fair value mark on loans sold as part of the structured and other loan sales in 2022. In 2023, we expect to continue to see volatility in fair value primarily as a result of macroeconomic conditions.
Charge-offs, net of recoveries
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total charge-offs, net of recoveries | | $ | 276,796 | | | $ | 119,413 | | | | | $ | 157,383 | | | 131.8 | % | | | | |
| Average Daily Principal Balance | | 2,740,318 | | | 1,756,170 | | | | | 984,148 | | | 56.0 | % | | | | |
| Annualized Net Charge-Off Rate | | 10.1 | % | | 6.8 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
Charge-offs, net of recoveries.
Our Annualized Net Charge-Off Rate increased to 10.1% for the year ended December 31, 2022 from 6.8% for the year ended December 31, 2021. Net charge-offs for the year ended December 31, 2022 increased primarily due to a higher mix of first-time borrowers in 2021 and the first half of 2022. In response to this increase, we tightened our credit underwriting standards and focused lending towards existing and returning members to improve credit outcomes in the second half of 2022. Further, due to credit tightening in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and government stimulus payments, our charge-offs were lower in 2021. Consistent with our charge-off policy, we evaluate our loan portfolio and charge a loan off at the earlier of when the loan is determined to be uncollectible or when the loan is 120 days contractually past due and we charge-off a credit card account when it is 180 days contractually past due.
Operating expenses
Operating expenses consist of technology and facilities, sales and marketing, personnel, outsourcing and professional fees and general, administrative and other expenses.
Technology and facilities
Technology and facilities expense is the largest segment of our operating expenses, representing the costs required to build and maintain our A.I.-enabled digital platform, and consists of three components. The first component comprises costs associated with our technology, engineering, information security, cybersecurity, platform development, maintenance, and end user services, including fees for software licenses, consulting, legal and other services as a result of our efforts to grow our business, as well as personnel expenses. The second component includes rent for retail and corporate locations, utilities, insurance, telephony costs, property taxes, equipment rental expenses, licenses and fees and depreciation and amortization. Lastly, the third component includes all software licenses, subscriptions, and technology service costs to support our corporate operations, excluding sales and marketing.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Technology and facilities | | $ | 216,120 | | | $ | 139,564 | | | | | $ | 76,556 | | | 54.9 | % | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue | | 22.7 | % | | 22.3 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
Technology and facilities. Technology and facilities expense increased by $76.6 million, or 54.9%, from $139.6 million for 2021 to $216.1 million for 2022. The increase is primarily due to a $31.7 million increase in salaries and benefits due to the increase in headcount, a $27.2 million increase in service costs related to higher usage of software and cloud services which includes a $7.4 million increase attributable to Digit bank processing fees, $13.5 million incurred for India off-shoring services and other temporary contractors to supplement staffing related to new product investment and $11.5 million of increased depreciation commensurate with growth in internally developed software. These increases are partially offset by $8.0 million lower expense due to higher capitalization of internally developed software in 2022 compared to 2021 and $1.9 million lower office rent due to retail location closures in early 2021 and early 2022. We expect our technology and facilities expense may increase in 2023 compared to 2022 due to increased depreciation related to internally developed software and increased service costs due to higher usage of software and cloud services.
Sales and marketing
Sales and marketing expenses consist of two components and represent the costs to acquire our members. The first component is comprised of the expense to acquire a member through various paid marketing channels including direct mail, digital marketing and brand marketing. The second component is comprised of the costs associated with our telesales, lead generation and retail operations, including personnel expenses, but excluding costs associated with retail locations.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars, except CAC) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | $ | 110,033 | | | $ | 116,882 | | | | | $ | (6,849) | | | (5.9) | % | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue | | 11.6 | % | | 18.6 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | | $ | 144 | | | $ | 155 | | | | | $ | (11) | | | (7.1) | % | | | | |
Sales and marketing. Sales and marketing expenses to acquire our members decreased by $6.8 million, or 5.9%, from $116.9 million for 2021 to $110.0 million for 2022. Our net decrease in marketing spend during the year ended December 31, 2022 was $14.8 million across various marketing channels, including digital advertising and direct mail. We decreased marketing spend as we shifted our strategy to focus lending towards existing and returning members to improve credit outcomes. The decrease in marketing spend was partially offset by an increase of $4.1 million related to outsourcing and professional fees primarily due to outsourced telesales FTEs as a result of an increase in demand for new applications and $2.7 million higher salaries and benefit costs due to increased headcount and increase in average compensation. As a result of our decreased marketing spend during the year ended December 31, 2022, our CAC decreased by 7.1%, from $155 for the year ended December 31, 2021 to $144 for the year ended December 31, 2022. We expect our sales and marketing expense to decrease in 2023 compared to 2022 as we maintain focus on our strategy to improve credit outcomes by focusing lending towards existing and returning members.
Personnel
Personnel expense represents compensation and benefits that we provide to our employees, and include salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, related employer taxes, medical and other benefits provided and stock-based compensation expense for all of our staff with the exception of our telesales, lead generation, and retail operations which are included in sales and marketing expenses and technology which is included in technology and facilities.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Personnel | | $ | 154,850 | | | $ | 115,833 | | | | | $ | 39,017 | | | 33.7 | % | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue | | 16.3 | % | | 18.5 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
Personnel. Personnel expense increased by $39.0 million, or 33.7%, from $115.8 million for 2021 to $154.9 million for 2022. $13.2 million of the increase is attributable to the Digit acquisition and the remaining increase is due to a 17.0% increase in U.S. headcount. We expect our personnel expense to decrease in 2023 compared to 2022 as a result of our recently announced plan to reduce headcount and streamline operations.
Outsourcing and professional fees
Outsourcing and professional fees consist of costs for various third-party service providers and contact center operations, primarily for the sales, customer service, collections and store operation functions. The costs related to our third-party contact centers located in Colombia, Jamaica and the Philippines are included in outsourcing and professional fees. These third-party contact centers provide business support, including application processing, verification, customer service and collections. Professional fees also include the cost of legal and audit services, credit reports, recruiting, cash transportation, collection services and fees and consultant expenses. Direct loan origination expenses related to application processing are expensed when incurred. In addition, outsourcing and professional fees include any financing expenses, including legal and underwriting fees, related to our asset-backed notes.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Outsourcing and professional fees | | $ | 67,630 | | | $ | 57,931 | | | | | $ | 9,699 | | | 16.7 | % | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue | | 7.1 | % | | 9.2 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
Outsourcing and professional fees. Outsourcing and professional fees increased by $9.7 million, or 16.7%, from $57.9 million for 2021 to $67.6 million for 2022. The increase is primarily attributable to $7.5 million of higher professional service costs related to credit card programs and other consulting services and $3.3 million related to 84.2% growth in contact center outsourced FTEs as a result of an increase in demand for new applications and the new Philippines contact center. These increases were partially offset by a $3.4 million decrease in debt financing fees and expenses incurred on asset-backed notes issued in 2022 compared to asset-backed notes issued in 2021. We expect our outsourcing and professional fees to decrease in 2023 compared to 2022 as a result of our continued focus on cost cutting and streamlining operations.
General, administrative and other
General, administrative and other expense includes non-compensation expenses for employees, who are not a part of the technology and sales and marketing organization, which include travel, lodging, meal expenses, political and charitable contributions, office supplies, printing and shipping. Also included are franchise taxes, bank fees, foreign currency gains and losses, transaction gains and losses, debit card expenses, litigation reserve, retail network optimization expenses and Digit-related acquisition and integration expenses.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| General, administrative and other | | $ | 58,838 | | | $ | 37,480 | | | | | $ | 21,358 | | | 57.0 | % | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue | | 6.2 | % | | 6.0 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
General, administrative and other. General, administrative and other expense increased by $21.4 million, or 57.0%, from $37.5 million for 2021 to $58.8 million for 2022, primarily due to an increase of $19.6 million of transaction and integration related expenses as a result of the Digit acquisition, $6.1 million of losses related to fraudulent loans, $2.7 million increase in litigation expense related to Digit CID litigation and $7.1 million increase in postage and printing expenses, travel expenses and other general and administrative expenses due to new products and services
and continuing growth of the business. These increases were partially offset by a $3.3 million decrease attributable to an impairment charge recognized in 2021 on a right-of-use asset related to our leased office space in San Carlos, California, not present in 2022 and a $10.9 million decrease in retail network optimization expenses incurred in the year ended December 31, 2022 compared to the year ended December 31, 2021. We expect our general, administrative and other expense to decrease in 2023 compared to 2022 as a result of our continued focus on cost cutting and strong expense discipline.
Goodwill impairment
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands, except percentages) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Goodwill impairment | | $ | 108,472 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | 108,472 | | | * | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue | | 11.4 | % | | — | % | | | | | | | | | | |
Goodwill impairment. In response to a sustained decline in our share price primarily driven by macroeconomic conditions, we conducted a quantitative test of our goodwill as of September 30, 2022. As a result of this quantitative test, we identified an impairment to goodwill resulting in recognition of a $108.5 million non-cash goodwill impairment charge for the year ended December 31, 2022. There were no goodwill impairment charges during the year ended December 31, 2021.
Income taxes
Income taxes consist of U.S. federal, state and foreign income taxes, if any. For the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 we recognized tax expense attributable to U.S. federal, state and foreign income taxes.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | 2022 vs. 2021 Change | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | $ | | % | | | | |
| Income tax expense | | $ | 2,458 | | | $ | 15,377 | | | | | $ | (12,919) | | | 84.0 | % | | | | |
| Percentage of total revenue | | 0.3 | % | | 2.5 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
| Effective tax rate | | (3.3) | % | | 24.5 | % | | | | | | | | | | |
Income tax expense. Income tax expense decreased by $12.9 million or 84.0%, from $15.4 million for 2021 to $2.5 million for 2022, primarily resulting from the tax benefits of the return-to-provision adjustments, generation of tax credits, and having lower pretax income for the year ended December 31, 2022 as a result of the goodwill impairment, which is non-deductible for income tax purposes.
Fair Value Estimate Methodology for Loans Receivable at Fair Value
Summary
Fair value is an electable option under GAAP to account for any financial instruments, including loans receivable and debt. It differs from amortized cost accounting in that loans receivable and debt are recorded on the balance sheet at fair value rather than on a cost basis. Under the fair value option credit losses are recognized through income as they are incurred rather than through the establishment of an allowance and provision for losses. The fair value of instruments under this election is updated at the end of each reporting period, with changes since the prior reporting period reflected in the Consolidated Statements of Operations as net increase (decrease) in fair value which impacts Net Revenue. Changes in interest rates, credit spreads, realized and projected credit losses and cash flow timing will lead to changes in fair value and therefore impact earnings. These changes in the fair value of the Loans Receivable at Fair Value may be partially offset by changes in the fair value of the asset-backed notes, depending upon the relative duration of the instruments.
Fair Value Estimate Methodology for Loans Receivable at Fair Value
We calculate the fair value of Loans Receivable at Fair Value using a model that projects and discounts expected cash flows. The fair value is a function of:
•Portfolio yield;
•Average life;
•Prepayments (or principal payment rate for our credit card receivables);
•Remaining cumulative charge-offs; and
•Discount rate.
Portfolio yield is the expected interest and fees collected from the loans and credit cards as an annualized percentage of outstanding principal balance. Portfolio yield is based upon (a) the contractual interest rate, reduced by expected delinquencies and interest charge-offs and (b) late fees, net of late fee charge-offs based upon expected delinquencies. Origination fees are not included in portfolio yield for personal loans since they are generally capitalized as part of the loan’s principal balance at origination.
Average life is the time-weighted average of expected principal payments divided by outstanding principal balance. The timing of principal payments is based upon the contractual amortization of loans, adjusted for the impact of prepayments, Good Customer Program refinances, and charge-offs.
For personal loans, prepayments are the expected remaining cumulative principal payments that will be repaid earlier than contractually required over the life of the loan, divided by the outstanding principal balance. For credit cards, we estimate principal payment rates which are the expected amount and timing of principal payments over the life of the receivable.
Remaining cumulative charge-offs is the expected net principal charge-offs over the remaining life of the loans and credit cards, divided by the outstanding principal balance.
For personal loans, the discount rate is the sum of the interest rate and the credit spread. The interest rate is based upon the interpolated treasury curve rate that corresponds to the average life. The credit spread is based upon the credit spread implied by the loan purchase price at the time loans are sold, updated for observable changes in the fixed income markets, which serve as a proxy for how a potential loan buyer would adjust their yield requirements relative to the originally agreed price.
For credit cards, the discount rate is the sum of our weighted average cost of funds and the spread implied by the personal loan discount rate. An implied spread is calculated by subtracting the weighted average borrowing cost of the Personal Loan Warehouse from the personal loan discount rate. This spread is then added to the weighted average borrowing cost of the Credit Card Warehouse to arrive at a discount rate for credit cards.
It is also possible to estimate the fair value of our loans using a simplified calculation. The table below illustrates a simplified calculation to aid investors in understanding how fair value may be estimated using the last eight quarters:
•Subtracting the servicing fee from the weighted average portfolio yield over the remaining life of the loans to calculate net portfolio yield;
•Multiplying the net portfolio yield by the weighted average life in years of the loans receivable, which is based upon the contractual amortization of the loans and expected remaining prepayments and charge-offs to calculate net cash flow;
•Subtracting the remaining cumulative charge-offs from the net portfolio yield to calculate the net cash flow;
•Subtracting the product of the discount rate and the average life from the net cash flow to calculate the gross fair value premium as a percentage of loan principal balance; and
•Subtracting the accrued interest and fees as a percentage of loan principal balance from the gross fair value premium as a percentage of loan principal balance to calculate the fair value premium as a percentage of loan principal balance.
The table below reflects the application of this methodology for the eight quarters since January 1, 2021, on loans held for investment. The data for the periods ending on or after December 31, 2021 in the table below represents all of our credit products. The data for the three months ended September 30, 2021 in the table below represents our secured and unsecured loan portfolio. For prior quarters, the data in the table below represents only our unsecured personal loan portfolio which was the primary driver of fair value during those periods.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Three Months Ended | | |
| | Dec 31, 2022 | | Sep 30, 2022 | | Jun 30, 2022 | | Mar 31, 2022 | | Dec 31, 2021 | | Sep 30, 2021 | | Jun 30, 2021 | | Mar 31, 2021 |
| Weighted average portfolio yield over the remaining life of the loans | | 29.50 | % | | 29.90 | % | | 30.27 | % | | 30.15 | % | | 30.14 | % | | 30.35 | % | | 30.28 | % | | 30.25 | % |
| Less: Servicing fee | | (5.00) | % | | (5.00) | % | | (5.00) | % | | (5.00) | % | | (5.00) | % | | (5.00) | % | | (5.00) | % | | (5.00) | % |
| Net portfolio yield | | 24.50 | % | | 24.90 | % | | 25.27 | % | | 25.15 | % | | 25.14 | % | | 25.35 | % | | 25.28 | % | | 25.25 | % |
Multiplied by: Weighted average life in years | | 1.000 | | | 0.924 | | | 0.895 | | | 0.847 | | | 0.859 | | | 0.761 | | | 0.769 | | | 0.778 | |
| Pre-loss cash flow | | 24.50 | % | | 23.01 | % | | 22.61 | % | | 21.30 | % | | 21.60 | % | | 19.26 | % | | 19.43 | % | | 19.64 | % |
| Less: Remaining cumulative charge-offs | | (10.38) | % | | (11.67) | % | | (11.25) | % | | (10.37) | % | | (9.60) | % | | (7.53) | % | | (7.59) | % | | (8.60) | % |
| Net cash flow | | 14.12 | % | | 11.34 | % | | 11.37 | % | | 10.93 | % | | 12.00 | % | | 11.73 | % | | 11.84 | % | | 11.04 | % |
| Less: Discount rate multiplied by average life | | (11.48) | % | | (9.42) | % | | (8.03) | % | | (5.73) | % | | (5.96) | % | | (4.96) | % | | (5.03) | % | | (5.17) | % |
| Gross fair value premium (discount) as a percentage of loan principal balance | | 2.64 | % | | 1.92 | % | | 3.34 | % | | 5.21 | % | | 6.04 | % | | 6.77 | % | | 6.81 | % | | 5.87 | % |
| Less: Accrued interest and fees as a percentage of loan principal balance | | (1.18) | % | | (1.19) | % | | (1.10) | % | | (1.09) | % | | (1.03) | % | | (0.90) | % | | (0.87) | % | | (0.92) | % |
| Fair value premium (discount) as a percentage of loan principal balance | | 1.45 | % | | 0.73 | % | | 2.24 | % | | 4.12 | % | | 5.01 | % | | 5.87 | % | | 5.94 | % | | 4.95 | % |
| Discount Rate | | 11.48 | % | | 10.19 | % | | 8.97 | % | | 6.76 | % | | 6.94 | % | | 6.52 | % | | 6.54 | % | | 6.65 | % |
The illustrative table included above is designed to assist investors in understanding the impact of our election of the fair value option.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
We believe that the provision of non-GAAP financial measures in this report, including Adjusted EBITDA, Adjusted Net Income, Adjusted EPS, Adjusted Operating Efficiency and Adjusted Return on Equity, can provide useful measures for period-to-period comparisons of our core business and useful information to investors and others in understanding and evaluating our operating results. However, non-GAAP financial measures are not calculated in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, and should not be considered as an alternative to any measures of financial performance calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP. There are limitations related to the use of these non-GAAP financial measures versus their most directly comparable GAAP measures, which include the following:
▪Other companies, including companies in our industry, may calculate these measures differently, which may reduce their usefulness as a comparative measure.
▪These measures do not consider the potentially dilutive impact of stock-based compensation.
▪Although depreciation and amortization are non-cash charges, the assets being depreciated and amortized may have to be replaced in the future and Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect cash capital expenditure requirements for such replacements or for new capital expenditure requirements.
▪Although the fair value mark-to-market adjustment is a non-cash adjustment, it does reflect our estimate of the price a third party would pay for our loans receivable held for investment or our asset-backed notes.
▪Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect tax payments that may represent a reduction in cash available to us.
Reconciliations of non-GAAP to GAAP measures can be found below.
Adjusted EBITDA
Adjusted EBITDA is a non-GAAP financial measure defined as our net income, adjusted to eliminate the effect of certain items as described below. We believe that Adjusted EBITDA is an important measure because it allows management, investors and our Board to evaluate and compare our operating results, including our return on capital and operating efficiencies, from period-to-period by making the adjustments described below. In addition, it provides a useful measure for period-to-period comparisons of our business, as it removes the effect of taxes, certain non-cash items, variable charges and timing differences.
•We believe it is useful to exclude the impact of income tax expense (benefit), as reported, because historically it has included irregular income tax items that do not reflect ongoing business operations.
•We believe it is useful to exclude the impact of depreciation and amortization and stock-based compensation expense because they are non-cash charges.
•We believe it is useful to exclude the impact of interest expense associated with the Company's Corporate Financing, as we view this expense as related to our capital structure rather than our funding.
•We believe it is useful to exclude the impact of certain non-recurring charges, such as expenses associated with a litigation reserve, our retail network optimization plan, impairment charges and acquisition and integration related expenses because these items do not reflect ongoing business operations.
•We also reverse origination fees for Loans Receivable at Fair Value, net. We recognize the full amount of any origination fees as revenue at the time of loan disbursement in advance of our collection of origination fees through principal payments. As a result, we believe it is beneficial to exclude the uncollected portion of such origination fees, because such amounts do not represent cash that we received.
•We also reverse the fair value mark-to-market adjustment because it is a non-cash adjustment as shown in the table below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Components of Fair Value Mark-to-Market Adjustment (in thousands) | | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2022 | | 2021 | | |
Fair value mark-to-market adjustment on loans receivable at fair value (1) | | $ | (68,897) | | | $ | 57,044 | | | |
| Fair value mark-to-market adjustment on asset-backed notes | | 184,906 | | | 15,408 | | | |
| Fair value mark-to-market adjustment on derivatives | | 3,702 | | | (3,097) | | | |
| Total fair value mark-to-market adjustment | | $ | 119,711 | | | $ | 69,355 | | | |
(1) The fair value mark-to-market adjustment on loans receivable at fair value shown for the year ended December 31, 2022, excludes $(46.1) million related to the cumulative fair value mark on loans sold as part of the structured and other loan sales in 2022. For details regarding the structured and other loan sales in 2022, refer to Note 5, Loans Held for Sale and Loans Sold of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report.
The following table presents a reconciliation of net income (loss) to Adjusted EBITDA for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
Adjusted EBITDA (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (77,744) | | | $ | 47,414 | | | |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Income tax expense | | 2,458 | | | 15,377 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Interest on corporate financing | | 5,987 | | | — | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 35,182 | | | 23,714 | | | |
| Impairment | | 108,472 | | | 3,324 | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | 27,620 | | | 18,857 | | | |
| Litigation reserve | | 2,750 | | | — | | | |
Retail network optimization expenses | | 1,882 | | | 12,828 | | | |
| Acquisition and integration related expenses | | 29,682 | | | 10,648 | | | |
| Origination fees for loans receivable at fair value, net | | (26,845) | | | (15,836) | | | |
| Fair value mark-to-market adjustment | | (119,711) | | | (69,355) | | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | (10,267) | | | $ | 46,971 | | | |
Adjusted Net Income
We define Adjusted Net Income as our net income, adjusted to exclude income tax expense, stock-based compensation expenses and certain non-recurring charges. We believe that Adjusted Net Income is an important measure of operating performance because it allows management, investors, and our Board to evaluate and compare our operating results, including our return on capital and operating efficiencies, from period to period.
•We believe it is useful to exclude the impact of income tax expense (benefit), as reported, because historically it has included irregular tax items that do not reflect our ongoing business operations.
•We believe it is useful to exclude the impact of certain non-recurring charges, such as expenses associated with a litigation reserve, our retail network optimization plan, impairment charges and acquisition and integration related expenses, because these items do not reflect ongoing business operations.
•We believe it is useful to exclude stock-based compensation expense because it is a non-cash charge.
•We include the impact of normalized statutory income tax expense by applying the income tax rate noted in the table.
The following table presents a reconciliation of net income (loss) to Adjusted Net Income for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
Adjusted Net Income (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (77,744) | | | $ | 47,414 | | | |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Income tax expense | | 2,458 | | | 15,377 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Impairment | | 108,472 | | | 3,324 | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | 27,620 | | | 18,857 | | | |
| Litigation reserve | | 2,750 | | | — | | | |
Retail network optimization expenses | | 1,882 | | | 12,828 | | | |
| Acquisition and integration related expenses | | 29,682 | | | 10,648 | | | |
| Adjusted income before taxes | | 95,120 | | | 108,448 | | | |
| Normalized income tax expense | | 25,682 | | | 29,715 | | | |
| Adjusted Net Income | | $ | 69,438 | | | $ | 78,733 | | | |
Income tax rate (1) | | 27.0 | % | | 27.4 | % | | |
(1) Income tax rates for the years ended December 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, are based on a normalized statutory rate.
Adjusted Earnings Per Share (“Adjusted EPS”)
Adjusted Earnings Per Share is a non-GAAP financial measure that allows management, investors and our Board to evaluate the operating results, operating trends and profitability of the business in relation to diluted adjusted weighted-average shares outstanding.
The following table presents a reconciliation of Diluted EPS to Diluted Adjusted EPS for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021. For the reconciliation of net income (loss) to Adjusted Net Income, see the immediately preceding table “Adjusted Net Income.”
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Diluted earnings (loss) per share | | $ | (2.37) | | | $ | 1.56 | | | |
| Adjusted EPS | | | | | | |
| Adjusted Net Income | | $ | 69,438 | | | $ | 78,733 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Basic weighted-average common shares outstanding | | 32,825,772 | | | 28,191,610 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Weighted average effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | | |
| Stock options | | 252,357 | | | 1,375,915 | | | |
| Restricted stock units | | 173,092 | | | 755,669 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Diluted adjusted weighted-average common shares outstanding | | 33,251,221 | | | 30,323,194 | | | |
| Adjusted Earnings Per Share | | $ | 2.09 | | | $ | 2.60 | | | |
Adjusted Return on Equity
We define Adjusted Return on Equity as annualized Adjusted Net Income divided by average stockholders’ equity. Average stockholders’ equity is an average of the beginning and ending stockholders’ equity balance for each period. We believe Adjusted Return on Equity is an important measure because it allows management, investors and our Board to evaluate the profitability of the business in relation to stockholders' equity and how efficiently we generate income from stockholders' equity.
The following table presents a reconciliation of Return on Equity to Adjusted Return on Equity for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021. For the reconciliation of net income (loss) to Adjusted Net Income, see the immediately preceding table “Adjusted Net Income.”
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of or for the Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Return on Equity | | (13.5) | % | | 8.9 | % | | |
| Adjusted Return on Equity | | | | | | |
| Adjusted Net Income | | $ | 69,438 | | | $ | 78,733 | | | |
| Average stockholders' equity | | $ | 575,740 | | | $ | 535,255 | | | |
| Adjusted Return on Equity | | 12.1 | % | | 14.7 | % | | |
Adjusted Operating Efficiency
We define Adjusted Operating Efficiency as total operating expenses adjusted to exclude stock-based compensation expense and certain non-recurring charges such as expenses associated with a litigation reserve, our retail network optimization plan, impairment charges and acquisition and integration related expenses divided by total revenue. We believe Adjusted Operating Efficiency is an important measure because it allows management, investors and our Board to evaluate how efficiently we manage costs relative to revenue.
The following table presents a reconciliation of Operating Efficiency to Adjusted Operating Efficiency for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of or for the Year Ended December 30, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Operating Efficiency | | 75.2 | % | | 74.6 | % | | |
| Adjusted Operating Efficiency | | | | | | |
| Total revenue | | $ | 952,545 | | | $ | 626,782 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Total operating expense | | 715,943 | | | 467,690 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Impairment | | (108,472) | | | (3,324) | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | (27,620) | | | (18,857) | | | |
| Litigation reserve | | (2,750) | | | — | | | |
Retail network optimization expenses | | (1,882) | | | (12,828) | | | |
| Acquisition and integration related expenses | | (29,682) | | | (10,648) | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Total adjusted operating expenses | | $ | 545,537 | | | $ | 422,033 | | | |
| Adjusted Operating Efficiency | | 57.3 | % | | 67.3 | % | | |
Liquidity and Capital Resources
To date, we fund the majority of our operating liquidity and operating needs through a combination of cash flows from operations, securitizations, secured borrowings, corporate financing and whole loan sales. We may utilize these or other sources in the future. Our material cash requirements relate to funding our lending activities, our debt service obligations, our operating expenses, and investments in the long-term growth of the company.
During 2022, available liquidity increased primarily due to the closing of our Corporate Financing facility and the issuance of additional asset-backed securitizations. We generally target liquidity levels to support at least twelve months of our expected net cash outflows, including new originations, without access to our Corporate Financing facility or equity markets. Rising interest rates, credit trends and other macroeconomic conditions could continue to have an impact on market volatility which could adversely impact our business, liquidity, and capital resources. Future decreases in cash flows from operations resulting from delinquencies, defaults, losses, would decrease the cash available for the capital uses described above. In addition to the $75.0 million that may be available under the recent amendment to the Corporate Financing facility and the associated warrants, we may incur additional indebtedness or issue equity in order to meet our capital spending and liquidity requirements, as well as to fund growth opportunities that we may pursue.
Cash and cash flows
The following table summarizes our cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash and cash flows for the periods indicated:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | | $ | 203,817 | | | $ | 192,960 | | | |
| Cash provided by (used in) | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | 247,875 | | | 163,447 | | | |
| Investing activities | | (1,171,548) | | | (884,786) | | | |
| Financing activities | | 934,530 | | | 745,709 | | | |
Our cash is held for working capital purposes and originating loans. Our restricted cash represents collections held in our securitizations and is applied currently after month-end to pay interest expense and satisfy any amount due to whole loan buyer with any excess amounts returned to us.
Operating Activities
Our net cash provided by operating activities was $247.9 million and $163.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Cash flows from operating activities primarily include net income or losses adjusted for (i) non-cash items included in net income or loss, including depreciation and amortization expense, goodwill impairment charges, fair value adjustments, net, origination fees for loans at fair value, net, gain on loan sales, stock-based compensation expense and deferred tax provision, net, (ii) originations of loans sold and held for sale, and proceeds from sale of loans and (iii) changes in the balances of operating assets and liabilities, which can vary significantly in the normal course of
business due to the amount and timing of various payments.
Investing Activities
Our net cash used in investing activities was $1,171.5 million and $884.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Our investing activities consist primarily of loan originations and loan repayments. We invest in purchases of property and equipment and incur system development costs. Purchases of property and equipment, and capitalization of system development costs may vary from period to period due to the timing of the expansion of our operations, the addition of employee headcount and the development cycles of our system development. The change in our net cash used in investing activities is primarily due to disbursements on originations of loans increasing by $920.6 million while repayments of loan principal only increased by $289.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022 compared to the year ended December 31, 2021. Our net cash used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2022, includes proceeds of $249.3 million related to a structured loan sale in the first quarter 2022 and other loan sales during the remainder of 2022. The change in our net cash used in investing activities is also driven by our acquisition of Digit, net of acquirer's cash received, of $111.7 million for the year ended December 31,2021.
Financing Activities
Our net cash provided by financing activities was $934.5 million and $745.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2022, net cash provided by financing activities was primarily driven the issuance of our Series 2022-A, Series 2022-2 and Series 2022-3 asset-backed notes and the borrowings under our Secured Financing facilities and Acquisition and Corporate Financing facilities, partially offset by repayments of borrowings on our Secured Financing facilities and scheduled amortization payments on our Acquisition Financing facility and our Series 2019-A, Series 2022-2 and Series 2022-3 asset-backed notes. For the year ended December 31, 2021, net cash provided by financing activities was primarily driven by the issuance of our Series 2021-A, Series 2021-B and Series 2021-C asset-backed notes and the borrowings under our Secured Financing facilities and Acquisition Financing, partially offset by redemptions of our Series 2018-A, Series 2018-B, Series 2018-C and Series 2018-D asset-backed notes and repayments of borrowings on our Secured Financing facility.
Sources of Funds
Debt and Available Credit
Asset-Backed Securitizations
As of December 31, 2022, we had $2.39 billion of outstanding asset-backed notes. During 2022, we issued $1.10 billion of asset-backed securities. Our securitizations utilize special purpose entities which are also variable interest entities (VIEs) that meet the requirements to be consolidated in our financial statements. For more information regarding our VIEs and asset-backed securitizations, see Note 4, Variable Interest Entities and Note 9, Borrowings of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report.
Our ability to utilize our asset-backed securitization facilities as described herein is subject to compliance with various requirements including eligibility criteria for the loan collateral and covenants and other requirements. As of December 31, 2022, we were in compliance with all covenants and requirements of all our asset-backed notes.
Secured Financings
As of December, 31, 2022, we had Secured Financing facilities with warehouse lines of $750.0 million in the aggregate with undrawn capacity of $430.0 million. On March 8, 2023, the Credit Card Warehouse facility was amended, reducing its commitment from $150.0 million to $120.0 million, thereby reducing the combined commitment to $720.0 million. Our ability to utilize our Secured Financing facilities as described herein is subject to compliance with various requirements, including eligibility criteria for collateral, concentration limits for our collateral pool, and covenants and other requirements.
Acquisition Financing
On December 20, 2021, Oportun RF, LLC, our wholly-owned subsidiary, issued a $116.0 million asset-backed floating rate variable funding note, and an asset-backed residual certificate, both of which are secured by certain residual cash flows from our securitizations and guaranteed by Oportun, Inc. The note was used to fund the cash consideration paid for the acquisition of Digit. On May 24, 2022, and subsequently on July 28, 2022, pursuant to amended indentures, Oportun RF, LLC issued an additional $20.9 million and $9.1 million asset-backed floating rate variable funding notes, and asset-backed residual certificates, both of which are also secured by certain cash flows from our securitizations and guaranteed by Oportun, Inc., increasing the size of the facility to $119.5 million. The amendments also replaced the interest rate based on LIBOR with an interest rate based on SOFR plus 8.00%. The Acquisition Financing facility was scheduled to pay down based on an amortization schedule with a final payment in May 2024. Subsequently, on February 10, 2023, the Acquisition Financing facility was further amended, including among other things, revising the interest rate to SOFR plus 11.00% and adjusting the amortization schedule to defer $42.0 million in principal payments through July 2023, with final payment in October 2024.
Corporate Financing
On September 14, 2022, we entered into an agreement to borrow $150.0 million of a senior secured term loan (the “Corporate Financing”). The term loan bears interest, payable in cash, at an amount equal to 1-month term SOFR plus 9.00%. The term loan is scheduled to mature on September 14, 2026, and is not subject to amortization. Certain prepayments of the term loan are subject to a prepayment premium. The obligations under the Credit Agreement are secured by our assets and certain of our subsidiaries guaranteeing the term loan, including pledges of the equity interests of certain subsidiaries that are directly or indirectly owned by us, subject to customary exceptions. On March 10, 2023 we upsized and amended our Corporate Financing facility to be able to borrow up to an additional $75.0 million. At closing and as part of the Incremental Tranche A-1, we borrowed $20.8 million and intend to borrow an additional $4.2 million in Incremental Tranche A-2 loans on or about March 27, 2023, which amount has been committed by the applicable lenders. We may borrow up to an aggregate additional amount of $50.0 million on an uncommitted basis in two $25.0 million additional Incremental Tranche B and Incremental Tranche C loans expected to be available, if provided by the applicable lenders, on or about April 21, 2023 and June 23, 2023, respectively. The term loan now bears interest at (a) an amount payable in cash equal to 1-month term SOFR plus 9.00% plus (b) an amount payable in cash or in kind, at the Company’s option, equal to 3.00%.
As of December 31, 2022, we were in compliance with all covenants and requirements on our outstanding debt and available credit. For more information regarding our Secured Financing facilities and Acquisition Financing and Corporate Financing, see Note 9, Borrowings of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report.
Structured Loan Sales
In March 2022, we participated in a securitization and sold loans through the issuance of amortizing asset-backed notes secured by a pool of our unsecured and secured personal installment loans. We also sold our share of the residual interest in the pool. The sold loans had an aggregate unpaid principal balance of approximately $227.6 million. For further information on the structured loan sale transactions, see Note 5, Loans Held for Sale and Loans Sold of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report.
Other Loan Sales
During 2022, we entered into agreements to sell certain populations of its personal loans and credit card receivables that had an aggregate unpaid principal balance, including unpaid interest and fees, of approximately $66.2 million. For further information on these sales, see Note 5, Loans Held for Sale and Loans Sold of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report.
Whole Loan Sales
Through March 4, 2022, we had a commitment to sell to a third-party institutional investor 10% of our unsecured loan originations that satisfy certain eligibility criteria, and an additional 5% subject to certain eligibility criteria and minimum and maximum volumes. We chose not to renew the arrangement and allowed the agreement to expire on its terms on March 4, 2022. The originations of loans sold and held for sale during the year ended December 31, 2022 was $52.7 million. For further information on the whole loan sale transactions, see Note 5, Loans Held for Sale and Loans Sold of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report.
Bank Partnership Program and Servicing Agreement
We entered into a bank partnership program with Pathward, N.A. on August 11, 2020. In accordance with the agreements underlying the bank partnership program, Oportun has a commitment to purchase an increasing percentage of program loans originated by Pathward based on thresholds specified in the agreements. Lending under the partnership was launched in August of 2021.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The material cash requirements for our contractual and other obligations primarily include those related our outstanding borrowings under our asset-backed notes, Acquisition Financing and Secured Financing, corporate and retail leases, and purchase commitments for technology used in the business. See Note 9, Borrowings and Note 16, Leases, Commitments and Contingencies of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in this report for more information.
Liquidity Risks
We believe that our existing cash balance, anticipated positive cash flows from operations and available borrowing capacity under our credit facilities will be sufficient to meet our anticipated cash operating expense and capital expenditure requirements through at least the next 12 months. We do not have any significant unused sources of liquid assets. On the Second Amendment Closing Date, the Company borrowed $20.8 million of incremental term loans and intends to borrow an additional $4.2 million of Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans on or about March 27, 2023, which amount has been committed by the applicable lenders. Under the Amended Credit Agreement, the Company may borrow up to an aggregate additional amount of $50.0 million on an uncommitted basis, in two $25.0 million tranches, the Incremental Tranche B Loans and Incremental Tranche C Loans expected to be available, if provided by the applicable lenders, on or about April 21, 2023 and June 23, 2023, respectively. We anticipate that we will likely draw down these additional incremental commitments, however, given their uncommitted nature there can be no assurance that we will be able to access such additional capital. If our available cash balances are insufficient to satisfy our liquidity requirements, we will seek additional debt or equity financing and we may have to take additional actions to decrease expenses, curtail the origination of loans, and our ability to continue to support our growth and to respond to challenges could be impacted. In a rising interest rate environment, our ability to issue additional equity or incur debt may be impaired and our borrowing costs may increase. If we raise additional funds through the issuance of additional debt, the agreements governing such debt could contain covenants that would restrict our operations and such debt would rank senior to shares of our
common stock. The sale of equity may result in dilution to our stockholders and those securities may have rights senior to those of our common stock. We may require additional capital beyond our currently anticipated amounts and additional capital may not be available on reasonable terms, or at all.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations is based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses and the related disclosures. In accordance with GAAP, we base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
While our significant accounting policies are more fully described in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report, we believe the following critical accounting policies affect the more significant estimates, assumptions and judgments we use to prepare our consolidated financial statements.
Fair Value of Loans Held for Investment
We elected the fair value option for our loans receivable held for investment. We primarily use a discounted cash flow model to estimate fair value based on the present value of estimated future cash flows. This model uses inputs that are not observable but reflect our best estimates of the assumptions a market participant would use to calculate fair value. The following describes the primary inputs that require significant judgment:
•Remaining Cumulative Charge-offs - Remaining cumulative charge-offs are estimates of the principal payments that will not be repaid over the life of a loan held for investment. Remaining cumulative loss expectations are adjusted to reflect the expected principal recoveries on charged-off loans. Remaining cumulative loss expectations are primarily based on the historical performance of our loans but also incorporate adjustments based on our expectations of future credit performance and are quantified by the remaining cumulative charge-off rate.
•Remaining Cumulative Prepayments - Remaining cumulative prepayments are estimates of the principal payments that will be repaid earlier than contractually required over the life of a loan held for investment. Remaining cumulative prepayment rates are primarily based on the historical performance of our loans but also incorporate adjustments based on our expectations of future borrower behavior and refinancings through our Good Customer Program. For credit card receivables, we estimate the principal payment rate which is the amount of principal we expect to get repaid each month.
•Average Life - Average life is the time weighted average of the estimated principal payments divided by the principal balance at the measurement date. The timing of estimated principal payments is impacted by scheduled amortization of loans, charge-offs, and prepayments.
•Discount Rates - The discount rates applied to the expected cash flows of loans held for investment reflect our estimates of the rates of return that investors would require when investing in financial instruments with similar risk and return characteristics. Discount rates are based on our estimate of the rate of return likely to be received on new loans. Discount rates for aged loans are adjusted to reflect the market relationship between interest rates and remaining time to maturity.
We developed an internal model to estimate the fair value of loans receivable held for investment. To generate future expected cash flows, the model combines receivable characteristics with assumptions about borrower behavior based on our historical loan performance. These cash flows are then discounted using a required rate of return that management estimates would be used by a market participant.
We test the fair value model by comparing modeled cash flows to historical loan performance to ensure that the model is complete, accurate and reasonable for our use.
Goodwill Impairment
Goodwill is tested for impairment annually and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. We have a single reporting unit for the purpose of conducting the goodwill impairment assessment. A goodwill impairment charge is recognized for the amount that the carrying value, including goodwill, exceeds the fair value, limited to the total amount of goodwill. Factors that could lead to a future impairment include material uncertainties such as a significant reduction in projected revenues, a deterioration of projected financial performance, future acquisitions and/or mergers, and a decline in our market value as a result of a significant decline in our stock price.
In response to a sustained decline in our share price primarily driven by macroeconomic conditions, we conducted a quantitative test of its goodwill as of September 30, 2022. We recognized a $108.5 million non-cash impairment charge for the year ended December 31, 2022. There were
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Market risk represents the risk of loss that may impact our financial position due to adverse changes in financial market prices, credit performance of loans and interest rates. Certain unobservable inputs may (in isolation) have either a directionally consistent or opposite impact on the fair value of the financial instrument for a given change in that input. When multiple inputs are used within the valuation techniques for loans, a change in one input in a certain direction may be offset by an opposite change from another input. We recorded a fair value mark-to-market adjustment related to our Loans Receivable at Fair Value and asset-backed notes of $119.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, an increase of approximately $50.4 million compared to the prior year.
Credit Performance Sensitivity
In a strong economic climate, credit losses may decrease due to low unemployment and rising wages, which will increase the fair value of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value, which increases Net Revenue. In a weak economic climate, credit losses may increase due to high unemployment and falling wages, which will decrease the fair value of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value, which decreases Net Revenue.
The following table presents estimates at December 31, 2022. Actual results could differ materially from these estimates:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remaining Cumulative Charge-Offs | | Projected percentage change in the fair value of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value | | Projected change in net fair value recorded in earnings
($ in thousands) |
| 120% of expected | | (2.0) | % | | $ | (60,706) | |
| 110% of expected | | (1.0) | % | | $ | (30,646) | |
| 100% of expected | | — | % | | $ | — | |
| 90% of expected | | 1.0 | % | | $ | 31,236 | |
| 80% of expected | | 2.0 | % | | $ | 63,089 | |
Market Rate and Interest Rate Sensitivity
The fair values of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value are estimated using a discounted cash flow methodology, where the discount rate considers various inputs such as the price that we can sell loans to a third party in a non-public market, market conditions such as interest rates, and credit spreads. The discount rates may change due to expected loan performance. We charge fixed rates on our loans and the average life of our loan portfolio is approximately 1.0 years. The fair value of fixed rate loans will generally change when interest rates change, because interest rates will impact the discount rate the market uses to value our loans. As of December 31, 2022, we had $2.39 billion of fixed-rate asset-backed notes outstanding with an average life of 1.4 years. Our borrowing cost does not vary with interest rates for our asset-backed notes, but the fair value will generally change when interest rates change, because interest rates will impact the discount rate the market uses to value our notes.
As of December 31, 2022, we had $243.0 million of outstanding borrowings under our Personal Loan Warehouse facility. The interest rate of the PLW is 1-month LIBOR plus a spread of 2.17% and the maximum borrowing amount is $600.0 million. As of December 31, 2022, we had $77.0 million of outstanding borrowings under our Credit Card Warehouse facility. The interest rate on the Secured Financing - CCW facility is LIBOR, with a floor of 1.00%, plus 6.00% on the first $18.8 million of principal outstanding and LIBOR, with a floor of 0.00%, plus 3.41% on the remaining outstanding principal balance and the maximum borrowing amount is $150.0 million. On March 8, 2023, the Credit Card Warehouse facility was amended, reducing the maximum borrowing amount from $150.0 million to $120.0 million.
As of December 31, 2022, we had $85.7 million outstanding under our Acquisition Financing. The interest rate of the Acquisition Financing is SOFR plus a spread of 8.00%. As of December 31, 2022, we had $150.0 million outstanding under our Corporate Financing. The interest rate of the Corporate Financing is SOFR plus a spread of 9.00%. On March 10, 2023 we upsized and amended our Corporate Financing facility to be able to borrow up to an additional $75.0 million. We borrowed $20.8 million of Incremental Tranche A-1 Loans and intend to borrow an additional $4.2 million of Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans on or about March 27, 2023, which amount has been committed by the applicable lenders. We may borrow up to an aggregate additional amount of $50.0 million on an uncommitted basis, in two $25.0 million tranches, expected to be available, if provided by the applicable lenders, on or about April 21, 2023 and June 23, 2023, respectively. The term loan now bears interest at an amount payable in cash equal to 1-month term SOFR plus 9.00%, plus an amount payable in cash or in kind, at the Company’s option, equal to 3.00%.
Changes in interest rates in the future will likely affect our borrowing costs of our Secured Financing facilities, Acquisition Financing and Corporate Financing. While not carried at fair value on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, we do not expect changes in interest rates to impact the fair value of our Secured Financing facilities, Acquisition Financing or Corporate Financing facility.
In a strong economic climate, interest rates may rise, which will decrease the fair value of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value, which reduces Net Revenue. Rising interest rates will also decrease the fair value of our asset-backed notes, which increases Net Revenue. Conversely, in a weak economic climate, interest rates may fall, which will increase the fair value of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value, which increases Net Revenue. Decreasing interest rates will also increase the fair value of our asset-backed notes, which reduces Net Revenue. Because the duration and fair value of our loans and asset-backed notes are different, the respective changes in fair value will not fully offset each other.
The following table presents estimates at December 31, 2022. Actual results could differ materially from these estimates:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Change in Interest Rates | | Projected percentage change in the fair value of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value | | Projected percentage change in the fair value of our asset-backed notes | | Projected change in net fair value recorded in earnings
($ in thousands) |
| -100 Basis Points | | 0.8 | % | | 0.8 | % | | $ | 4,354 | |
| -50 Basis Points | | 0.4 | % | | 0.4 | % | | $ | 2,149 | |
| -25 Basis Points | | 0.2 | % | | 0.2 | % | | $ | 1,065 | |
| Basis Interest Rate | | — | % | | — | % | | $ | — | |
| +25 Basis Points | | (0.2) | % | | (0.2) | % | | $ | (1,067) | |
| +50 Basis Points | | (0.4) | % | | (0.4) | % | | $ | (2,115) | |
| +100 Basis Points | | (0.8) | % | | (0.8) | % | | $ | (4,177) | |
Prepayment Sensitivity
In a strong economic climate, borrowers’ incomes may increase which may lead them to prepay their loans more quickly. In a weak economic climate, borrowers' incomes may decrease which may lead them to prepay their loans more slowly. The availability of government stimulus payments to consumers during a weak economy may cause prepayments to increase. Additionally, changes in the eligibility requirements for our Good Customer Program, which allows borrowers with existing loans to take out a new loan and use a portion of the proceeds to pay-off their existing loan, could impact prepayment rates. In the future, we may introduce new products or features that could impact the prepayment behavior of our existing loans. Increased competition may also lead to increased prepayment, if our borrowers take out a loan from another lender to refinance our loan.
The following table presents estimates at December 31, 2022. Actual results could differ materially from these estimates:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Remaining Cumulative Prepayments | | Projected percentage change in the fair value of our Loans Receivable at Fair Value | | Projected change in net fair value recorded in earnings
($ in thousands) |
| 120% of expected | | (0.1) | % | | $ | (3,073) | |
| 110% of expected | | (0.1) | % | | $ | (1,559) | |
| 100% of expected | | — | % | | $ | — | |
| 90% of expected | | 0.1 | % | | $ | 1,594 | |
| 80% of expected | | 0.1 | % | | $ | 3,233 | |
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
All of our revenue and substantially all of our operating expenses are denominated in U.S. dollars. Our non-U.S. dollar operating expenses in Mexico and India made up 4.1% of total operating expenses in 2022. All of our interest income is denominated in U.S. dollars and is therefore not subject to foreign currency exchange risk.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the stockholders and the Board of Directors of Oportun Financial Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Oportun Financial Corporation and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2022 and 2021, the related consolidated statements of operations, changes in stockholders' equity, and cash flows, for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2022, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2022, and 2021, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of two years in the period ended December 31, 2022, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2022, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated March 13, 2023, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
Loans Receivable at Fair Value — Refer to Notes 2 and 15 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Company’s loans receivable at fair value were at $3,144 million as of December 31, 2022. The loans receivable at fair value were valued as Level 3 financial instruments. Level 3 financial instruments are valued utilizing pricing inputs that are unobservable and significant to the entire fair value measurement. The Company estimates the fair value of the Level 3 loans receivable using a discounted cash flow model based on estimated future cash flows, which considers various inputs that require significant judgment. The model uses inputs that are not observable and inherently judgmental and reflect management’s best estimates of the assumptions a market participant would use to calculate fair value.
We identified the Company’s unsecured personal loans receivable at fair value portfolio as a critical audit matter because of the subjective process in determining significant inputs, assumptions, and judgments used to estimate the fair value. Auditing management’s assessment of unsecured personal loans receivable at fair value involved exercising subjective and complex judgments, required specialized skills and knowledge, and required an increased extent of audit effort, including obtaining audit evidence of the data sources used to estimate fair value and understanding the assumptions applied and the nature of significant inputs utilized.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to the valuation of unsecured personal loans receivable at fair value included the following, among others:
•We tested the effectiveness of management’s controls covering the overall estimate and the review of the accuracy and completeness of the underlying unsecured personal loan data utilized in the model calculations.
•We subjected the significant unobservable inputs to sensitivity analyses to evaluate changes in the fair value that would result from changes in the assumptions.
•We tested the accuracy and completeness of the significant unobservable inputs used in the valuation of unsecured personal loans receivable at fair value by detail testing the segmentation of the portfolio and underlying payment history and historical performance of the unsecured personal loans.
•With the assistance of our fair value specialists, we developed independent estimates of the unsecured personal loans receivable at fair value and compared our estimates to the Company’s estimates.
•We performed a retrospective review of management’s ability to accurately estimate the unsecured personal loans receivable at fair value by comparing modeled monthly cash flows to actual past performance.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
San Francisco, CA
March 13, 2023
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2010.
OPORTUN FINANCIAL CORPORATION
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Assets | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 98,817 | | | $ | 130,959 | |
| Restricted cash | | 105,000 | | | 62,001 | |
| Loans receivable at fair value | | 3,143,653 | | | 2,386,807 | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Interest and fees receivable, net | | 31,796 | | | 20,916 | |
| Capitalized software and other intangibles, net | | 139,801 | | | 131,181 | |
| Goodwill | | — | | | 104,014 | |
| Right of use assets - operating | | 30,448 | | | 38,403 | |
| | | | |
| Other assets | | 64,180 | | | 72,344 | |
| Total assets | | $ | 3,613,695 | | | $ | 2,946,625 | |
| | | | |
| Liabilities and stockholders' equity | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | |
| Secured financing | | $ | 317,568 | | | $ | 393,889 | |
| Asset-backed notes at fair value | | 2,387,674 | | | 1,651,706 | |
| Acquisition and corporate financing | | 222,879 | | | 114,092 | |
| | | | |
| Lease liabilities | | 37,947 | | | 47,699 | |
| | | | |
| Other liabilities | | 100,028 | | | 135,358 | |
| Total liabilities | | 3,066,096 | | | $ | 2,342,744 | |
| Stockholders' equity | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
Common stock, $0.0001 par value - 1,000,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021; 33,626,630 shares issued and 33,354,607 shares outstanding at December 31, 2022; 32,276,419 shares issued and 32,004,396 shares outstanding at December 31, 2021 | | 7 | | | 6 | |
| Common stock, additional paid-in capital | | 547,799 | | | 526,338 | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Retained earnings | | 6,102 | | | 83,846 | |
Treasury stock at cost, 272,023 and 272,023 shares at December 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021 | | (6,309) | | | (6,309) | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | 547,599 | | | 603,881 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | | $ | 3,613,695 | | | $ | 2,946,625 | |
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
OPORTUN FINANCIAL CORPORATION
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Revenue | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | $ | 876,114 | | | $ | 575,839 | | | |
| Non-interest income | | 76,431 | | | 50,943 | | | |
| Total revenue | | 952,545 | | | 626,782 | | | |
| Less: | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | 93,046 | | | 47,669 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Net decrease in fair value | | (218,842) | | | (48,632) | | | |
| Net revenue | | 640,657 | | | 530,481 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Technology and facilities | | 216,120 | | | 139,564 | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | 110,033 | | | 116,882 | | | |
| Personnel | | 154,850 | | | 115,833 | | | |
| Outsourcing and professional fees | | 67,630 | | | 57,931 | | | |
| General, administrative and other | | 58,838 | | | 37,480 | | | |
| Goodwill impairment | | 108,472 | | | — | | | |
| Total operating expenses | | 715,943 | | | 467,690 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Income (loss) before taxes | | (75,286) | | | 62,791 | | | |
| Income tax expense | | 2,458 | | | 15,377 | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (77,744) | | | $ | 47,414 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders | | $ | (77,744) | | | $ | 47,414 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Share data: | | | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per share: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | $ | (2.37) | | | $ | 1.68 | | | |
| Diluted | | $ | (2.37) | | | $ | 1.56 | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | 32,825,772 | | | 28,191,610 | | | |
| Diluted | | 32,825,772 | | | 30,323,194 | | | |
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
OPORTUN FINANCIAL CORPORATION
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity
(in thousands, except share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 |
| | | | | | | Common Stock | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Shares | | Par Value | | Additional Paid-in Capital | | | | Retained Earnings | | Treasury Stock | | Total Stockholders' Equity |
| Balance – January 1, 2022 | | | | | | | | | | | | | 32,004,396 | | | $ | 6 | | | $ | 526,338 | | | | | $ | 83,846 | | | $ | (6,309) | | | $ | 603,881 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options, net of shares withheld | | | | | | | | | | | | | 546,312 | | | 1 | | | (4,636) | | | | | — | | | — | | | (4,635) | |
| Repurchase of stock options | | | | | | | | | | | | | (2,706) | | | — | | | (28) | | | | | — | | | — | | | (28) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | — | | | 30,125 | | | | | — | | | — | | | 30,125 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld | | | | | | | | | | | | | 806,605 | | | — | | | (4,000) | | | | | — | | | — | | | (4,000) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (77,744) | | | — | | | (77,744) | |
| Balance – December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | | | | | | | 33,354,607 | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | 547,799 | | | | | $ | 6,102 | | | $ | (6,309) | | | $ | 547,599 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance – January 1, 2021 | | | | | | | | | | | | | 27,679,263 | | | $ | 6 | | | $ | 436,499 | | | | | $ | 36,432 | | | $ | (6,309) | | | $ | 466,628 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | | | | | | | | | | | | | 240,047 | | | — | | | 3,272 | | | | | — | | | — | | | 3,272 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | — | | | 19,888 | | | | | — | | | — | | | 19,888 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Vesting of restricted stock units, net of shares withheld | | | | | | | | | | | | | 562,904 | | | — | | | (6,502) | | | | | — | | | — | | | (6,502) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of equity on business acquisition | | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,522,182 | | | — | | | 73,181 | | | | | — | | | — | | | 73,181 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | 47,414 | | | — | | | 47,414 | |
| Balance – December 31, 2021 | | | | | | | | | | | | | 32,004,396 | | | $ | 6 | | | $ | 526,338 | | | | | $ | 83,846 | | | $ | (6,309) | | | $ | 603,881 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
OPORTUN FINANCIAL CORPORATION
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flow
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (77,744) | | | $ | 47,414 | | | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 47,533 | | | 27,112 | | | |
| Goodwill impairment | | 108,472 | | | — | | | |
| Fair value adjustment, net | | 218,842 | | | 48,632 | | | |
| Origination fees for loans receivable at fair value, net | | (26,845) | | | (15,836) | | | |
| Gain on loan sales | | (5,703) | | | (26,750) | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | 27,620 | | | 18,857 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Deferred tax provision, net | | — | | | 16,451 | | | |
| Other, net | | 30,336 | | | 30,567 | | | |
| Originations of loans sold and held for sale | | (52,742) | | | (214,598) | | | |
| Proceeds from sale of loans | | 58,844 | | | 242,015 | | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | | (80,738) | | | (10,417) | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | 247,875 | | | 163,447 | | | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | |
| Originations of loans | | (2,762,828) | | | (1,842,211) | | | |
| Proceeds from loan sales originated as held for investment | | 249,271 | | | — | | | |
| Repayments of loan principal | | 1,396,896 | | | 1,107,850 | | | |
| Capitalization of system development costs | | (48,892) | | | (26,477) | | | |
| Acquisition of Digit, net of acquirer's cash received | | — | | | (111,652) | | | |
| Other, net | | (5,995) | | | (12,296) | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | (1,171,548) | | | (884,786) | | | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | |
| Borrowings under secured financing | | 1,972,000 | | | 1,291,795 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Borrowings under asset-backed notes, acquisition and corporate financing | | 1,262,059 | | | 1,479,332 | | | |
| Repayments of secured financing | | (2,050,000) | | | (1,144,996) | | | |
| Repayments of asset-backed notes, acquisition and corporate financing | | (232,675) | | | (875,007) | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Payments of deferred financing costs | | (8,189) | | | (2,183) | | | |
| Net payments related to stock-based activities | | (8,665) | | | (3,232) | | | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | 934,530 | | | 745,709 | | | |
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash | | 10,857 | | | 24,370 | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash, beginning of period | | 192,960 | | | 168,590 | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash, end of period | | $ | 203,817 | | | $ | 192,960 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 98,817 | | | $ | 130,959 | | | |
| Restricted cash | | 105,000 | | | 62,001 | | | |
| Total cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash | | $ | 203,817 | | | $ | 192,960 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Cash paid for income taxes, net of refunds | | $ | (3,457) | | | $ | 3,884 | | | |
| Cash paid for interest | | $ | 85,775 | | | $ | 46,831 | | | |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of operating lease liabilities | | $ | 15,696 | | | $ | 17,603 | | | |
| Supplemental disclosures of non-cash investing and financing activities | | | | | | |
| Right of use assets obtained in exchange for operating lease obligations | | $ | 4,161 | | | $ | 12,392 | | | |
| Net issuance of stock related to Digit acquisition | | $ | — | | | $ | 73,181 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Non-cash investment in capitalized assets | | $ | 2,672 | | | $ | 2,103 | | | |
| Non-cash financing activities | | $ | 1,550 | | | $ | 33 | | | |
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
OPORTUN FINANCIAL CORPORATION
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2022
| | | | | |
| 1. | Organization and Description of Business |
Oportun Financial Corporation (together with its subsidiaries, "Oportun" or the "Company") is a digital banking platform that puts its members’ financial goals within reach. With intelligent borrowing, savings, budgeting, and spending capabilities, the Company empowers members with the confidence to build a better financial future. Oportun takes a holistic approach to serving its members and view as its purpose to responsibly meet their current capital needs, help grow its members' financial profiles, increase their financial awareness and put them on a path to a financially healthy life. With its acquisition of Hello Digit, Inc. ("Digit") on December 22, 2021, the Company can now offer access to a comprehensive suite of digital banking products, offered either directly or through partners, including lending, savings and investing powered by A.I. and tailored to each member's goals to make achieving financial health automated. The Company's credit products include personal loans, secured personal loans and credit cards. The Company's digital banking products include automated savings, digital banking, long-term investing and retirement savings. The Company is headquartered in San Carlos, California. The Company has been certified by the United States Department of the Treasury as a Community Development Financial Institution ("CDFI") since 2009.
Segments
Segments are defined as components of an enterprise for which discrete financial information is available and evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker ("CODM") in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company’s Chief Executive Officer and the Company's Chief Financial Officer are collectively considered to be the CODM. The CODM reviews financial information presented on a consolidated basis for purposes of allocating resources and evaluating financial performance. The Company’s operations constitute a single reportable segment.
| | | | | |
| 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Basis of Presentation ‑ The Company meets the SEC's definition of a "Smaller Reporting Company”, and therefore qualifies for the SEC's reduced disclosure requirements for smaller reporting companies. The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("GAAP"). These statements reflect all normal, recurring adjustments that are, in management's opinion, necessary for the fair presentation of results. The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Certain prior-period financial information has been reclassified to conform to current period presentation.
Use of Estimates ‑ The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements, and the reported amounts of income and expenses during the reporting period. These estimates are based on information available as of the date of the consolidated financial statements; therefore, actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
Business Combinations - The Company accounts for business combinations using the acquisition method of accounting which requires the fair values of the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed to be recognized in the consolidated financial statements. Assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination are recognized at their estimated fair value as of the acquisition date. Determining fair value of identifiable assets, particularly intangibles, and liabilities acquired requires management to make estimates, which are based on all available information and in some cases assumptions with respect to the timing and amount of future revenues and expenses associated with an asset or liability. The excess purchase price over the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed is recorded as goodwill. The allocation of fair values may be subject to adjustment after the initial allocation for up to a one-year period, with the corresponding offset to goodwill. Acquisition-related costs, such as legal and consulting fees, are recognized separately from the business combination and are expensed as incurred.
Consolidation and Variable Interest Entities ‑ The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiaries. The Company’s policy is to consolidate the financial statements of entities in which it has a controlling financial interest. The Company determines whether it has a controlling financial interest in an entity by evaluating whether the entity is a voting interest entity or variable interest entity ("VIE") and if the accounting guidance requires consolidation.
VIEs are entities that, by design, either (i) lack sufficient equity to permit the entity to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support from other parties, or (ii) have equity investors that do not have the ability to make significant decisions relating to the entity’s operations through voting rights, or do not have the obligation to absorb the expected losses, or do not have the right to receive the residual returns of the entity. The Company determines whether it has a controlling financial interest in a VIE by considering whether its involvement with the VIE is significant and whether it is the primary beneficiary of the VIE based on the following:
•The Company has the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance;
•The aggregate indirect and direct variable interests held by us have the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits from the entity that could be significant to the VIE; an
•Qualitative and quantitative factors regarding the nature, size, and form of the Company’s involvement with the VIE.
Foreign Currency Re-measurement ‑ The functional currency of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries is the U.S. dollar. Monetary assets and liabilities of these subsidiaries are re-measured into U.S. dollars from the local currency at rates in effect at period-end and nonmonetary assets and liabilities are re-measured at historical rates. Revenue and expenses are re-measured at average exchange rates in effect during each period. Foreign currency gains and losses from re-measurement and transaction gains and losses are recorded as general, administrative and other expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Concentration of Credit Risk ‑ Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of loans receivable at fair value.
As of December 31, 2022, 45%, 26%, 9%, 5% and 4% of the owned principal balance related to borrowers from California, Texas, Florida, Illinois and New Jersey, respectively. Owned principal balance related to borrowers from each of the remaining states of operation continues to be at or below 3%. As of December 31, 2021, 49%, 27%, 7% and 6% of the owned principal balance related to borrowers from California, Texas, Florida and Illinois, respectively, and the owned principal balance related to borrowers from each of the remaining states was at or below 3%.
Cash and Cash Equivalents ‑ Cash and cash equivalents consist of unrestricted cash balances and short-term, liquid investments with a maturity date of three months or less at the time of purchase. Digit's savings platform connects to members’ checking accounts and analyzes their income and spending patterns to find amounts that can safely be set aside towards savings goals. Digit calculates these amounts by identifying upcoming bills and regular spending habits to ensure optimal amounts are flagged for savings and transferred to savings accounts. The funds in these saving accounts are owned by Digit members and are not the assets of the Company. Therefore, these funds are not included in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Restricted Cash ‑ Restricted cash represents cash held at a financial institution as part of the collateral for the Company’s Secured Financing, asset-backed notes and loans designated for sale.
Loans Receivable at Fair Value ‑ Loans that we have the intent and ability to hold for the foreseeable future or until maturity or payoff are considered as loans held for investment. The Company elected the fair value option for all loans receivable held for investment. Under fair value accounting, direct loan origination fees are recognized in income immediately and direct loan origination costs are expensed in the period the loan originates. In addition, the Company recognizes annual fees on credit card receivables into income immediately upon activation of the credit card by the credit card holder and subsequent annual fees when billed upon the anniversary of the credit card account. Loans are charged off at the earlier of when loans are determined to be uncollectible or when loans are 120 days contractually past due, or 180 days contractually past due in the case of credit cards. Recoveries are recorded when cash is received on loans that had been previously charged off. The Company estimates the fair value of the loans using a discounted cash flow model, which considers various unobservable inputs such as remaining cumulative charge-offs, remaining cumulative prepayments or principal payment rates for our credit card receivables, average life and discount rate. The Company re-evaluates the fair value of loans receivable at the close of each measurement period. Changes in fair value are recorded in "Net decrease in fair value" in the Consolidated Statements of Operations in the period of the fair value changes.
Fair Value Measurements ‑ The Company follows applicable guidance that establishes a fair value measurement framework, provides a single definition of fair value and requires expanded disclosure summarizing fair value measurements. Such guidance emphasizes that fair value is a market-based measurement, not an entity-specific measurement. Therefore, a fair value measurement should be determined based on the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability.
Fair value guidance establishes a three-level hierarchy for inputs used in measuring the fair value of a financial asset or financial liability.
•Level 1 financial instruments are valued based on unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities, accessible by the Company at the measurement date.
•Level 2 financial instruments are valued using quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices in markets that are not active, or models using inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data of substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities.
•Level 3 financial instruments are valued using pricing inputs that are unobservable and reflect the Company’s own assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability.
Loans Held for Sale ‑ Loans held for sale are recorded at the lower of cost or fair value, until the loans are sold. Loans held for sale are sold within four days of origination. Cost of loans held for sale is inclusive of unpaid principal plus net deferred origination costs.
Derivatives - Derivative financial instruments are recognized as either assets or liabilities in the consolidated balance sheet at fair value. Changes in fair value and settlements of derivative instruments are reflected in earnings as a component of "net decrease in fair value" in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company does not use derivative instruments for trading or speculative purposes. Based on the agreements entered into with Pathward, N.A. (formerly known as MetaBank, N.A.) for all loans originated and retained by Pathward, Pathward receives a fixed interest rate. Oportun bears the risk of credit loss and has the benefit of any excess interest proceeds after satisfying various obligations under the agreements.
Goodwill ‑ Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of identifiable net assets acquired. The Company performs impairment testing for goodwill annually or more frequently if an event or change in circumstances indicates that goodwill may be impaired. The Company first assesses qualitative factors to determine if it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying
value. If the Company concludes the fair value is less than its carrying value a quantitative test is performed. The Company performs a quantitative goodwill impairment test by determining the fair value of the reporting unit and comparing it to the carrying value of the reporting unit. If the fair value of the reporting unit is greater than the reporting unit's fair value, then the carrying value of the reporting unit is deemed to be recoverable. If the carrying value of the reporting unit is greater than the reporting unit's fair value, goodwill is impaired and written down to the reporting unit's fair value.
In response to a sustained decline in the Company's share price primarily driven by macroeconomic conditions, the Company conducted a quantitative test of our goodwill as of September 30, 2022. As a result of this quantitative test, the Company identified an impairment to goodwill resulting in recognition of a $108.5 million non-cash goodwill impairment charge for the year ended December 31, 2022. There were no goodwill impairment charges during the year ended December 31, 2021. For further discussion, refer to Note 7, Capitalized Software, Other Intangibles and Goodwill.
Intangible Assets other than Goodwill - At the time intangible assets are initially recognized, a determination is made with regard to each asset as it relates to its useful life. We have determined that each of our intangible assets has a finite useful life with the exception of certain trade names, which we have determined have indefinite lives.
Intangible assets with a finite useful life are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives. Intangible assets with a finite useful life are presented net of accumulated amortization on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company reviews the intangible assets with finite useful lives for impairment at least annually and whenever changes in circumstances indicate their carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Impairment is indicated if the sum of undiscounted estimated future cash flows is less than the carrying value of the respective asset. Impairment is permanently recognized by writing down the asset to the extent that the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value.
For indefinite-lived intangible assets, we review for impairment at least annually and whenever events occur or circumstances change that would indicate the assets are more likely than not to be impaired. We first complete an annual qualitative assessment to determine whether it is necessary to perform a quantitative impairment test. If the qualitative assessment indicates that the assets are more likely than not to have been impaired, we proceed with the fair value calculation of the assets. If the fair value is less than the carrying value, an impairment loss will be recognized in an amount equal to the difference and the indefinite life classification will be evaluated to determine whether such classification remains appropriate.
Fixed Assets ‑ Fixed assets are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets, which is generally three years for computer and office equipment and furniture and fixtures, and three to five years for purchased software, vehicles and leasehold improvements. When assets are sold or retired, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss, if any, is included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Maintenance and repairs are charged to the Consolidated Statements of Operations as incurred.
The Company does not own any buildings or real estate. The Company enters into term leases for its corporate offices, call center and store locations. Leasehold improvements are capitalized and depreciated over the lesser of their physical life or lease term of the building.
Systems Development Costs ‑ The Company capitalizes software developed or acquired for internal use, and these costs are included in Capitalized software and other intangibles, net on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company has internally developed its proprietary Web-based technology platform, which consists of application processing, credit scoring, loan accounting, servicing and collections, debit card processing, data and analytics and digital banking services.
The Company capitalizes its costs to develop software when preliminary development efforts are successfully completed; management has authorized and committed project funding; and it is probable the project will be completed and the software will be used as intended. Costs incurred prior to meeting these criteria, together with costs incurred for training and maintenance, are expensed as incurred. When the software developed for internal use has reached its technological feasibility, such costs are amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of the assets, which is generally three years. Costs incurred for upgrades and enhancements that are expected to result in additional functionality are capitalized and amortized over the estimated useful life of the upgrades.
The Company acquired developed technology with its acquisition of Digit. Developed technology is included in capitalized software. Such costs are amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of the assets, which was determined to be seven years.
Impairment ‑ The Company reviews long-lived assets, including fixed assets, right of use assets and system development costs, for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be fully recoverable. An impairment loss is recognized when estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition are less than its carrying amount. The Company determined that there were no events or changes in circumstances that indicated our long-lived assets were impaired for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, except as disclosed in Note 7, Capitalized Software, Other Intangibles and Goodwill.
Asset-Backed Notes at Fair Value ‑ The Company elected the fair value option to account for all asset-backed notes. The Company calculates the fair value of the asset-backed notes using independent pricing services and broker price indications, which are based on quoted prices for identical or similar notes, which are Level 2 input measures. The Company re-evaluates the fair value of the asset-backed notes at the close of each measurement period. Changes in fair value are recorded in Net decrease in fair value in the Consolidated Statements of Operations in the period of the fair value changes.
Acquisition Financing ‑ The Acquisition Financing is an asset-backed note carried at amortized cost. The Company reports issuance costs associated with the financing on its balance sheet as a direct reduction in the carrying amount of the note, and they are amortized over the life of the
note using the effective interest method. The Acquisition Financing was used to fund the cash component of the purchase price for the Digit acquisition and, as a result, the interest payments are recorded to General, administrative and other in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Revenue Recognition ‑ The Company’s primary sources of revenue consist of interest and non-interest income.
Interest Income
Interest income includes interest and fees on loans. Generally, the Company’s loans require semi-monthly or biweekly borrower payments of interest and principal. Fees on loans include billed late fees offset by charged-off fees and provision for uncollectible fees. The Company charges borrowers a late fee if a scheduled installment payment becomes delinquent. Depending on the loan, late fees are assessed when the loan is eight to 16 days delinquent. Late fees are recognized when they are billed. When a loan is charged off, uncollected late fees are also written off. For Loans Receivable at Fair Value, interest income includes (i) billed interest and late fees, plus (ii) origination fees recognized at loan disbursement, less (iii) charged-off interest and late fees, less (iv) provision for uncollectible interest and late fees. Additionally, direct loan origination expenses are recognized in operating expenses as incurred. For Loans Receivable at Fair Value, loan origination fees and costs are recognized when incurred.
Interest income on our personal loan receivables is recognized based upon the amount the Company expects to collect from its borrowers. When a loan becomes delinquent for a period of 90 days or more, interest income continues to be recorded until the loan is charged off. Delinquent loans are charged off at month-end during the month it becomes 120 days’ delinquent. For personal loans receivable, the Company mitigates the risk of income recorded for loans that are delinquent for 90 days or more by establishing a 100% provision and the provision for uncollectible interest and late fees is offset against interest income. Previously accrued and unpaid interest is also charged off in the month the Company receives a notification of bankruptcy, a judgment or mediated agreement by the court, or loss of life, unless there is evidence that the principal and interest are collectible.
Interest income on our credit card receivables is recognized on the current balance on the account, inclusive of outstanding principal balance plus previously unpaid interest and fees, at the end of the monthly billing cycle. Delinquent credit card accounts, including unpaid interest and fees are charged off at month-end during the month they become 180 days contractually past due.
Non-Interest Income
Non-interest income includes subscription revenue, servicing fees, gain on loan sales, debit card income, documentation fees, sublease income and other income.
Subscription Revenue - The Company earns revenue on a subscription basis from users of its platform. Revenue is recognized ratably over each month as the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Deferred revenue is recognized when the service period spans into the following month.
Servicing Fees ‑ The Company retains servicing rights on sold loans. Servicing fees comprise the contractual annual servicing fee based upon the average daily principal balance of loans sold that the Company earns for servicing loans sold to a third-party financial institution. The servicing fee compensates the Company for the costs incurred in servicing the loans, including providing customer services, receiving borrower payments and performing appropriate collection activities. Management believes the fee approximates a market rate and accordingly has not recognized a servicing asset or liability.
Gain on Loan Sales ‑ The Company recognizes a gain on sale from the difference between the proceeds received from the purchaser and the carrying value of the loans on the Company’s books. The Company sells a certain percentage of new loans twice weekly.
A transfer of a financial asset, a group of financial assets, or a participating interest in a financial asset is accounted for as a sale if all of the following conditions are met:
•The financial assets are isolated from the transferor and its consolidated affiliates as well as its creditors.
•The transferee or beneficial interest holders have the right to pledge or exchange the transferred financial assets.
•The transferor does not maintain effective control of the transferred assets.
For the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 all of the Company's loan sales met the requirements for sale treatment. The Company records the gain on the sale of a loan at the sale date in an amount equal to the proceeds received less outstanding principal, accrued interest, late fees and net deferred origination costs.
Debit card income is the revenue from interchange fees when borrowers use our reloadable debit card for purchases as well as the associated card user fees.
Documentation Fees - On a monthly basis Pathward, N.A. pays the Company documentation fees as compensation for its role in facilitation of loan originations by Pathward. The documentation fees are equivalent to loan origination fees charged by Pathward to its borrowers. Documentation fees to which the Company expects to be entitled are variable consideration because loan volume originated over the contractual term is not known at the contract’s inception. The transaction fee is determined each time a loan is issued based on that loan’s initial principal amount and is recognized when performance is complete and upon the successful origination of a borrower's loan.
Sublease income is the rental income from subleasing a portion of our existing right of use assets.
Other income includes marketing incentives paid directly to us by the merchant clearing company based on transaction volumes, interest earned on cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash, and gain (loss) on asset sales.
Interest expense ‑ Interest expense consists of interest expense associated with the Company’s asset-backed notes, Corporate Financing and Secured Financing, and it includes the amortization of deferred origination costs for the Corporate Financing and Secured Financing facilities as well as fees for the unused portion of the Secured Financing facility. The Company elected the fair value option for all asset-backed notes. Accordingly, all origination costs for such asset-backed notes at fair value are expensed as incurred.
Income Taxes ‑ The Company accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the difference between the consolidated financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. Valuation allowances are established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to an amount that is more likely than not to be realized.
The Company evaluates uncertain tax positions by reviewing against applicable tax law all positions taken by the Company with respect to tax years for which the statute of limitations is still open. A tax benefit from an uncertain tax position may be recognized when it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including resolutions of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits. The Company recognizes interest and penalties related to the liability for unrecognized tax benefits, if any, as a component of the Income tax expense line in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Stock-Based Compensation ‑ The Company accounts for stock-based employee awards based on the fair value of the award which is measured at grant date. Accordingly, stock-based compensation cost is recognized in operating expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations over the requisite service period. The fair value of stock options granted or modified is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur and does not estimate forfeitures as of the award grant date.
The Company granted restricted stock units ("RSUs") to employees that vest upon the satisfaction of time-based criterion of up to four years and previously some included a performance criterion, a liquidity event in connection with an initial public offering or a change in control. These RSUs were not considered vested until both criteria were met and provided that the participant was in continuous service on the vesting date. Compensation cost for awards with performance criteria, measured on the grant date, was recognized when both the service and performance conditions were probable of being achieved. For grants and awards with just a service condition, the Company recognizes stock-based compensation expenses using the straight-line basis over the requisite service period net of forfeitures. For grants and awards with both service and performance conditions, the Company recognizes expenses using the accelerated attribution method.
As a result of shares vesting as part of the Company's stock-based plans shares are surrendered to the Company to satisfy the tax withholding obligations and the Company pays the associated payroll taxes and the shares go back to the plan for future use.
Treasury Stock ‑ Treasury stock is reported at cost, and no gain or loss is recorded on stock repurchase transactions. Repurchased shares are held as treasury stock until they are retired or re-issued. The Company did not retire or re-issue any treasury stock for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021.
Basic and Diluted Earnings per Share ‑ Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net income per share available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period and excludes the effects of any potentially dilutive securities. The Company computes earnings per share using the two-class method required for participating securities. The Company considers all series of convertible preferred stock to be participating securities due to their noncumulative dividend rights. As such, net income allocated to these participating securities, which includes participation rights in undistributed earnings, are subtracted from net income to determine total undistributed net income to be allocated to common stockholders. All participating securities are excluded from basic weighted-average common shares outstanding.
Diluted earnings per share reflects the potential dilution that could occur if securities or other contracts to issue common stock were exercised. It is computed by dividing net income attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average common shares plus the effect of dilutive potential common shares outstanding during the period using the treasury stock method or the two-class method, whichever is more dilutive.
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
None.
| | | | | |
| 3. | Earnings (Loss) per Share |
Basic and diluted earnings (loss) per share are calculated as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (77,744) | | | $ | 47,414 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders | | $ | (77,744) | | | $ | 47,414 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Basic weighted-average common shares outstanding | | 32,825,772 | | | 28,191,610 | | | |
| Weighted average effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | | |
| Stock options | | — | | | 1,375,915 | | | |
| Restricted stock units | | — | | | 755,669 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Diluted weighted-average common shares outstanding | | 32,825,772 | | | 30,323,194 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per share: | | | | | | |
| Basic | | $ | (2.37) | | | $ | 1.68 | | | |
| Diluted | | $ | (2.37) | | | $ | 1.56 | | | |
The following common share equivalent securities have been excluded from the calculation of diluted weighted-average common shares outstanding because the effect is anti-dilutive for the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Stock options | | 3,527,096 | | | 2,038,022 | | | |
| Restricted stock units | | 4,347,899 | | | 19,073 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Total anti-dilutive common share equivalents | | 7,874,995 | | | 2,057,095 | | | |
| | | | | |
| 4. | Variable Interest Entities |
Variable interest entities ("VIEs") are legal entities that either have an insufficient amount of equity at risk for the entity to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support or, as a group, the holders of equity investment at risk lack the ability to direct the entity's activities that most significantly impact economic performance through voting or similar rights, or do not have the obligation to absorb the expected losses or the right to receive expected residual returns of the entity.
For all VIEs in which we are involved, we assess whether we are the primary beneficiary of the VIE on an ongoing basis. In circumstances where we have both the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIEs performance and the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive the benefits of the VIE that could be significant, we would conclude that we are the primary beneficiary of the VIE, and we consolidate the VIE. In situations where we are not deemed to be the primary beneficiary of the VIE, we do not consolidate the VIE and only recognize our interests in the VIE.
Consolidated VIEs
As part of the Company’s overall funding strategy, the Company transfers a pool of designated loans receivable to wholly owned special-purpose subsidiaries ("VIEs") to collateralize certain asset-backed financing transactions. For these VIEs where the Company has determined that it is the primary beneficiary because it has the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIEs’ economic performance and the obligation to absorb the losses or the right to receive benefits from the VIEs that could potentially be significant to the VIEs the VIEs assets and related liabilities are consolidated with the results of the Company. Such power arises from the Company’s contractual right to service the loans receivable securing the VIEs’ asset-backed debt obligations. The Company has an obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits that are potentially significant to the VIEs because it retains the residual interest of each asset-backed financing transaction in the form of an asset-backed certificate. Accordingly, the Company includes the VIEs’ assets, including the assets securing the financing transactions, and related liabilities in its consolidated financial statements.
Each consolidated VIE issues a series of asset-backed securities that are supported by the cash flows arising from the loans receivable securing such debt. Cash inflows arising from such loans receivable are distributed monthly to the transaction’s lenders and related service providers in accordance with the transaction’s contractual priority of payments. The creditors of the VIEs above have no recourse to the general credit of the Company as the primary beneficiary of the VIEs and the liabilities of the VIEs can only be settled by the respective VIE’s assets. The Company retains the most subordinated economic interest in each financing transaction through its ownership of the respective residual interest in each VIE. The Company has no obligation to repurchase loans receivable that initially satisfied the financing transaction’s eligibility criteria but subsequently became delinquent or a defaulted loans receivable.
The following table represents the assets and liabilities of consolidated VIEs recorded on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Consolidated VIE assets | | | | |
| Restricted cash | | $ | 91,395 | | | $ | 41,803 | |
| Loans receivable at fair value | | 3,081,557 | | | 2,267,205 | |
| | | | |
| Interest and fee receivable | | 30,443 | | | 19,869 | |
| Total VIE assets | | 3,203,395 | | | 2,328,877 | |
| Consolidated VIE liabilities | | | | |
Secured financing (1) | | 320,000 | | | 398,000 | |
| Asset-backed notes at fair value | | 2,387,674 | | | 1,651,706 | |
Acquisition financing (1) | | 85,679 | | | 116,000 | |
| Total VIE liabilities | | $ | 2,793,353 | | | $ | 2,165,706 | |
(1) Amounts exclude deferred financing costs. See Note 9, Borrowings for additional information.
| | | | | |
| 5. | Loans Held for Sale and Loans Sold |
Structured Loan Sales - On March 31, 2022, the Company participated in a securitization whereby the Company and funds managed by Ellington Management Group both contributed collateral and were co-sponsors of the transaction, which totaled $400.0 million in issued asset-backed notes. As part of the securitization, the Company sold loans to OPTN Funding Grantor Trust 2022-1 through the issuance of amortizing asset-backed notes secured by a pool of its unsecured and secured personal installment loans. The Company also sold its share of the residual interest in the pool. The Company's continued involvement in the unconsolidated VIEs is in the form of servicer of these loans. The Company does not have variable interest in the Grantor Trust or the issuer established for this transaction. The sold loans were accounted for under the fair value option and had an aggregate unpaid principal balance of approximately $227.6 million, a cumulative fair value mark of $15.9 million and unpaid interest of $1.5 million. The Company received $245.0 million of net proceeds and by selling both its notes and residual interest, the Company derecognized these loans from its Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Other Loan Sales - The Company enters into agreements to sell certain populations of its personal loans and credit card receivables from time to time. The sold loans were accounted for under the fair value option. During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company sold loans that had an aggregate unpaid principal balance, including unpaid interest and fees, of approximately $66.2 million, and a cumulative fair value mark of $(61.9) million. The Company received $4.3 million of net proceeds. The loan sales qualified for sale accounting treatment and the Company derecognized these loans from its Consolidated Balance Sheets when the loans were sold.
Whole Loan Sale Program ‑ In November 2014, the Company entered into a whole loan sale agreement with an institutional investor. Pursuant to the agreement, the Company sold at least 10% of its unsecured loan originations, with an option to sell an additional 5%, subject to certain eligibility criteria and minimum and maximum volumes. The Company chose not to renew the arrangement and allowed the agreement to expire on its terms on March 4, 2022.
The originations of loans sold and held for sale during the year ended December 31, 2022 was $52.7 million and the Company recorded a gain on sale of $5.7 million and servicing revenue of $17.4 million. The originations of loans sold and held for sale during the year ended December 31, 2021 was $214.6 million and the Company recorded a gain on sale of $26.8 million and servicing revenue of $13.3 million.
On December 22, 2021, the Company completed its acquisition of Digit. Digit is a digital banking platform that provides automated savings, investing and banking tools. Digit members can keep and integrate their existing bank accounts into the platform, or they can make Digit their primary banking relationship by opening new accounts via Digit’s bank partner. By acquiring Digit, Oportun has further expanded its A.I. and digital banking capabilities, adding to its services to provide consumers a holistic offering built to address their financial needs.
The total consideration the Company provided for Digit was approximately $205.3 million, comprised of $73.2 million in equity and $132.1 million in cash, subject to customary adjustments. The Company acquired 100% of the voting interests of Digit.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2021 |
Fair value of Oportun common stock issued to Digit stockholders(1) | | $ | 73,181 | |
Cash paid to common and preferred stockholders, warrant holders, and vested option holders(2) | | 132,151 | |
Total purchase consideration (3) | | $ | 205,332 | |
(1) The fair value is based on 3,522,182 shares of Company common stock at $20.72 per share, which represents the mid-point of the trading price of Oportun shares on December 22, 2021. The mid-point was used because the transaction closed during the trading day. $0.2 million relates to replacement restricted stock units awarded to Digit unvested option holders.
(2) $1.3 million of the cash paid is being held in escrow as security for purpose of securing any amounts payable by the selling parties on account of indemnification obligations, purchase price adjustments, and other amounts payable under the merger agreement.
(3) The total consideration as reported herein differs from the amounts previously disclosed due to changes in the underlying value of the stock between the date of the definitive agreement and the closing of the acquisition. The number of shares of Company common stock comprising the stock portion of the consideration was determined using the stock price as of the signing of the definitive agreement.
The acquisition has been accounted for as a business combination. The purchase consideration was allocated to the tangible and intangible assets and liabilities acquired and assumed as of the acquisition date, with the excess recorded to goodwill as shown below.
The following table summarizes the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date:
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 22, |
| (in thousands) | | 2021 |
Goodwill | | $ | 104,014 | |
Acquired intangible assets | | 35,300 | |
| Developed technology | | 48,500 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 20,499 | |
| Other assets acquired and liabilities assumed, net | | (2,981) | |
Total purchase consideration | | $ | 205,332 | |
The goodwill of $104.0 million arising from the acquisition consists largely of revenue synergies expected from combining the operations of the Company and Digit. The goodwill is not deductible for U.S. federal income tax purposes. We recognized a $108.5 million non-cash impairment charge for the year ended December 31, 2022. For details regarding the impairment charge, refer to Note 7, Capitalized Software, Other Intangibles and Goodwill.
The table below summarizes the acquired intangible assets and developed technology, with estimated useful lives, as of the acquisition date:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Estimated fair values (in thousands) | | Estimated useful life (years) |
| Member relationships | | $ | 34,500 | | | 7.0 |
| Trade name | | 800 | | | 3.0 |
| Developed technology | | 48,500 | | | 7.0 |
| Total acquired intangibles and developed technology | | $ | 83,800 | | | |
The fair values of the acquired intangibles and developed technology were determined using the following methodologies: We valued the developed technology using the multi-period excess earnings method under the income approach. Member relationships were valued using the with-and-without method under the income approach. Trade names were valued by applying the relief-from-royalty method under the income approach. The acquired intangibles and developed technology have a total weighted average amortization period of 7.0 years.
The unaudited pro forma information does not necessarily reflect the actual results of operations of the combined entities that would have been achieved, nor are they necessarily indicative of future results of operations. The unaudited pro forma information reflects certain adjustments that were directly attributable to the acquisition of Digit, including additional depreciation and amortization adjustments for the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The pro forma net loss for the year ended December 31, 2021 was adjusted to exclude nonrecurring acquisition-related costs of $29.7 million.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2021 |
Total revenues | | $ | 666,158 | |
Net income (loss) attributable to shareholders | | $ | 33,971 | |
The Company recognized acquisition and integration related costs of approximately $29.7 million and $10.6 million in the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively, which are included in the General, administrative and other expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
| | | | | |
7. | Capitalized Software, Other Intangibles and Goodwill |
Capitalized software, net consists of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Capitalized software, net: | | | | |
| System development costs | | $ | 135,303 | | | $ | 84,550 | |
| Acquired developed technology | | 48,500 | | | 48,500 | |
| Less: Accumulated amortization | | (79,679) | | | (45,433) | |
| Total capitalized software, net | | $ | 104,124 | | | $ | 87,617 | |
Capitalized software, net
Amortization of system development costs and acquired developed technology for years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 was $34.2 million and $16.9 million, respectively. System development costs capitalized in the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 were $51.5 million and $77.1 million, respectively.
Acquired developed technology was $48.5 million and is related to the acquisition of Digit.
Intangible Assets
The gross carrying amount and accumulated amortization, in total and by major intangible asset class are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | | | | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | | | 2021 |
| Intangible assets: | | | | | | |
| Member relationships | | 34,500 | | | | | $ | 34,500 | |
| Trademarks | | 6,426 | | | | | 6,364 | |
| Other | | 3,000 | | | | | 3,000 | |
Less: Accumulated amortization
| | (8,249) | | | | | $ | (300) | |
Total intangible assets, net
| | 35,677 | | | | | $ | 43,564 | |
Amortization of intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 was $7.9 million and $0.3 million.
Expected future amortization expense for intangible assets as of December 31, 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | | Fiscal Years |
2023 | | $ | 7,948 | |
2024 | | 7,798 | |
| 2025 | | 4,929 | |
| 2026 | | 4,929 | |
| 2027 | | 4,929 | |
| Thereafter | | 4,780 | |
Total | | $ | 35,313 | |
Goodwill
The Company recorded goodwill of $104.0 million arising from the acquisition of Digit on December 22, 2021. The Company recorded increases to goodwill of $4.5 million, during the twelve months ended December 31, 2022, as part of the twelve-month measurement period. These increases were primarily due to changes in deferred taxes resulting from the filing of Digit's pre-acquisition tax returns.
Goodwill represents the difference between the purchase price and the estimated fair value of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The Company performs impairment tests related to its goodwill on an annual basis or when certain triggering events or circumstances are identified that would more likely than not reduce the estimated fair value of the goodwill below its carrying amount.
In response to a sustained decline in the Company’s share price primarily driven by macroeconomic conditions, the Company conducted a quantitative test of its goodwill as of September 30, 2022. The Company considered the income approach, the guideline public company multiples approach and the market approach in determining a fair value for the Company which was determined to be the only reporting unit for purposes of testing the goodwill. Given the uncertain macroeconomic environment there was a wide range of indications of fair value across the approaches.
Although the corresponding value was the lowest in the range, the Company utilized the market approach because it was based on market observable inputs. The market approach estimates fair value using the market capitalization of the Company as a basis.
As of September 30, 2022, the market capitalization plus the estimated control premium was less than the carrying value of the Company. As a result, the Company recognized a non-cash pre-tax impairment charge of $108.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2022 to write down the carrying value of goodwill. The non-cash impairment charge is included in Goodwill impairment in the Consolidated Statements of Operations for the year ended December 31, 2022. There were no goodwill impairment charges during the year ended December 31, 2021.
The following table represents the changes in goodwill since December 31, 2021:
| | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | | Goodwill |
| Balance as of December 31, 2021 | | $ | 104,014 | |
Measurement adjustments during period | | 4,458 | |
| Impairment | | (108,472) | |
Balance as of December 31, 2022 | | $ | — | |
Other assets consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Fixed assets | | | | |
| Total fixed assets | | $ | 48,212 | | | $ | 44,100 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | | (37,688) | | | (34,185) | |
| Total fixed assets, net | | $ | 10,524 | | | $ | 9,915 | |
| | | | |
| Other assets | | | | |
| | | | |
| Loans held for sale | | $ | 50 | | | $ | 491 | |
| Prepaid expenses | | 24,167 | | | 25,355 | |
| Deferred tax assets | | 1,793 | | | 3,923 | |
| Current tax assets | | 8,245 | | | 13,330 | |
| Other | | 19,401 | | | 19,330 | |
| Total other assets | | $ | 64,180 | | | $ | 72,344 | |
Fixed Assets
Depreciation and amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 was $5.2 million and $9.4 million, respectively.
The following table presents information regarding the Company's Secured Financing facilities:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | December 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| Variable Interest Entity | | Facility Amount | | Maturity Date | | Interest Rate | | Balance | | Balance |
| (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | |
Oportun CCW Trust (1) | | $ | 150,000 | | | December 1, 2023 | | Variable (1) | | $ | 76,574 | | | $ | 40,108 | |
| Oportun PLW Trust | | 600,000 | | | September 1, 2024 | | LIBOR (minimum of 0.00%) + 2.17% | | 240,994 | | | 353,781 | |
| Total secured financing | | $ | 750,000 | | | | | | | $ | 317,568 | | | $ | 393,889 | |
(1) The interest rate on the Secured Financing - CCW facility is LIBOR (minimum of 1.00%) plus 6.00% on the first $18.8 million of principal outstanding and LIBOR (minimum of 0.00%) plus 3.41% on the remaining outstanding principal balance.
The following table presents information regarding asset-backed notes:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2022 |
| Variable Interest Entity | | Initial note amount issued (1) | | Initial collateral balance (2) | | Current balance (1) | | Current collateral balance (2) | | Weighted average interest rate (3) | | Original revolving period (4) |
| (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Asset-backed notes recorded at fair value: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oportun Issuance Trust (Series 2022-3) | | $ | 300,000 | | | $ | 310,993 | | | $ | 285,218 | | | $ | 301,967 | | | 8.43 | % | | N/A |
| Oportun Issuance Trust (Series 2022-2) | | 400,000 | | | 410,212 | | | 313,689 | | | 344,218 | | | 7.03 | % | | N/A |
| Oportun Issuance Trust (Series 2022-A) | | 400,000 | | | 410,211 | | | 380,313 | | | 414,293 | | | 5.44 | % | | 2 years |
| Oportun Issuance Trust (Series 2021-C) | | 500,000 | | | 512,762 | | | 435,951 | | | 518,929 | | | 2.48 | % | | 3 years |
| Oportun Issuance Trust (Series 2021-B) | | 500,000 | | | 512,759 | | | 432,123 | | | 519,182 | | | 2.05 | % | | 3 years |
| Oportun Funding XIV, LLC (Series 2021-A) | | 375,000 | | | 383,632 | | | 348,046 | | | 389,740 | | | 1.79 | % | | 2 years |
| Oportun Funding XIII, LLC (Series 2019-A) | | 279,412 | | | 294,118 | | | 192,334 | | | 218,571 | | | 3.46 | % | | 3 years |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total asset-backed notes recorded at fair value | | $ | 2,754,412 | | | $ | 2,834,687 | | | $ | 2,387,674 | | | $ | 2,706,900 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2021 |
| Variable Interest Entity | | Initial note amount issued (1) | | Initial collateral balance (2) | | Current balance (1) | | Current collateral balance (2) | | Weighted average interest rate(3) | | Original revolving period (4) |
| (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Asset-backed notes recorded at fair value: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oportun Issuance Trust (Series 2021-C) | | $ | 500,000 | | | $ | 512,762 | | | $ | 497,774 | | | $ | 525,436 | | | 2.48 | % | | 3 years |
| Oportun Issuance Trust (Series 2021-B) | | 500,000 | | | 512,759 | | | 498,487 | | | 521,174 | | | 2.05 | % | | 3 years |
| Oportun Funding XIV, LLC (Series 2021-A) | | 375,000 | | | 383,632 | | | 374,363 | | | 391,325 | | | 1.79 | % | | 2 years |
| Oportun Funding XIII, LLC (Series 2019-A) | | 279,412 | | | 294,118 | | | 281,082 | | | 299,310 | | | 3.46 | % | | 3 years |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total asset-backed notes recorded at fair value: | | $ | 1,654,412 | | | $ | 1,703,271 | | | $ | 1,651,706 | | | $ | 1,737,245 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
(1) Initial note amount issued includes notes retained by the Company as applicable. The current balances are measured at fair value for asset-backed notes recorded at fair value.
(2) Includes the unpaid principal balance of loans receivable, the balance of required reserve funds, cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash pledged by the Company.
(3) Weighted average interest rate excludes notes retained by the Company. There were no notes retained by the Company as of December 31, 2022. The weighted average interest rate for Series 2022-2 and Series 2022-3 will change over time as the notes pay sequentially (in class priority order).
(4) The revolving period for Series 2019-A ended on August 1, 2022 and the asset-backed notes have been amortizing since then. Series 2022-2 and Series 2022-3 are both amortizing deals with no revolving period.
The following table presents information regarding the Company's Acquisition and Corporate Financings:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | December 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| Entity | | | | Original Balance (1) | | Maturity Date (2) | | Interest Rate (3) | | Balance | | Balance |
| (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oportun Financial Corporation | | | | $ | 150,000 | | | September 14, 2026 | | SOFR (minimum of 0.00% + 9.00% | | $ | 141,957 | | | $ | — | |
| Oportun RF, LLC | | | | 116,000 | | | May 1, 2024 | | SOFR (minimum of 0.00%) + 8.00% | | 80,922 | | 114,092 |
| Total acquisition and corporate financing | | | | $ | 266,000 | | | | | | | $ | 222,879 | | | $ | 114,092 | |
(1) The Acquisition Financing Facility (Oportun RF, LLC) was amended on May 24, 2022 and upsized for an additional $20.9 million and was amended again on July 28, 2022 and upsized for an additional $9.1 million.
(2) Pursuant to an amendment on November 2, 2022, the maturity date of the Acquisition Financing Facility (Oportun RF, LLC) was changed from October 2024 to June 2024. The Acquisition Financing Facility was further amended on December 2, 2022 to change the maturity date to May 2024.
(3) The interest rate on the Acquisition Financing Facility (Oportun RF, LLC) was LIBOR (minimum of 0.00%) plus 8.00% as of December 31, 2021.
On May 24, 2022 the Company completed the issuance of $400.0 million of two-year asset-backed notes in a private asset-backed securitization secured by a pool of its unsecured and secured personal installment loans (the “2022-A Securitization”). The 2022-A Securitization included four classes of fixed rate notes: Class A, Class B, Class C and Class D notes. The Class A, Class B and Class C notes were priced with a weighted average yield of 5.68% per annum. The Class D notes were initially retained by an affiliate of the Company and subsequently sold to third parties on July 28, 2022.
Also on May 24, 2022, and subsequently on July 28, 2022, pursuant to amended indentures, Oportun RF, LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company issued an additional $20.9 million and $9.1 million asset-backed floating rate variable funding notes, and asset-backed residual certificates, both of which are secured by certain cash flows from the Company's securitizations and guaranteed by Oportun, Inc., increasing the size of the Acquisition Financing facility to $119.5 million The amendments also replaced the interest rate based on LIBOR with an interest rate based on SOFR plus 8.00%. The Acquisition Financing facility was scheduled to pay down based on an amortization schedule with a final payment in May 2024. Subsequently, on February 10, 2023, the Acquisition Financing facility was further amended, including among other things, revising the interest rate to SOFR plus 11.00% and adjusting the amortization schedule to defer $42.0 million in principal payments through July 2023, with final payment in October 2024.
On July 22, 2022 the Company completed the issuance of $400.0 million of Series 2022-2 fixed rate asset-backed notes in a private asset-backed securitization transaction secured by a pool of unsecured and secured installment loans. The notes were priced with a weighted average yield of 8.00% per annum and weighted average interest rate over the term of the transaction of 7.77% per annum.
On September 14, 2022, the Company entered into a credit agreement to borrow $150.0 million of a senior secured term loan (the “Corporate Financing”). The term loan bears interest, payable in cash, at an amount equal to 1-month term SOFR plus 9.00%. The term loan is scheduled to mature on September 14, 2026, and is not subject to amortization. Certain prepayments of the term loan is subject to a prepayment premium. The obligations under the credit agreement are secured by the assets of the Company and certain of its subsidiaries guaranteeing the term loan, including pledges of the equity interests of certain subsidiaries that are directly or indirectly owned by the Company, subject to customary exceptions. On March 10, 2023 we upsized and amended our Corporate Financing facility to be able to borrow up to an additional $75 million. At closing and as part of the Incremental Tranche A-1, we borrowed $20.8 million and will receive an additional $4.2 million in Incremental Tranche A-2 loans on or about March 27, 2023. We may borrow up to an aggregate additional amount of $50.0 million on an uncommitted basis, in two $25.0 million tranches, expected to be available, if provided by the applicable lenders, on or about April 21, 2023 and June 23, 2023, respectively. The term loan now bears interest at an amount payable in cash equal to 1-month term SOFR plus 9.00% plus an amount payable in cash or in kind, at the Company’s option, equal to 3.00%.
On November 3, 2022, the Company completed the issuance of $300 million of Series 2022-3 fixed rate asset-backed notes in a private asset-backed securitization transaction secured by a pool of unsecured and secured installment loans. The notes were priced with a weighted average yield of 10.94% per annum and weighted average interest rate of 9.51% per annum.
On March 8, 2023, the Credit Card Warehouse was amended. This amendment, among other things, extends the revolving period by a year, to December 31, 2024, and reduces the commitment from $150.0 million to $120.0 million.
As of December 31, 2022 and 2021, the Company was in compliance with all covenants and requirements of the Secured Financing, Acquisition Financing and Corporate Financing facilities and asset-backed notes.
Other liabilities consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Accounts payable | | $ | 9,670 | | | $ | 8,343 | |
| Accrued compensation | | 12,502 | | | 36,417 | |
| Accrued expenses | | 26,193 | | | 36,464 | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Accrued interest | | 8,445 | | | 3,276 | |
| Amount due to whole loan buyer | | 3,073 | | | 14,062 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | 30,575 | | | 28,424 | |
| Current tax liabilities and other | | 9,570 | | | 8,372 | |
| Total other liabilities | | $ | 100,028 | | | $ | 135,358 | |
Preferred Stock - The Board has the authority, without further action by the Company's stockholders, to issue up to 100,000,000 shares of undesignated preferred stock with rights and preferences, including voting rights, designated from time to time by the Board. There were no shares of undesignated preferred stock issued or outstanding as of December 31, 2022 or 2021.
Common Stock - As of December 31, 2022 and 2021, the Company was authorized to issue 1,000,000,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. As of December 31, 2022, 33,626,630 and 33,354,607 shares were issued and outstanding, respectively, and 272,023 shares were held in treasury stock. As of December 31, 2021, 32,276,419 and 32,004,396 shares were issued and outstanding, respectively, and 272,023 shares were held in treasury stock.
| | | | | |
| 12. | Equity Compensation and Other Benefits |
2019 Equity Incentive Plan
We currently have one stockholder-approved plan from which we can issue stock-based awards, which was approved by our stockholders in fiscal year 2019 (the "2019 Plan"). The 2019 Plan became effective on September 25, 2019 and replaced the Amended and Restated 2005 Stock Option / Stock Issuance Plan and the 2015 Stock Option/Stock Issuance Plan (collectively, the “Previous Plans”). The Previous Plans solely exist to satisfy outstanding options previously granted under those plans. The 2019 Plan provides for the grant of incentive stock options ("ISOs"), nonstatutory stock options ("NSOs"), stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, restricted stock unit awards, performance-based awards, and other awards (collectively, "awards"). ISOs may be granted only to the Company's employees, including officers, and the employees of its affiliates. All other awards may be granted to the employees, including officers, non-employee directors and consultants and the employees and consultants of the Company's affiliates. The maximum number of shares of our common stock that may be issued under the 2019 Plan will not exceed 9,072,159 shares, of which, 1,802,994 were available for future awards as of December 31, 2022. The number of shares of the Company's common stock reserved for issuance under its 2019 Plan will automatically increase on January 1 of each year for the remaining term of the plan, by 5% of the total number of shares of its common stock outstanding on December 31 of the immediately preceding calendar year, or a lesser number of shares determined by the Board prior to the applicable January 1st. The shares available for issuance increased by 1,600,219 shares, on January 1, 2022, pursuant to the automatic share reserve increase provision.
2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan
In September 2019, the Board adopted, and stockholders approved, the Company's 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the "ESPP"). The ESPP became effective on September 25, 2019. The purpose of the ESPP is to secure the services of new employees, to retain the services of existing employees and to provide incentives for such individuals to exert maximum efforts toward the Company's success and that of its affiliates. The ESPP includes two components. One component is designed to allow eligible U.S. employees to purchase common stock in a manner that may qualify for favorable tax treatment under Section 423 of the Code. In addition, purchase rights may be granted under a component that does not qualify for such favorable tax treatment when necessary or appropriate to permit participation by eligible employees who are foreign nationals or employed outside of the United States while complying with applicable foreign laws. The maximum aggregate number of shares of common stock that may be issued under the ESPP is 1,593,052 shares and as of December 31, 2022, no shares have been issued under the ESPP. The number of shares of the Company's common stock reserved for issuance under its ESPP will automatically increase on January 1 of each calendar year for the remaining term of the plan by the lesser of (1) 1% of the total number of shares of its capital stock outstanding on December 31 of the preceding calendar year, (2) 726,186 shares, and (3) a number of shares determined by the Board. The shares available for issuance increased by 320,043 shares, on January 1, 2022, pursuant to the automatic share reserve increase provision.
Generally, all regular employees, including executive officers, employed by the Company or by any of its designated affiliates, will be eligible to participate in the ESPP and may contribute, normally through payroll deductions, up to 15% of their earnings (as defined in the ESPP) for the purchase of common stock under the ESPP. Unless otherwise determined by the Board, common stock will be purchased for the accounts of
employees participating in the ESPP at a price per share equal to the lower of (a) 85% of the fair market value of a share of the Company's common stock on the first date of an offering or (b) 85% of the fair market value of a share of the common stock on the date of purchase.
2021 Inducement Equity Incentive Plan
Effective December 30, 2021, the Company adopted the 2021 Inducement Equity Incentive Plan (the “2021 Inducement Plan”), pursuant to which the Company reserved 563,955 shares of its common stock to be used exclusively for grants of awards to individuals who were not previously employees or directors of the Company, as an inducement material to the individual’s entry into employment with the Company within the meaning of Rule 5635(c)(4) of the Nasdaq Listing Rules. The maximum number of shares of our common stock that may be issued under the 2021 Inducement Plan will not exceed 563,955 shares, of which, 39,635 were available for future awards as of December 31, 2022. The 2021 Inducement Plan was approved by the Company’s Board without stockholder approval in accordance with such rule.
Stock Options
The term of an option may not exceed 10 years as determined by the Board, and each option generally vests over a four-year period with 25% vesting on the first anniversary date of the grant and 1/36th of the remaining amount vesting at monthly intervals thereafter. Option holders are allowed to exercise unvested options to acquire restricted shares. Upon termination of employment, option holders have a period of up to three months in which to exercise any remaining vested options. The Company has the right to repurchase at the original purchase price any unvested but issued common shares upon termination of service. Unexercised options granted to participants who separate from the Company are forfeited and returned to the pool of stock options available for grant.
The Company estimates the fair value of stock options granted using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The fair value is then amortized ratably over the requisite service periods of the awards, which is generally the vesting period.
The fair value of stock option grants was estimated with the following assumptions:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Expected volatility (employee) | | 63.4% | | 62.5% | | |
| Risk-free interest rate (employee) | | 2.3% | | 0.9% | | |
| Expected term (employee, in years) | | 6.1 | | 6.1 | | |
| Expected dividend | | —% | | —% | | |
These assumptions are defined as follows:
•Expected Volatility ‑ Since the Company does not have enough trading history to use the volatility of its own common stock, the option’s expected volatility is estimated based on historical volatility of a peer group’s common stock.
•Risk-Free Interest Rate‑ The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury zero-coupon issues in effect at the time of grant for periods corresponding with the expected term of the option.
•Expected Term ‑ The option’s expected term represents the period that the Company’s stock-based awards are expected to be outstanding.
•Expected Dividend - The Company has no plans to pay dividends.
Stock Option Activity - A summary of the Company's stock option activity under the 2005 Plan, 2015 Plan, and 2019 Plan at December 31, 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | | Options Outstanding | | Options Weighted-Average Exercise Price | | Weighted Average Remaining Life
(in years) | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
| Balance – January 1, 2022 | | 4,187,855 | | | 14.63 | | | 4.59 | | $ | 27,011 | |
| Options granted | | 541,713 | | | 13.02 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Options exercised | | (1,005,738) | | | 1.58 | | | | | |
| Options canceled | | (331,273) | | | 20.25 | | | | | |
| Options forfeited | | (94,019) | | | 17.24 | | | | | |
| Balance – December 31, 2022 | | 3,298,538 | | | 17.71 | | | 5.43 | | $ | 202 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Options vested and expected to vest - December 31, 2022 | | 3,298,538 | | | 17.71 | | | 5.43 | | $ | 202 | |
| Options vested and exercisable - December 31, 2022 | | 2,482,741 | | | 18.39 | | | 4.55 | | $ | 202 | |
Information on stock options granted, exercised and vested is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands, except per share data) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Weighted average fair value per share of options granted | | $ | 7.76 | | | $ | 12.11 | | | |
| | | | | | |
Cash received from options exercised, net (1) | | (4,636) | | | 3,272 | | | |
| Aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised | | 11,884 | | | 2,380 | | | |
| Fair value of shares vested | | 3,863 | | | 4,974 | | | |
(1) The amount reflected for the year ended December 31, 2022 is the net of cash received from options exercised of $1.6 million and the cash paid for employee tax withholding settled in shares of $6.2 million.
As of December 31, 2022 and 2021, the Company’s total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested stock-based option awards granted to employees was, $6.2 million and $6.9 million, respectively, which will be recognized over a weighted-average vesting period of approximately 2.6 years and 2.2 years, respectively.
Restricted Stock Units
The Company’s restricted stock units ("RSUs") vest upon the satisfaction of time-based criterion of up to four years. In most cases, the service-based requirement will be satisfied in installments as follows: 25% of the total number of RSUs awarded will have the service-based requirement satisfied during the month in which the 12-month anniversary of the vesting commencement date occurs, and thereafter 1/16th of the total award in a series of 12 successive equal quarterly installments or 1/4th of the total award in a series of three successive equal annual installments following the first anniversary of the initial service vest date.
Stock-based compensation cost for RSUs is measured based on the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant.
As part of the Digit acquisition in 2021, 501,906 shares of the Company’s restricted stock units were issued to certain Digit employees to replace the outstanding unvested stock options that were previously issued to the employees of Digit. The RSUs are subject to the same service-based requirements as the historical stock option grants. The Company awarded an additional 650,460 RSUs to certain Digit employees that vest upon satisfaction of time-based criterion of up to four years. For grants with a one-year vesting term, 50% will vest on the six-month anniversary of the vesting commencement date with the balance vesting in two successive equal quarterly installments thereafter. For grants with a two-year vesting term, 25% will vest on the six-month anniversary of the vesting commencement date with the balance vesting in six equal quarterly installments thereafter or 50% will vest on the twelve-month anniversary of the vesting commencement date with the balance vesting in four successive equal quarterly installments thereafter. For grants with a three-year vesting term, 16.667% will vest on the six-month anniversary of the vesting commencement date, with the balance vesting in ten successive equal quarterly installments thereafter. For grants with four-year vesting term, 12.5% will vest on the six-month anniversary of the vesting commencement date, with the balance vesting in 14 successive equal quarterly installments thereafter.
A summary of the Company’s RSU activity under the 2015 Plan, 2019 Plan and 2021 Inducement Plan for the year ended December 31, 2022 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | RSU Outstanding | | Weighted Average Grant-Date Fair Value |
| Balance – January 1, 2022 | | 3,354,333 | | | 19.48 | |
| Granted | | 3,091,511 | | | 11.48 | |
Vested (1) | | (1,224,579) | | | 19.52 | |
| Forfeited | | (726,318) | | | 16.95 | |
Balance – December 31, 2022 | | 4,494,947 | | | 14.37 | |
Expected to vest after December 31, 2022 | | 4,420,579 | | | 14.45 | |
(1) The Company allows its Board to defer all or a portion of monetary remuneration paid to the Director. As of December 31, 2022, there were 74,368 restricted stock units vested for which the holders elected to defer delivery of the Company's shares.
As of December 31, 2022 and 2021, the Company's total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested restricted stock unit awards granted to employees was, $51.6 million and $54.1 million, respectively, which will be recognized over a weighted average vesting period of approximately 2.7 years and 2.6 years, respectively.
Stock-based Compensation - Total stock-based compensation expense included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations, net of amounts capitalized to system development costs is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Technology and facilities | | $ | 6,993 | | | $ | 2,844 | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | 143 | | | 125 | | | |
| Personnel | | 20,484 | | | 15,888 | | | |
Total stock-based compensation (1) | | $ | 27,620 | | | $ | 18,857 | | | |
(1) Amounts shown are net of $2.5 million and $1.0 million of capitalized stock-based compensation for the year ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Cash flows from the tax shortfalls or benefits for tax deductions resulting from the exercise of stock options in comparison to the compensation expense recorded for those options are required to be classified as cash from financing activities. The Company recognized $8.1 million and $5.4 million of income tax benefit in its consolidated statement of operations related to stock-based compensation expense during the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Additionally, the total income tax expense (benefit) recognized in the income statement for share-based compensation exercises was $3.3 million and $(0.2) million for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Retirement Plan
The Company maintains a 401(k) Plan, which enables employees to make pre-tax or post-tax deferral contributions to the participating employees account. Employees may contribute a portion of their pay up to the annual amount as set periodically by the Internal Revenue Service. The Company provides for an employer 401(k) contribution match of up to 4% of an employee’s eligible compensation. The total amount contributed by the Company for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 was $6.4 million and $3.7 million, respectively. All employee and employer contributions will be invested according to participants’ individual elections.
Interest Income - Total interest income included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Interest income | | | | | | |
| Interest on loans | | $ | 854,245 | | | $ | 566,155 | | | |
| Fees on loans | | 21,869 | | | 9,684 | | | |
| Total interest income | | $ | 876,114 | | | $ | 575,839 | | | |
Non-interest Income - Total non-interest income included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Non-interest income | | | | | | |
| Gain on loan sales | | $ | 5,703 | | | $ | 26,750 | | | |
| Servicing fees | | 19,928 | | | 13,253 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Subscription revenue | | 31,186 | | | 813 | | | |
| Other income | | 19,614 | | | 10,127 | | | |
| Total non-interest income | | $ | 76,431 | | | $ | 50,943 | | | |
The following are the domestic and foreign components of the Company’s income before taxes:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Domestic | | $ | (83,793) | | | $ | 61,087 | | | |
| Foreign | | 8,507 | | | 1,704 | | | |
| Income (loss) before taxes | | $ | (75,286) | | | $ | 62,791 | | | |
The provision for income taxes consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Current | | | | | | |
| Federal | | $ | (1,217) | | | $ | (1,394) | | | |
| State | | $ | 1,505 | | | $ | (516) | | | |
| Foreign | | $ | 2,227 | | | $ | 836 | | | |
| Total current | | $ | 2,515 | | | $ | (1,074) | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Deferred | | | | | | |
| Federal | | (712) | | | 11,005 | | | |
| State | | 806 | | | 5,372 | | | |
| Foreign | | (151) | | | 74 | | | |
| Total deferred | | $ | (57) | | | $ | 16,451 | | | |
| Total provision for income taxes | | $ | 2,458 | | | $ | 15,377 | | | |
Income tax expense was $2.5 million and $15.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, which represents an effective tax rate of (3.3)% and 24.5%, respectively.
A reconciliation of income tax expense with the amount computed by applying the statutory U.S. federal income tax rates to income before provision for income taxes is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense computed at U.S. federal statutory rate | | $ | (15,810) | | | $ | 13,186 | | | |
| State tax | | 1,403 | | | 4,646 | | | |
| Foreign rate differential | | 289 | | | 552 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Federal tax credits | | (2,621) | | | (1,962) | | | |
| Share based compensation expense | | 506 | | | (353) | | | |
| Change in unrecognized tax benefit reserves | | 1,326 | | | 853 | | | |
| Net operating loss carryback tax rate differential | | — | | | (172) | | | |
| Return to provision adjustment | | (5,798) | | | (2,812) | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Non-deductible acquisition costs | | — | | | 1,458 | | | |
| Goodwill impairment | | 22,779 | | | — | | | |
| Fines and penalties | | 578 | | | 6 | | | |
| Other | | (194) | | | (25) | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Income tax expense | | $ | 2,458 | | | $ | 15,377 | | | |
| Effective tax rate | | (3.3) | % | | 24.5 | % | | |
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes, and operating losses and tax credit carryforwards.
The primary components of the Company’s net deferred tax assets and liabilities are composed of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | |
| Accrued expenses and reserves | | $ | 3,361 | | | $ | 3,356 | |
| | | | |
| Leases | | 10,174 | | | 12,859 | |
| Share-based compensation | | 8,335 | | | 7,410 | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| CARES Act payroll taxes | | — | | | 536 | |
| Net operating loss & credit carryforward | | 41,169 | | | 23,916 | |
| Other | | 245 | | | — | |
| Total deferred tax assets | | $ | 63,284 | | | $ | 48,077 | |
| Valuation allowance | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | |
| System development costs | | $ | (11,803) | | | $ | (22,323) | |
| Right of use assets | | (8,163) | | | (10,353) | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | (6,813) | | | (7,112) | |
| | | | |
| Fair value adjustment - Loans Receivable | | (12,077) | | | (30,718) | |
| Fair value adjustment - Bonds Payable | | (53,210) | | | (1,838) | |
| Other | | — | | | (234) | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | | (92,066) | | | (72,578) | |
| Net deferred taxes | | $ | (28,782) | | | $ | (24,501) | |
As provided for in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, our historical earnings were subject to the one-time transition tax and can now be repatriated to the U.S. with a de minimis tax cost due to the participation exemption put in place by the 2017 Tax Act. The Company continues to assert that both its historical and current earnings in its foreign subsidiaries are permanently reinvested and therefore no deferred taxes have been provided.
On December 22, 2021, the Company completed the acquisition of Digit, in which Digit became a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, triggering an ownership change under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended. This transaction was considered a stock acquisition for tax purposes. The tax attributes acquired were updated during the year due to the twelve-month measurement period. Digit has a $53.3 million federal net operating loss carryforward, all of which is available to offset future taxable income during the carryforward periods based on limitations under IRC Section 382. The Company also acquired state NOLs of $27.4 million. The Company has not recorded a valuation allowance on the federal or state net operating loss balances as it believes that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized.
As of December 31, 2022, the Company had federal net operating loss carryforwards of $135.2 million, of which $17.7 million expires beginning in 2033 and $117.5 million carries forward indefinitely. Additionally, the Company had state net operating loss carryforwards of $119.1 million which are set to begin expiring in 2031. As of December 31, 2022, the Company had federal and California research and development tax credit carryforwards of $5.2 million and $5.0 million, respectively. The federal research and development tax credit expires beginning in 2041, and the California research and development tax credits are not subject to expiration.
The following table summarizes the activity related to the unrecognized tax benefits:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Balance as of January 1, | | $ | 5,170 | | | $ | 3,927 | | | |
| Increases related to current year tax positions | | 894 | | | 680 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Increases related to prior year tax positions | | 544 | | | 638 | | | |
| Decreases related to prior year tax positions | | — | | | (75) | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, | | $ | 6,608 | | | $ | 5,170 | | | |
Interest and penalties related to the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits accrued as of December 31, 2022 and 2021 were $0.9 million and $0.4 million, respectively. The Company’s policy is to recognize interest and penalties associated with income taxes in income tax expense. The Company does not expect to release any of the uncertain tax positions within the next twelve months. The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits that would impact the effective tax rate, if recognized, is $4.5 million.
Due to the net operating loss carryforwards, the Company’s United States federal and significant state returns are open to examination by the Internal Revenue Service and state jurisdictions for years ended December 31, 2012 and 2013, respectively, and forward. For Mexico, all tax years ended December 31, 2017 and forward remain open for examination by the Mexico taxing authorities. For India, all tax years remain open for examination by the India taxing authorities.
| | | | | |
| 15. | Fair Value of Financial Instruments |
Financial Instruments at Fair Value
The Company elected the fair value option for all loans receivable held for investment and for all asset-backed notes. Loans that the Company designates for sale will continue to be accounted for as held for sale and recorded at the lower of cost or fair value until the loans receivable are sold.
The table below compares the fair value of loans receivable and asset-backed notes to their contractual balances as of the dates shown:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| (in thousands) | | Unpaid Principal Balance | | Fair Value | | Unpaid Principal Balance | | Fair Value |
| Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Loans receivable - personal loans | | $ | 2,967,266 | | | $ | 3,027,401 | | | $ | 2,205,537 | | | $ | 2,321,150 | |
| Loans receivable - credit cards | | 131,343 | | | 116,252 | | | 67,327 | | | 65,657 | |
| Total loans receivable | | $ | 3,098,609 | | | $ | 3,143,653 | | | $ | 2,272,864 | | | $ | 2,386,807 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Asset-backed notes | | $ | 2,582,025 | | | $ | 2,387,674 | | | $ | 1,654,412 | | | $ | 1,651,706 | |
The Company calculates the fair value of the asset-backed notes using independent pricing services and broker price indications, which are based on quoted prices for identical or similar notes, which are Level 2 input measures.
The Company primarily uses a discounted cash flow model to estimate the fair value of Level 3 instruments based on the present value of estimated future cash flows. This model uses inputs that are inherently judgmental and reflect management’s best estimates of the assumptions a market participant would use to calculate fair value. The following tables present quantitative information about the significant unobservable inputs used for the Company’s Level 3 fair value measurements for Loans Receivable at Fair Value. The personal loan receivables balance at fair value as of 12/31/2022, consists of $2,903.2 million of unsecured personal loan receivables and $124.2 million of secured personal loan receivables.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 (3) |
| Personal Loan Receivables | | Minimum | | Maximum | | Weighted Average (2) | | Minimum | | Maximum | | Weighted Average (2) |
Remaining cumulative charge-offs (1) | | 5.06% | | 51.45% | | 9.86% | | 6.75% | | 51.86% | | 9.53% |
Remaining cumulative prepayments (1) | | —% | | 33.59% | | 28.73% | | —% | | 44.25% | | 32.47% |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Average life (years) | | 0.05 | | 1.52 | | 1.01 | | 0.22 | | 1.51 | | 0.87 |
| Discount rate | | 11.34% | | 11.34% | | 11.34% | | 6.90% | | 6.90% | | 6.90% |
(1) Figure disclosed as a percentage of outstanding principal balance.
(2) Unobservable inputs were weighted by outstanding principal balance, which are grouped by risk (type of borrower, original loan maturity terms).
(3) The weighted average amounts disclosed for remaining cumulative charge-offs, average life and discount rate and the minimum and maximum discount rate as of December 31, 2021 differ from what was previously disclosed for comparability to amounts disclosed as of December 31, 2022. The amounts disclosed previously as of December 31, 2021 included aggregated inputs for both personal loan receivables and credit card receivables. This disclosure has been disaggregated as of December 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | December 31, 2022 | | | | | | December 31, 2021 |
| Credit Card Receivables | | | | | | Range | | | | | | Range |
Remaining cumulative charge-offs (1) | | | | | | 22.80% | | | | | | 11.81% |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Principal payment rate (1) | | | | | | 9.28% | | | | | | 18.07% |
| Average life (years) | | | | | | 0.69 | | | | | | 0.34 |
| Discount rate | | | | | | 14.84% | | | | | | 8.35% |
(1) Figure disclosed as a percentage of outstanding principal balance.
Fair value adjustments related to financial instruments where the fair value option has been elected are recorded through earnings for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021. Certain unobservable inputs may (in isolation) have either a directionally consistent or opposite impact on the fair value of the financial instrument for a given change in that input. When multiple inputs are used within the valuation techniques for loans, a change in one input in a certain direction may be offset by an opposite change from another input.
For personal loan receivables, the Company developed an internal model to estimate the fair value of loans receivable held for investment. To generate future expected cash flows, the model combines receivable characteristics with assumptions about borrower behavior based on the
Company’s historical loan performance. These cash flows are then discounted using a required rate of return that management estimates would be used by a market participant.
The Company tested the unsecured personal loan fair value model by comparing modeled cash flows to historical loan performance to ensure that the model was complete, accurate and reasonable for the Company’s use. The Company also engaged a third party to create an independent fair value estimate for the Loans Receivable at Fair Value, which provides a set of fair value marks using the Company’s historical loan performance data and whole loan sale prices to develop independent forecasts of borrower behavior.
For credit card receivables, the Company uses historical data to derive assumptions about certain loan portfolio characteristics such as principal payment rates, interest yields and fee yields. Similar to the model used for personal loan receivables, the Company engaged a third party to create an independent fair value estimate, which provides a range of fair values that are compared for reasonableness.
The table below presents a reconciliation of Loans Receivable at Fair Value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Balance – beginning of period | | $ | 2,386,807 | | | $ | 1,696,526 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Principal disbursements | | 3,111,276 | | | 2,052,280 | | | |
| Principal payments from borrowers | | (1,974,832) | | | (1,276,058) | | | |
| Gross charge-offs | | (310,701) | | | (142,985) | | | |
| Net (decrease) increase in fair value | | (68,897) | | | 57,044 | | | |
| Balance ‑ end of period | | $ | 3,143,653 | | | $ | 2,386,807 | | | |
As of December 31, 2022, the aggregate fair value of loans that are 90 days or more past due and in non-accrual status was $4.1 million, and the aggregate unpaid principal balance for loans that are 90 days or more past due was $35.2 million. As of December 31, 2021, the aggregate fair value of loans that are 90 days or more past due and in non-accrual status was $3.5 million, and the aggregate unpaid principal balance for loans that are 90 days or more past due was $20.7 million.
Financial Instruments Disclosed But Not Carried at Fair Value
The following table presents the carrying value and estimated fair values of financial assets and liabilities disclosed but not carried at fair value and the level within the fair value hierarchy:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2022 |
| | Carrying value | | Estimated fair value | | Estimated fair value |
| (in thousands) | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 98,817 | | | $ | 98,817 | | | $ | 98,817 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Restricted cash | | 105,000 | | | 105,000 | | | 105,000 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable | | 9,670 | | | 9,670 | | | 9,670 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Secured financing (Note 9) | | 320,000 | | | 306,574 | | | — | | | 306,574 | | | — | |
| Acquisition and corporate financing (Note 9) | | 235,679 | | | 233,166 | | | — | | | 233,166 | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2021 |
| | Carrying value | | Estimated fair value | | Estimated fair value |
| (in thousands) | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 130,959 | | | $ | 130,959 | | | $ | 130,959 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Restricted cash | | 62,001 | | | 62,001 | | | 62,001 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans held for sale (Note 5) | | 491 | | | 547 | | | — | | | — | | | 547 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable | | 8,343 | | | 8,343 | | | 8,343 | | | — | | | — | |
| Secured financing (Note 9) | | 398,000 | | | 396,081 | | | — | | | 396,081 | | | — | |
| Acquisition and corporate financing (Note 9) | | 116,000 | | | 116,000 | | | — | | | 116,000 | | | — | |
The Company uses the following methods and assumptions to estimate fair value:
•Cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and accounts payable ‑ The carrying values of certain of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash and accounts payable, approximate Level 1 fair values of these financial instruments due to their short-term nature.
•Loans held for sale ‑ The fair values of loans held for sale are based on a negotiated agreement with the purchaser.
•Secured financing and acquisition and corporate financing ‑ The fair values of the secured financing and acquisition and corporate financing facilities have been calculated using discount rates equivalent to the weighted-average market yield of comparable debt securities, which is a Level 2 input measure.
There were no transfers in or out of Level 3 assets and liabilities for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021.
| | | | | |
| 16. | Leases, Commitments and Contingencies |
Leases - The Company’s leases are primarily for real property consisting of retail locations and office space and have remaining lease terms of 10 years or less.
During the first quarter of 2022, the Company made the decision to close an additional 27 retail locations in April 2022. The Company incurred $1.4 million in expenses related to the accelerated amortization of right-of-use assets for the year ended December 31, 2022. The retail location closures were substantially completed in the second quarter of 2022 and the Company does not expect any additional expenses to be incurred.
As a result of the retail network optimization plan, for the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company incurred $12.8 million in expenses related to retail location closures. $5.2 million of the expenses related to the retail location closures for the year ended December 31, 2021 relate to the accelerated amortization of right-of-use assets and the renegotiation of lease liabilities. The initial retail network optimization plan was substantially completed in the third quarter of 2021.
The Company has elected the practical expedient to keep leases with terms of 12 months or less off the balance sheet as no recognition of a lease liability and a right-of-use asset is required. Operating lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term in "Technology and facilities" in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
All of the Company’s existing lease arrangements are classified as operating leases. At the inception of a contract, the Company determines if the contract is or contains a lease. At the commencement date of a lease, the Company recognizes a lease liability equal to the present value of the lease payments and a right-of-use asset representing the Company's right to use the underlying asset for the duration of the lease term. The Company’s leases include options to extend or terminate the arrangement at the end of the original lease term. The Company generally does not include renewal or termination options in its assessment of the leases unless extension or termination for certain assets is deemed to be reasonably certain. Variable lease payments and short-term lease costs were deemed immaterial. The Company’s leases do not provide an explicit rate. The Company uses its contractual borrowing rate to determine lease discount rates.
As of December 31, 2022, maturities of lease liabilities, excluding short-term leases and leases on a month-to-month basis, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | | | | Operating Leases |
| Lease expense | | | | |
| 2023 | | | | $ | 13,879 | |
| 2024 | | | | 11,940 | |
| 2025 | | | | 9,969 | |
| 2026 | | | | 3,918 | |
| 2027 | | | | 1,032 | |
| Thereafter | | | | 25 | |
| Total lease payments | | | | 40,763 | |
| Imputed interest | | | | (2,816) | |
| Total leases | | | | $ | 37,947 | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Total sublease income | | | | $ | — | |
| | | | |
| Net lease liabilities | | | | $ | 37,947 | |
| Weighted average remaining lease term | | | | 3.2 years |
| Weighted average discount rate | | | | 4.06 | % |
As of December 31, 2021, maturities of lease liabilities, excluding short-term leases and leases on a month-to-month basis, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | | | | Operating Leases |
| Lease expense | | | | |
| 2022 | | | | $ | 14,927 | |
| 2023 | | | | 13,214 | |
| 2024 | | | | 11,142 | |
| 2025 | | | | 9,238 | |
| 2026 | | | | 3,387 | |
| Thereafter | | | | 706 | |
| Total lease payments | | | | 52,614 | |
| Imputed interest | | | | (4,030) | |
| Total leases | | | | $ | 48,584 | |
| | | | |
| Sublease income | | | | |
| 2022 | | | | $ | (896) | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| 2023 and thereafter | | | | — | |
| Total lease payments | | | | (896) | |
| Imputed interest | | | | 11 | |
| Total sublease income | | | | $ | (885) | |
| | | | |
| Net lease liabilities | | | | $ | 47,699 | |
| Weighted average remaining lease term | | | | 3.9 years |
| Weighted average discount rate | | | | 4.01 | % |
Rental expenses under operating leases for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 were $18.5 million and $24.3 million, respectively.
Purchase Commitment ‑ The Company has commitments to purchase information technology and communication services in the ordinary course of business, with various terms through 2023. These amounts are not reflective of the Company’s entire anticipated purchases under the related agreements; rather, they are determined based on the non-cancelable amounts to which the Company is contractually obligated. The Company’s purchase obligations are $26.4 million in 2023, $14.1 million in 2024, $5.5 million in 2025, $2.0 million in 2026, and $0.0 million in 2027 and thereafter.
Bank Partnership Program and Servicing Agreement - The Company entered into a bank partnership program with Pathward, N.A. on August 11, 2020. In accordance with the agreements underlying the bank partnership program, Oportun has a commitment to purchase an increasing percentage of program loans originated by Pathward based on thresholds specified in the agreements. Lending under the partnership was launched in August of 2021 and as of December 31, 2022, the Company has a commitment to purchase an additional $0.6 million of program loans based on originations through December 31, 2022.
Whole Loan Sale Program ‑ Through March 4, 2022, the Company had a commitment to sell to a third-party institutional investor 10% of its unsecured loan originations that satisfy certain eligibility criteria, and an additional 5% at the Company’s sole option. The Company chose not to renew the arrangement and allowed the agreement to expire on its terms on March 4, 2022. For details regarding the whole loan sale program, refer to Note 5, Loans Held for Sale.
Unfunded Loan and Credit Card Commitments - Unfunded loan and credit card commitments at December 31, 2022 and 2021 were $45.0 million and $39.8 million, respectively. WebBank has a direct obligation to borrowers to fund such credit card commitments subject to the respective account agreements with such borrowers; however, pursuant to the Receivables Purchase Agreement between WebBank and Oportun, Inc., the Company has the obligation to purchase receivables from WebBank representing these unfunded amounts.
Litigation
Regulatory Proceedings
On March 3, 2021, the Company received a Civil Investigative Demand (CID) from the CFPB. The stated purpose of the CID is to determine whether small-dollar lenders or associated persons, in connection with lending and debt-collection practices, have failed to comply with certain federal consumer protection laws over which the CFPB has jurisdiction. The Company received additional information requests related to the CID. The information requests are focused on the Company's legal collection practices from 2019 to 2021 and hardship treatments offered to members during the COVID-19 pandemic. On September 15, 2022, the Company received a Notice and Opportunity to Respond and Advise (“NORA”) letter from the staff of the CFPB in connection with the CID, stating that it is considering whether to recommend that the CFPB take legal action against the Company based on alleged violations focused on the Company's failure to timely dismiss certain lawsuits and the hardship treatments offered during the COVID-19 pandemic, including credit reporting related thereto. On October 14, 2022, the Company provided the CFPB with its written response to the NORA letter disputing the allegations. The Company is cooperating fully with the CFPB with respect to this matter and the Company believes that its business practices have been in full compliance with applicable laws. Because the CFPB has broad authority to determine what it views as potentially unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices, at this time, the Company is unable to predict the ultimate outcome of this matter.
Digit received a CID from the CFPB in June 2020. The CID was disclosed and discussed during the acquisition process. The stated purpose of the CID is to determine whether Digit, in connection with offering its products or services, misrepresented the terms, conditions, or costs of the products or services in a manner that is unfair, deceptive, or abusive. While the Company believes that the business practices of the Company, including Digit, have been in full compliance with applicable laws, in the interest of resolving this matter, on August 11, 2022, Digit agreed to a consent order with the CFPB resolving such CID. In connection with such consent order, Digit agreed to implement a redress and compliance plan to pay at least $68,145 in consumer redress to consumers who may have been harmed and paid a $2.7 million civil penalty to the CFPB in the third quarter of 2022. The Company had previously established a reserve for the redress and civil penalty in the second quarter of 2022.
From time to time, the Company may bring or be subject to other legal proceedings and claims in the ordinary course of business, including legal proceedings with third parties asserting infringement of their intellectual property rights, consumer litigation, and regulatory proceedings. The Company is not presently a party to any other legal proceedings that, if determined adversely to the Company, would individually or taken together have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, cash flows or results of operations.
On February 9, 2023, the Company announced that it is taking a series of measures to streamline its operations, including reducing the size of its corporate staff by 10%, impacting approximately 155 employees, and reducing its expenditures on external contractors. In relation to these and other personnel related activities, management expects to incur non-recurring, pre-tax charges of $6 to $7 million in the first quarter of 2023. The estimates of the charges and expenditures that the Company expects to incur in connection with these activities, and the timing thereof, are subject to a number of assumptions, and actual amounts may differ materially from estimates. The Company may also incur charges and expenditures not currently contemplated due to unanticipated events that may occur in connection with these measures.
On February 10, 2023, the Acquisition Financing facility was further amended. This fifth amendment, among other things, revises the interest rate from SOFR plus 8.00% to SOFR plus 11.00% and adjusts the amortization schedule to defer $42.0 million in principal payments through July 2023, with a final payment in October 2024.
On March 8, 2023, the Credit Card Warehouse was further amended. This amendment, among other things, extends the revolving period by a year, to December 31, 2024, and reduces the commitment from $150.0 million to $120.0 million.
On March 10, 2023 (the “Second Amendment Closing Date”), the Company amended its Corporate Financing facility by entering into an Amendment No. 2 (the “Second Amendment”) by and among the Company, as borrower, the subsidiaries of the Company party thereto as guarantors, certain affiliates of Neuberger Berman Specialty Finance as lenders, and Wilmington Trust, National Association, as administrative agent and collateral agent (the “Agent”), which amended the Credit Agreement, dated as of September 14, 2022 (as amended, supplemented or otherwise modified, including by the Second Amendment, the “Amended Credit Agreement”), by and among the Company, the lenders from time to time party thereto and the Agent.
On the Second Amendment Closing Date, the Company borrowed $20.8 million of incremental term loans (the “Incremental Tranche A-1 Loans”) and intends to borrow an additional $4.2 million of incremental term loans (the “Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans”) on or about March 27, 2023, which amount has been committed by the applicable lenders. Under the Amended Credit Agreement, the Company may borrow up to an aggregate additional amount of $50.0 million on an uncommitted basis, in two $25.0 million tranches (the “Incremental Tranche B Loans” and the “Incremental Tranche C Loans”) expected to be available, if provided by the applicable lenders, on or about April 21, 2023 and June 23, 2023, respectively.
The loans (the “Loans”) and other obligations under the Amended Credit Agreement are secured by the assets of the Company and certain of its subsidiaries guaranteeing the Loans, including pledges of the equity interests of certain subsidiaries that are directly or indirectly owned by the Company, subject to customary exceptions.
Following the Second Amendment Closing Date the Loans bear interest, at (a) an amount equal to 1-month term SOFR plus 9.00% plus (b) an amount payable in cash or in kind, at the Company's option, equal to 3.00%. The Loans are scheduled to mature on September 14, 2026, and are not subject to amortization. Certain prepayments of the Loans are subject to a prepayment premium.
On the Second Amendment Closing Date, pursuant to the Second Amendment, the Company issued warrants (the “Warrants”) to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche A-1 Loans to purchase 1,980,242 shares of the Company’s common stock at an exercise price of $0.01 per share. In addition, (a) in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche A-2 Loans to purchase 116,485 shares of the Company’s common stock, (b) in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche B Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche B loans to purchase 1,048,363 shares of the Company's common stock, and (c) in connection with the funding of the Incremental Tranche C Loans, the Company will issue Warrants to the lenders providing the Incremental Tranche C Loans to purchase 1,048,363 shares of the Company’s common stock, in each case, at an exercise price of $0.01 per share. The Company also entered into a Registration Rights Agreement with the applicable lenders on the Second Amendment Closing Date (the “Registration Rights Agreement”), which stipulates that the Company will file a registration statement with the Securities and Exchange Commission with respect to the shares underlying the Warrants.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures designed to provide reasonable assurance that information we are required to disclose in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure and that such information is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms.
As of December 31, 2022, we carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures, as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act. This evaluation was conducted under the supervision of, and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives and management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures. Based on our evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of December 31, 2022 our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to provide the reasonable assurance described above.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Management has assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2022 based on the criteria established in "Internal Control-Integrated Framework" (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO").
As a result of this assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2022, our internal control over financial reporting was effective in providing reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP.
Our independent registered public accounting firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP, has audited the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and, as part of their audit, has issued an audit report, included herein, on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. Their report is set forth below.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting identified in connection with the evaluation required by Rule 13a-15(d) and 15d-15(d) of Exchange Act that occurred during the during the quarter ended December 31, 2022 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Inherent Limitations on Effectiveness of Controls
Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, does not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal controls over financial reporting will prevent all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Our disclosure controls and procedures and our internal controls over financial reporting have been designed to provide reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision making can be faulty, and that breakdowns can occur because of a simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of controls also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions; over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or the degree of compliance with policies or procedures may deteriorate. Because of the inherent limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the stockholders and the Board of Directors of Oportun Financial Corporation
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Oportun Financial Corporation and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2022, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2022, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2022, of the Company and our report dated March 13, 2023, expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
San Francisco, CA
March 13, 2023
Item 9B. Other Information
None.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
None.
GLOSSARY
Terms and abbreviations used in this report are defined below.
| | | | | | | | |
| Term or Abbreviation | | Definition |
| 30+ Day Delinquency Rate | | Unpaid principal balance for our owned loans and credit card receivables that are 30 or more calendar days contractually past due as of the end of the period divided by Owned Principal Balance as of such date |
| | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | | Adjusted EBITDA is a non-GAAP financial measure calculated as net income (loss), adjusted to eliminate the effect of the following items: income tax expense (benefit), stock-based compensation expense, depreciation and amortization, interest expense from corporate financing, certain non-recurring charges, origination fees for Loans Receivable at Fair Value, net and fair value mark-to-market adjustments |
| Acquisition Financing | | Asset-backed floating rate variable funding note and asset-backed residual certificate secured by certain residual cash flows of the Company's securitizations. The Acquisition Financing was used to fund the cash consideration for the Digit acquisition. Included as "Acquisition and corporate financing" on the Consolidated Balance Sheets |
| Adjusted Earnings Per Share ("EPS") | | Adjusted EPS is a non-GAAP financial measure calculated by dividing Adjusted Net Income by diluted adjusted weighted-average common shares outstanding |
| Adjusted Net Income | | Adjusted Net Income is a non-GAAP financial measure calculated by adjusting our net income (loss) adjusted to exclude income tax expense (benefit), stock-based compensation expense, and certain non-recurring charges |
| Adjusted Operating Efficiency | | Adjusted Operating Efficiency is a non-GAAP financial measure calculated by dividing adjusted total operating expenses (excluding stock-based compensation expense and certain non-recurring charges) by total revenue |
| Adjusted Return on Equity ("ROE") | | Adjusted Return on Equity is a non-GAAP financial measure calculated by dividing annualized Adjusted Net Income by average total stockholders’ equity |
| | |
| | |
| Aggregate Originations | | Aggregate amount disbursed to borrowers and credit granted on credit cards during a specified period, including amounts originated by us through our Lending as a Service partners or under our bank partnership programs. Aggregate Originations exclude any fees in connection with the origination of a loan |
| Annualized Net Charge-Off Rate | | Annualized loan and credit card principal losses (net of recoveries) divided by the Average Daily Principal Balance of owned loans and credit card receivables for the period |
| | |
| APR | | Annual Percentage Rate |
| | |
| Average Daily Debt Balance | | Average of outstanding debt principal balance at the end of each calendar day during the period |
| Average Daily Principal Balance | | Average of outstanding principal balance of owned loans and credit card receivables at the end of each calendar day during the period |
| Board | | Oportun’s Board of Directors |
| | |
| | |
| Corporate Financing | | Senior secured term loan secured by the assets of the Company and certain of its subsidiaries guaranteeing the term loan, including pledges of the equity interests of certain subsidiaries that are directly or indirectly owned by the Company. Included as "Acquisition and corporate financing" on the Consolidated Balance Sheets |
| Cost of Debt | | Annualized interest expense divided by Average Daily Debt Balance |
| Credit Card Warehouse (or "CCW") | | Revolving credit card warehouse debt facility, collateralized by credit card accounts. Included as "Secured Financing" on the Consolidated Balance Sheets |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (or "CAC") | | Sales and marketing expenses, which include the costs associated with various paid marketing channels, including direct mail, digital marketing and brand marketing and the costs associated with our telesales and retail operations divided by number of loans originated and new credit cards activated to new and returning borrowers during a period |
| Emergency Hardship Deferral | | Any receivable that currently has one or more payments deferred and added at the end of the loan payment schedule in connection with a local or wide-spread emergency declared by local, state or federal government |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| FICO® score or FICO® | | A credit score created by Fair Isaac Corporation |
| | |
| GAAP | | Generally Accepted Accounting Principles |
| | |
| Leverage | | Average Daily Debt Balance divided by Average Daily Principal Balance |
| | |
| Loans Receivable at Fair Value | | All loans receivable held for investment. Loans Receivable at Fair Value include loans receivable on our unsecured and secured personal loan products and credit card receivable balances |
| Managed Principal Balance at End of Period | | Total amount of outstanding principal balance for all loans and credit card receivables, including loans sold, which we continue to service, at the end of the period. Managed Principal Balance at End of Period also includes loans and accounts originated under a bank partnership program that we service |
| Members | | Members include borrowers with an outstanding or successfully paid off loan, originated by us or under a bank partnership program that we service, or individuals who have been approved for a credit card issued under a bank partnership program. Members also include individuals who have signed-up to use or are using any of our Digit Savings, Digit Direct, Digit Investing and/or Digit Retirement products |
| Net Revenue | | Net Revenue is calculated by subtracting interest expense from total revenue and adding the net increase (decrease) in fair value |
| Operating Efficiency | | Total operating expenses divided by total revenue |
| Owned Principal Balance at End of Period | | Total amount of outstanding principal balance for all loans and credit card receivables, excluding loans and receivables sold or loans retained by a bank partner, at the end of the period |
| Personal Loan Warehouse (or "PLW") | | Revolving personal loan warehouse debt facility, collateralized by unsecured personal loans and secured personal loans that replaced the VFN facility. Included as "Secured Financing" on the Consolidated Balance Sheets |
| Portfolio Yield | | Annualized interest income as a percentage of Average Daily Principal Balance |
| | | | | | | | |
| Term or Abbreviation | | Definition |
| Principal Balance | | Original principal balance reduced by principal payments received and principal charge-offs to date for our personal loans. Purchases and cash advances, reduced by returns and principal payments received and principal charge-offs to date for our credit cards |
| Products | | Products refers to the aggregate number of personal loans and/or credit card accounts that our Members have had or been approved for that have been originated by us or through one of our bank partners. Products also include the aggregate number of digital banking products we offer as a result of our acquisition of Digit, including Digit Savings, Digit Direct, Digit Investing and Digit Retirement, that our Members use or have signed-up to use |
| Return on Equity | | Annualized net income divided by average stockholders' equity for a period |
| | |
| | |
| Secured Financing | | Asset-backed revolving debt facilities, including (1) the VFN facility which was collateralized by unsecured personal loans, terminated September 8, 2021 and replaced with the PLW facility that is collateralized by unsecured personal loans and secured personal loans and (2) the CCW facility that is collateralized by credit card accounts |
| Variable Funding Note Warehouse (or "VFN") | | Asset-backed revolving debt facility, collateralized by unsecured personal loans, terminated on September 8, 2021. Formerly defined solely as "Secured Financing" on the Consolidated Balance Sheets |
| | |
| Weighted Average Interest Rate | | Annualized interest expense as a percentage of average debt |
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this item, including information about our directors, executive officers and audit committee and code of conduct, will be included in our proxy statement for the 2023 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2022 ("2023 Proxy Statement") and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this item will be included in the 2023 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholders Matters
The information required by this item will be included in the 2023 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this item will be included in the 2023 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information required by this item will be included in the 2023 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) (1) The following consolidated financial statements of Oportun, Inc. and its subsidiaries are included in PART II - Item 8:
Consolidated Balance Sheets, December 31, 2022 and 2021
Consolidated Statements of Operations, years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity, years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flow, years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(2) Financial Statement Schedules:
All other schedules have been omitted because they are either not required or inapplicable.
(3) Exhibits:
Exhibits are listed in the Exhibit Index below.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
Exhibit Index
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Incorporated by Reference | | |
| Exhibit | Description | | Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | | Filed Herewith |
| 2.1** | | | 8-K | 001-39050 | 2.1 | 11/16/2021 | | |
| 3.1 | | | 8-K | 001-39050 | 3.1 | 9/30/2019 | | |
| 3.2 | | | 8-K/A | 001-39050 | 3.1 | 12/9/2022 | | |
| 4.1 | | | S-1/A | 333-232685 | 4.1 | 9/16/2019 | | |
| 4.2 | | | S-1 | 333-232685 | 4.2 | 7/17/2019 | | |
| 4.3 | | | 10-K | 001-39050 | 4.3 | 3/1/2022 | | |
| 4.4 | | | | | | | | x |
| 4.5 | | | 8-K | 001-39050 | 4.1 | 3/13/2023 | | |
| 4.6 | | | 8-K | 001-39050 | 4.2 | 3/13/2023 | | |
| 10.1+ | | | S-1 | 333-232685 | 10.1 | 7/17/2019 | | |
| 10.2+ | | | S-1 | 333-232685 | 10.2 | 7/17/2019 | | |
| 10.3+ | | | S-1 | 333-232685 | 10.3 | 7/17/2019 | | |
| 10.4+ | | | 10-K | 001-39050 | 10.4 | 2/23/2021 | | |
| 10.5+ | | | S-1/A | 333-232685 | 10.5 | 9/16/2019 | | |
| 10.6+ | | | S-8 | 333-261964 | 4.3 | 1/3/2022 | | |
| 10.7+ | | | S-1 | 333-232685 | 10.6 | 7/17/2019 | | |
| 10.8+ | | | S-1 | 333-232685 | 10.7 | 7/17/2019 | | |
| 10.8 | | | S-1 | 333-232685 | 10.8 | 7/17/2019 | | |
| 10.9-1^ | | | S-1 | 333-232685 | 10.9 | 7/17/2019 | | |
| 10.9-2** | | | S-1/A | 001-39050 | 10.9.2 | 9/16/2019 | | |
| 10.9-3 | | | S-1/A | 333-232685 | 10.9.3 | 9/16/2019 | | |
| 10.9-4** | | | S-1/A | 333-232685 | 10.9.4 | 9/16/2019 | | |
| 10.9-5** | | | 10-K | 333-232685 | 10.2 | 2/28/2020 | | |
| 10.10** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.2 | 5/7/2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.11-1 | | | S-1/A | 333-232685 | 10.17.1 | 9/16/2019 | | |
| 10.11-2 | | | S-1/A | 333-232685 | 10.17.2 | 9/16/2019 | | |
| 10.12-1 | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.3.1 | 5/7/2021 | | |
| 10.12-2 | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.3.2 | 5/7/2021 | | |
| 10.13 | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.1 | 8/6/2021 | | |
| 10.14 | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.3 | 11/4/2021 | | |
| 10.16-1** | | | 10-K | 001-39050 | 10.16.1 | 2/23/2021 | | |
| 10.16-2 ** | | | 10-K | 001-39050 | 10.16.2 | 2/23/2021 | | |
| 10.17-1** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.1.1 | 8/6/2021 | | |
| 10.17-2** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.1.2 | 8/6/2021 | | |
| 10.17-3** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.1.3 | 11/4/2021 | | |
| 10.17-4** | | | 10-K | 001-39050 | 10.17.4 | 03/1/2022 | | |
| 10.18-1** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.2 | 11/4/2021 | | |
| 10.18-2** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.4.1 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| 10.18-3** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.4.2 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| 10.18-4** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.4.3 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| 10.18-5** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.2 | 11/8/2022 | | |
| 10.19-1** | | | 10-K | 001-39050 | 10.19 | 3/1/2022 | | |
| 10.19-2 | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.3.1 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| 10.19-3 | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.3.2 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.19-4 | | | | | | | | x |
| 10.19-5 | | | | | | | | x |
| 10.19-6 | | | | | | | | x |
| 10.20-1** | | | 10-K | 001-39050 | 10.2 | 3/1/2022 | | |
| 10.20-2 | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.5.1 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| 10.20-3** | Master Amendment to Transaction Documents by and between Oportun CCW Trust, Oportun Depositor, LLC, Oportun, Inc., Wilmington Trust, National Association, and Wilmington Savings Fund Society, FSB, dated as of June 21, 2022. | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.5.2 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| 10.20-4** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.3 | 11/8/2022 | | |
| 10.20-5** | Master Amendment to Transaction Documents by and between Oportun CCW Trust, Oportun Depositor, LLC, Oportun, Inc., Wilmington Trust, National Association, and Wilmington Savings Fund Society, FSB, dated as of September 28, 2022. | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.4 | 11/8/2022 | | |
| 10.20-6** | | | | | | | | x |
| 10.21-1 | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.2.1 | 5/10/2022 | | |
| 10.21-2** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.2.2 | 5/10/2022 | | |
| 10.22** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.1 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| 10.23** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.2 | 8/9/2022 | | |
| 10.24-1** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.1 | 11/8/2022 | | |
| 10.24-2 | | | | | | | | x |
| 10.24-3** | | | 8-K | 001-39050 | 10.1 | 3/13/2023 | | |
| 10.25** | | | 10-Q | 001-39050 | 10.5 | 11/8/2022 | | |
| 21.1 | | | | | | | | x |
| 23.1 | | | | | | | | x |
| 24.1 | | | | | | | | x |
| 31.1 | | | | | | | | x |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 31.2 | | | | | | | | x |
| 32.1* | | | | | | | | x |
| 101 | Interactive data files pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T: | | | | | | | |
| (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets, | | | | | | | |
| (ii) Consolidated Statements of Operations, | | | | | | | |
| (iii) Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity, | | | | | | | |
| (iv) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, and | | | | | | | |
| (v) Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements | | | | | | | |
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File in Inline XBRL format (included in Exhibit 101). | | | | | | | |
* The certifications attached as Exhibit 32.1 that accompany this Annual Report on Form 10-K are not deemed filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission and are not to be incorporated by reference into any filing of the Registrant under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, whether made before or after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, irrespective of any general incorporation language contained in such filing.
+ Management contract or compensatory plan.
^ Confidential treatment has been requested with respect to certain portions of this exhibit. Omitted portions have been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
** Portions of this exhibit have been omitted pursuant to Item 601 of Regulation S-K. The registrant agrees to furnish supplementally to the SEC a copy of any omitted schedule or exhibit upon request by the SEC.
The instance document does not appear in the interactive data file because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document.
Signatures
OPORTUN FINANCIAL CORPORATION
(Registrant)
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, on March 14, 2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| Date: | March 14, 2023 | By: | /s/ Jonathan Coblentz |
| | | Jonathan Coblentz |
| | | Chief Financial Officer and Chief Administrative Officer |
| | | (Principal Financial Officer) |
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Raul Vazquez and Jonathan Coblentz, jointly and severally, his or her attorneys-in-fact, each with the power of substitution, for him or her in any and all capacities, to sign any amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith with the Securities and Exchange Commission, hereby ratifying and confirming all that each of said attorneys-in-fact, or his substitute or substitutes, may do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| /s/ Raul Vazquez | | /s/ Jonathan Coblentz |
| Raul Vazquez | | Jonathan Coblentz |
| (President, Chief Executive Officer, and Director) | | (Chief Financial Officer and Chief Administrative Officer) |
| (Principal Executive Officer) | | (Principal Financial Officer) |
| Date: March 14, 2023 | | Date: March 14, 2023 |
| | | |
| /s/ Casey Mueller | | /s/ Roy Banks |
| Casey Mueller | | Roy Banks |
| (Senior Vice President, Global Controller and Principal Accounting Officer) | | (Director) |
| (Principal Accounting Officer) | | Date: March 14, 2023 |
| Date: March 14, 2023 | | |
| | | |
| /s/ Jo Ann Barefoot | | /s/ Ginny Lee |
| Jo Ann Barefoot | | Ginny Lee |
| (Director) | | (Director) |
| Date: March 14, 2023 | | Date: March 14, 2023 |
| | | |
| /s/ Louis P. Miramontes | | /s/ Carl Pascarella |
| Louis P. Miramontes | | Carl Pascarella |
| (Director) | | (Director) |
| Date: March 14, 2023 | | Date: March 14, 2023 |
| | | |
| /s/ Sandra Smith | | /s/ David Strohm |
| Sandra Smith | | David Strohm |
| (Director) | | (Director) |
| Date: March 14, 2023 | | Date: March 14, 2023 |
| | | |
| /s/ Frederic Welts | | /s/ R. Neil Williams |
| Frederic Welts | | R. Neil Williams |
| (Director) | | (Director) |
| Date: March 14, 2023 | | Date: March 14, 2023 |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |